Natural Resources
Conservation Service
Ecological site R236XY172AK
Boreal Dwarf Scrub Peat Flood Plains Depressions
Last updated: 2/13/2024
Accessed: 02/16/2026
General information
Provisional. A provisional ecological site description has undergone quality control and quality assurance review. It contains a working state and transition model and enough information to identify the ecological site.
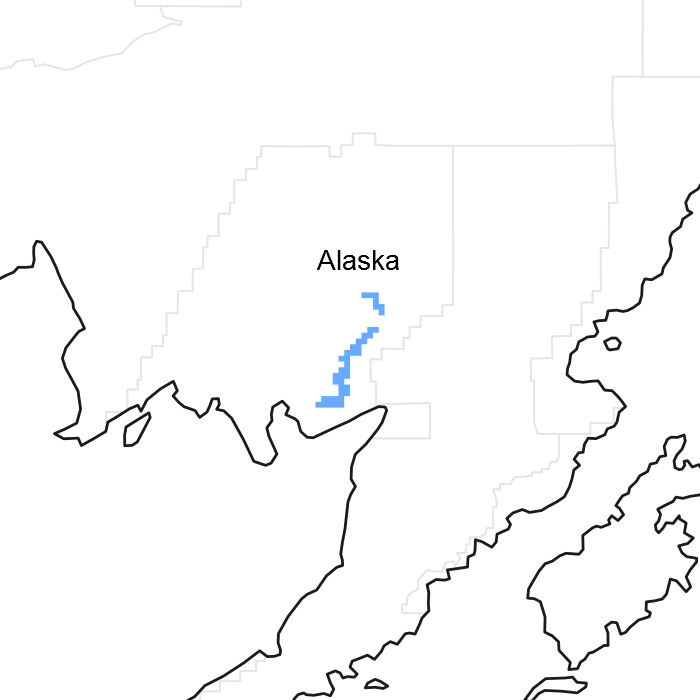
Figure 1. Mapped extent
Areas shown in blue indicate the maximum mapped extent of this ecological site. Other ecological sites likely occur within the highlighted areas. It is also possible for this ecological site to occur outside of highlighted areas if detailed soil survey has not been completed or recently updated.
MLRA notes
Major Land Resource Area (MLRA): 236X–Bristol Bay-Northern Alaska Peninsula Lowlands
The Bristol Bay-Northern Alaska Peninsula Lowland Major Land Resource Area (MLRA 236) is located in Western Alaska. This MLRA covers approximately 19,500 square miles and is defined by an expanse of nearly level to rolling lowlands, uplands and low to moderate hills bordered by long, mountain footslopes. Major rivers include the Egegik, Mulchatna, Naknek, Nushagak, and Wood River. MLRA 236 is in the zone of discontinuous permafrost. It is primarily in areas with finer textured soils on terraces, rolling uplands and footslopes. This MLRA was glaciated during the early to middle Pleistocene. Moraine and glaciofluvial deposits cover around sixty percent of the MLRA. Alluvium and coastal deposits make up a large portion of the remaining area (Kautz et al., 2012; USDA, 2006).
Climate patterns across this MLRA shift as one moves away from the coast. A maritime climate is prominent along the coast, while continental weather, commonly associated with Interior Alaska, is more influential inland. Across the MLRA, summers are general short and warm while winters are long and cold. Mean annual precipitation is 13 to 50 inches, with increased precipitation at higher elevations and areas away from the coast. Mean annual temperatures is between 30 and 36 degrees F (USDA, 2006).
The Bristol Bay-Northern Alaska Peninsula MLRA is principally undeveloped wilderness. Federally managed land includes parts of the Katmai and Aniakchak National Parks, and the Alaska Peninsula, Becharof, Togiak and Alaska Maritime National Wildlife Refuges. The MLRA is sparsely populated. Principal communities include Dillingham, Naknek, and King Salmon. Commercial fishing in Bristol Bay and the Bering Sea comprises a major part of economic activity in the MLRA. Other land uses include subsistence activities (fishing, hunting, and gathering) and sport hunting and fishing (USDA, 2006).
Ecological site concept
This lowland ecological site is in low braided river flood plain depressions. Site elevation is between sea level and 80 feet. Slopes are nearly level (0 percent). Site and soil hydrology caused by slope topography, highly organic soil and a ponding regime shape the vegetation on this landform. Soils are very poorly drained and support aquic soil conditions during the growing season. A water table is present at the soil surface in May and June, restricting vegetation during the important early growing season months. Ponding is occasional and brief in these concave depressions, further restricting vegetation.
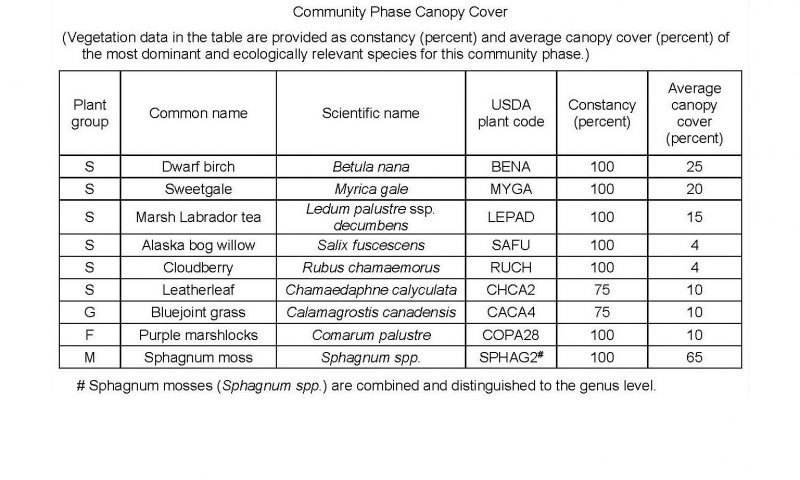
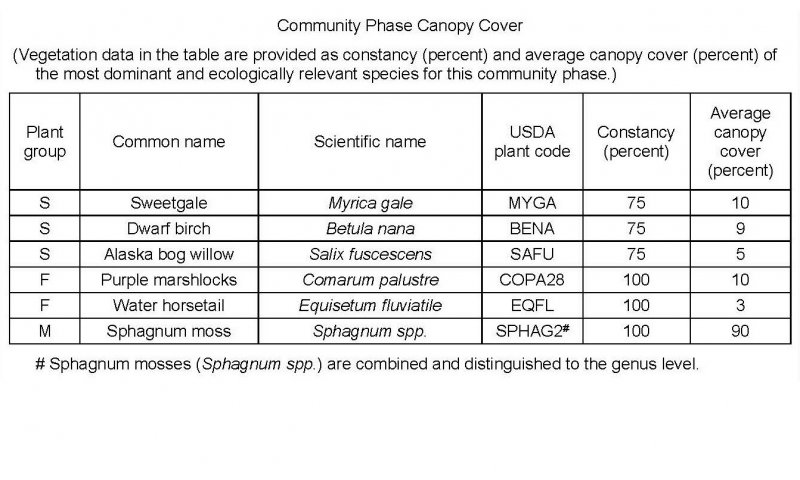
The reference state supports two communities. The reference plant community is characterized as an open low scrubland (Viereck et al., 1992). It is composed of a facultative to obligate wetland scrubs with hydrophytic graminoids and forbs throughout. Depression centers are typically wetter than other areas, and support only facultative to obligate wetland species.
Associated sites
| R236XY163AK |
Boreal Herbaceous Loamy Flood Plain Sloughs R236XY163AK describes gravelly flood plain sloughs. Site hydrology and soil characteristics support a different reference state and reference plant community than that of R236XY172AK. |
|---|
Similar sites
| R236XY163AK |
Boreal Herbaceous Loamy Flood Plain Sloughs Both sites describe flood plain features. R236XY163AK describes channels on low flood plains of braided rivers. This site is in large depressions. While both support hydrophytic vegetation, spatial and temporal differences in site factors such as ponding, flooding, soil characteristics and a water table are great enough to support two unique ecological sites. |
|---|---|
| R236XY155AK |
Boreal Scrub Loamy Flood Plains, Wet Both sites are flood plain features. R236XY155AK describes channels on mid flood plains. This site is in large depressions. While both support hydrophytic vegetation, spatial and temporal differences in site factors such as ponding, flooding, soil characteristics and a water table are great enough to support two unique ecological sites. |
Table 1. Dominant plant species
| Tree |
Not specified |
|---|---|
| Shrub |
(1) Myrica gale |
| Herbaceous |
(1) Comarum palustre |
Click on box and path labels to scroll to the respective text.
Ecosystem states
State 1 submodel, plant communities
| 1.1a | - | Increased hydrologic pressure. |
|---|---|---|
| 1.2a | - | Decreased hydrologic pressure |