Natural Resources
Conservation Service
Ecological site R237XY222AK
Western Alaska Maritime Scrubland Loamy Hummocks
Last updated: 7/23/2020
Accessed: 02/26/2026
General information
Provisional. A provisional ecological site description has undergone quality control and quality assurance review. It contains a working state and transition model and enough information to identify the ecological site.
MLRA notes
Major Land Resource Area (MLRA): 237X–Ahklun Mountains
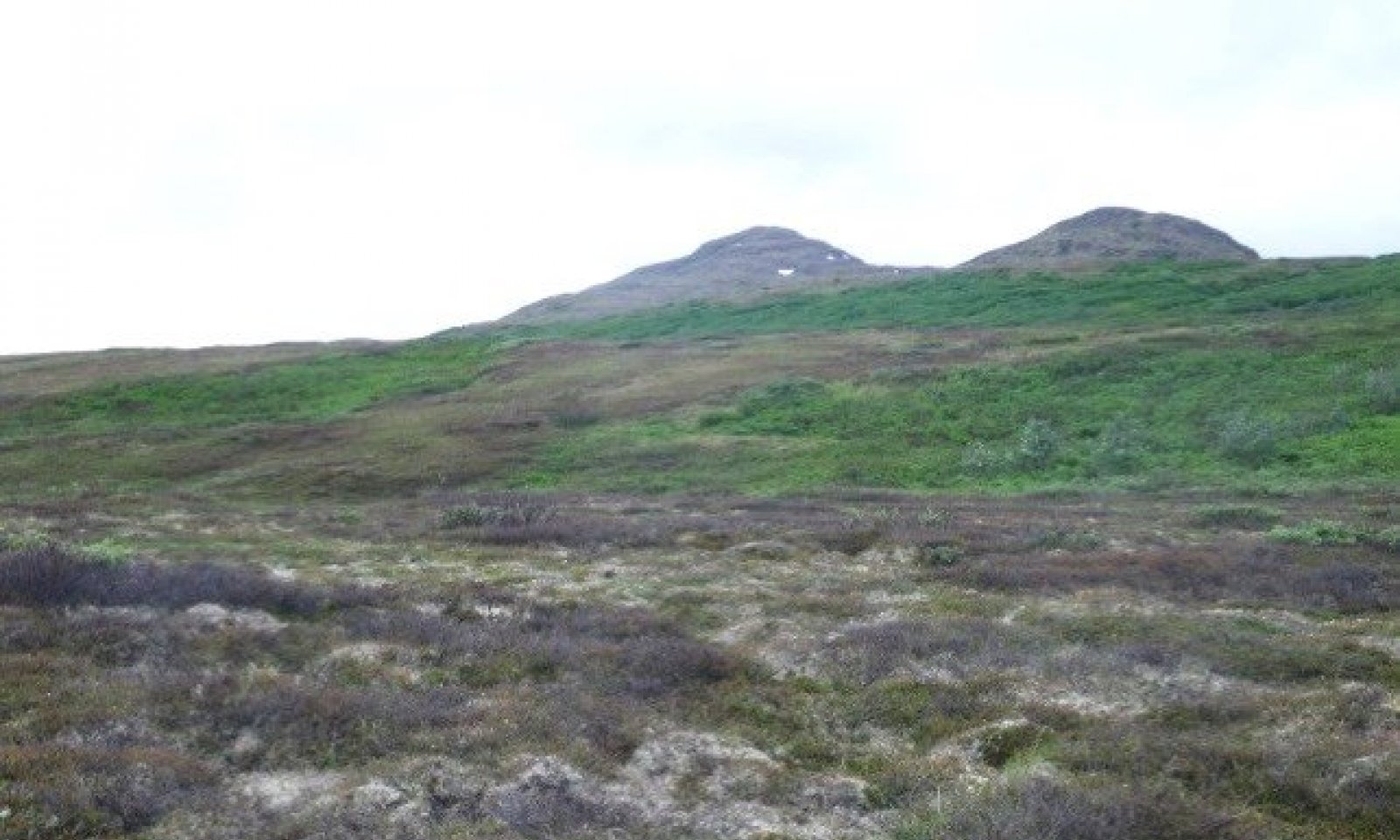
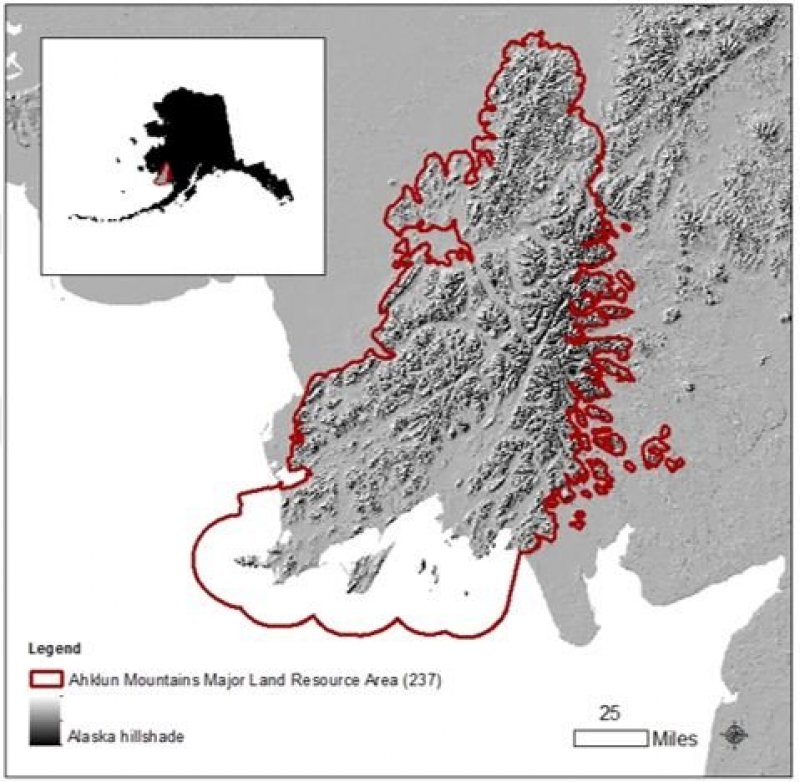
The Ahklun Mountains Major Land Resource Area (MLRA 237) is in western Alaska (fig. 1). This MLRA covers approximately 14,555 square miles, and it includes the mountains, hills, and valleys of the Kilbuck Mountains in the north and the Ahklun Mountains in the south. Except for the Kilbuck Mountains and the highest ridges of the Ahklun Mountains, the MLRA was extensively glaciated during the Pleistocene (Kautz et al., 2004). Today, a few small glaciers persist in mountainous cirques (Gallant et al., 1995). The present-day landscape and landforms reflect this glacial history; glacial moraines and glacial drift cover much of the area (USDA-NRCS, 2006). The landscape of the MLRA is primarily defined by low, steep, rugged mountains cut by narrow-to-broad valleys. Flood plains and terraces of varying sizes are common at the lower elevations in the valley bottoms. Glacially carved valleys host many lakes. Togiak Lake is one of the largest lakes in the region. It is 13 miles long and about 9,500 acres in size. Major rivers include the Goodnews, Togiak, Kanektok, Osviak, Eek, and Arolik Rivers. Where the Goodnews and Togiak Rivers reach the coast, the nearly level to rolling deltas support numerous small lakes.
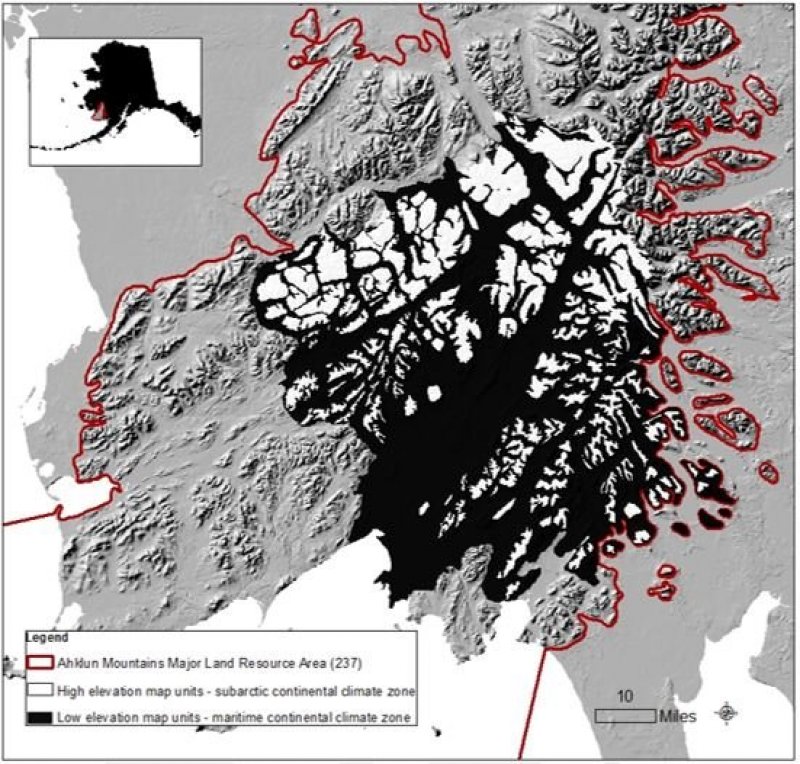
This MLRA has two distinct climatic zones: subarctic continental and maritime continental (fig. 2). The high-elevation areas are in the subarctic continental zone. The mean annual precipitation is more than 75 inches, and the mean annual air temperature is below about 27 degrees F (-3 degrees C) in extreme locations. The warmer, drier areas at the lower elevations are in the maritime continental zone. The mean annual precipitation is 20 to 50 inches, and the mean annual air temperature is about 30 to 32 degrees F (-0.2 to 1.2 degrees C) (PRISM). This climatic zone is influenced by both maritime and continental factors. The temperatures in summer are moderated by the open waters of the Bering Sea, and the temperatures in winter are more continental due to the presence of ice in the sea (Western Regional Climate Center, 2017). The seasonal ice reaches its southernmost extent off the coast of Alaska in Bristol Bay (Alaska Climate Research Center, 2017). The western coast of Alaska is also influenced by high winds from strong storms and airmasses in the Interior Region of Alaska (Hartmann, 2002).
The Ahklun Mountains MLRA is principally undeveloped wilderness. Federally managed lands include the Togiak and Alaska Maritime National Wildlife Refuges. The MLRA is sparsely populated, but it has several communities, including Togiak, Manokotak, Twin Hills, and Goodnews Bay. Togiak is the largest village. It has a population of approximately 855, most of which are Yup’ik Alaska Natives (U.S. Census Bureau, 2016). Major land uses include subsistence activities (fishing, hunting, and gathering) and wildlife recreation (USDA-NRCS, 2006; Kautz et al., 2004).
Ecological site concept
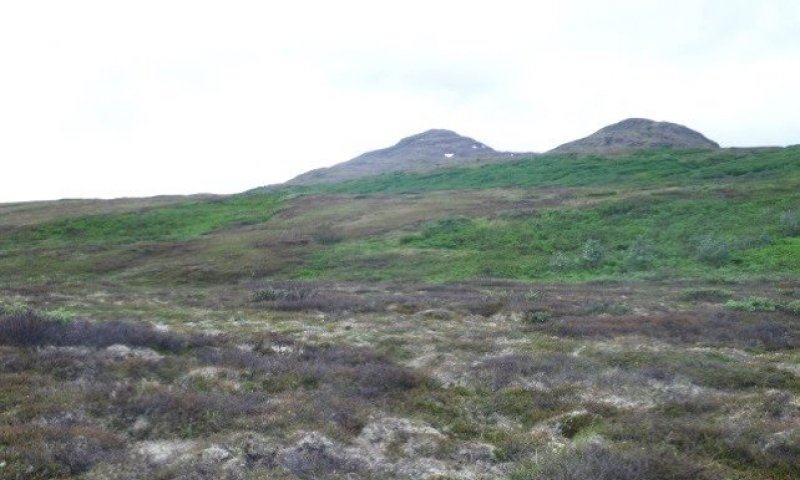
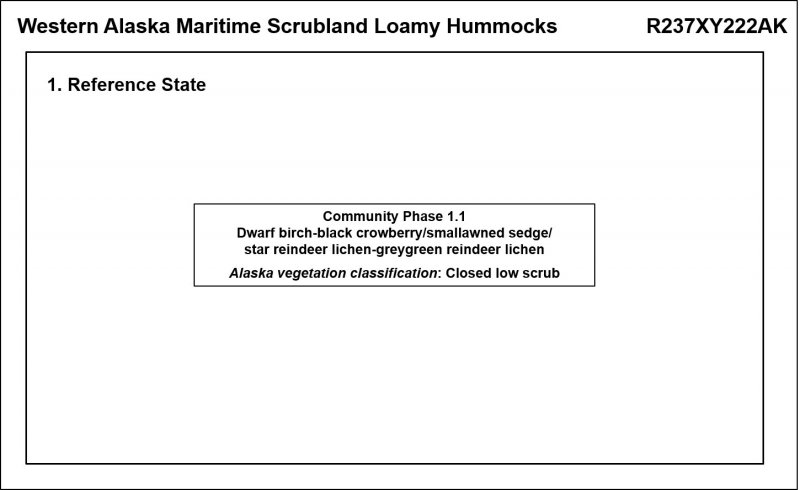
Ecological site R237XY222AK is on linear outwash terraces and glaciated plains. It is associated with earth hummocks of well drained soils. This site is throughout the Ahklun Mountains area. The formation of earth hummocks via frost heave is the major disturbance. This site does not support an alternate state.
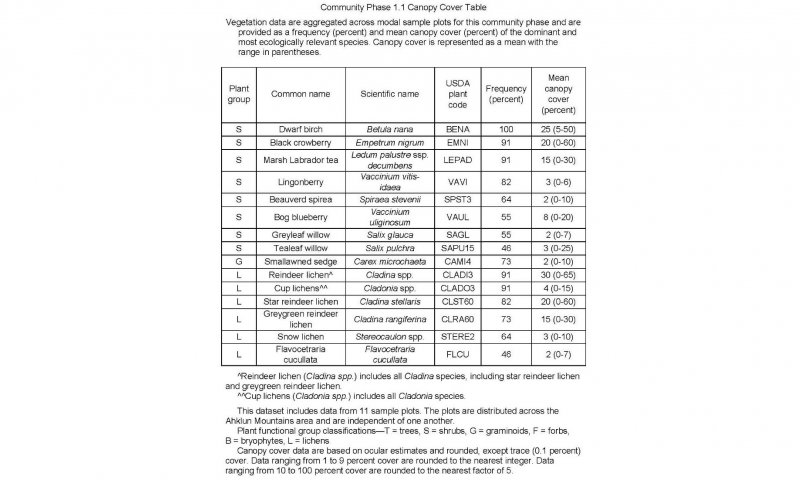
This ecological site is on small, rolling earth hummocks. The vegetation is not in a mosaic pattern based on micro-topographical features. The reference plant community supports many shrub species, mixed lichens, and sporadic graminoids. Common species include dwarf birch (Betula nana), black crowberry (Empetrum nigrum), marsh Labrador tea (Ledum palustre ssp. decumbens), bog blueberry (Vaccinium uliginosum), greyleaf willow (Salix glauca), and smallawned sedge (Carex microchaeta).
Associated sites
| R237XY201AK |
Western Alaska Maritime Scrubland Gravelly Slopes Ecological site R237XY222AK is on outwash terraces and outwash plains. Several other ecological sites are associated with this site, including R237XY201AK, R237XY205AK, R237XY208AK, and R237XY220AK. These sites typically are differentiated by one or more criteria, including landform, landform position, associated soils, associated disturbance regimes, and the type and amount of plants. Ecotonal plant communities that have characteristics from more than one ecological site are in areas where these sites abut. |
|---|---|
| R237XY205AK |
Western Alaska Maritime Scrubland Loamy Swales Ecological site R237XY222AK is on outwash terraces and outwash plains. Several other ecological sites are associated with this site, including R237XY201AK, R237XY205AK, R237XY208AK, and R237XY220AK. These sites typically are differentiated by one or more criteria, including landform, landform position, associated soils, associated disturbance regimes, and the type and amount of plants. Ecotonal plant communities that have characteristics from more than one ecological site are in areas where these sites abut. |
| R237XY208AK |
Western Alaska Maritime Scrubland Peat Depressions Ecological site R237XY222AK is on outwash terraces and outwash plains. Several other ecological sites are associated with this site, including R237XY201AK, R237XY205AK, R237XY208AK, and R237XY220AK. These sites typically are differentiated by one or more criteria, including landform, landform position, associated soils, associated disturbance regimes, and the type and amount of plants. Ecotonal plant communities that have characteristics from more than one ecological site are in areas where these sites abut. |
| R237XY220AK |
Western Alaska Maritime Mosaic Loamy Hummocks Ecological site R237XY222AK is on outwash terraces and outwash plains. Several other ecological sites are associated with this site, including R237XY201AK, R237XY205AK, R237XY208AK, and R237XY220AK. These sites typically are differentiated by one or more criteria, including landform, landform position, associated soils, associated disturbance regimes, and the type and amount of plants. Ecotonal plant communities that have characteristics from more than one ecological site are in areas where these sites abut. |
Similar sites
| R237XY220AK |
Western Alaska Maritime Mosaic Loamy Hummocks Ecological site R237XY220AK is on earth hummocks. Site R237XY222AK is throughout the Ahklun Mountains area, and site R237XY220AK is in the southern part of the area. The large earth hummocks associated with site R237XY220AK are in areas of wet soils. A mosaic of vegetative communities is in the micro-topographic high and low areas of site R237XY220AK. Site R237XY222AK does not support a mosaic pattern of vegetation. |
|---|
Table 1. Dominant plant species
| Tree |
Not specified |
|---|---|
| Shrub |
(1) Betula nana |
| Herbaceous |
(1) Carex microchaeta |
Click on box and path labels to scroll to the respective text.