Ecological site group R014XG904CA
Dry Clayey Bottom
Last updated: 09/07/2023
Accessed: 03/14/2026
Ecological site group description
Key Characteristics
None specified
Provisional. A provisional ecological site description has undergone quality control and quality assurance review. It contains a working state and transition model and enough information to identify the ecological site.
Physiography
This ESG is associated with flood basins, flood plains, in swales of drainageways, basins, and depressions where water and fine sediments are often deposited with slopes ranging from 0 to 5 percent at elevations from 10 to 2000 feet.
Representative soils include:
Clear Lake, a fine, smectitic, thermic Xeric Endoaquerts
Hangerone, a fine, smectitic, thermic Cumulic Vertic Endoaquolls
Sunnyvale, a fine, thermic Typic Calciaquolls
Pacheco, a fine-loamy, mixed, superactive, thermic Fluvaquentic Haploxerolls
Climate
The average annual precipitation in this area is 11 to 53 inches (272 to 1,353 millimeters). The higher amounts of precipitation occur at the higher elevations in the area north of San Francisco. Most of the rainfall occurs as low- or moderate-intensity, Pacific frontal storms during winter. This area is very dry from midspring to midautumn. Snowfall is rare. The average annual temperature is 54 to 61 degrees F (12 to 16 degrees C). The freeze-free period averages 315 days and ranges from 265 to 365 days. It is longest near the coast, and it becomes shorter with elevation.
Soil features
The soils associated with this ESG consist of mainly very deep, moderately well and well drained clayey soils that have slickensides and formed in alluvium from mixed rock sources.
The soils that represent this ESG include:
Clear Lake, a fine, smectitic, thermic Xeric Endoaquerts
Hangerone, a fine, smectitic, thermic Cumulic Vertic Endoaquolls
Sunnyvale, a fine, thermic Typic Calciaquolls
Pacheco, a fine-loamy, mixed, superactive, thermic Fluvaquentic Haploxerolls
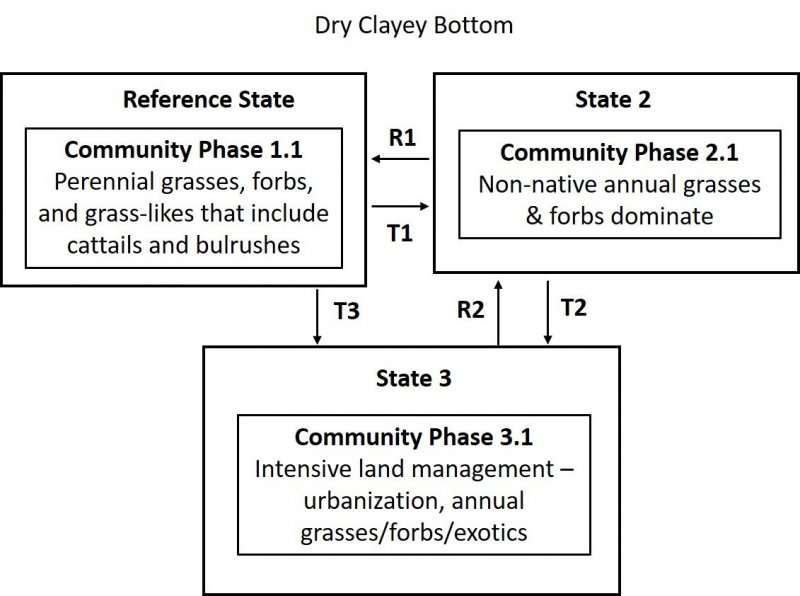
Vegetation dynamics
This ESG covers the areas of the valleys in MLRA 14 that were at one time part of a vast complex of marshes, tidal flats, estuaries, wetlands and wet meadows. The urbanized landscape in the valleys within this MLRA that exists today makes it difficult to imagine the natural landscape prior to human development.
These dry clayey bottoms were likely the fine-textured depressional and deposition areas and isolated oxbows that were created from the network of freshwater and salt marshes, rivers and streams that ran through these valleys as their seasonal and tidally influenced flood waters stretched across the floodplains and terraces in spring and deposited sediment as they receded during summer. Once the area began to be settled, many of these water dominated ecosystems were drained, leveed, cleared for crops and other agriculture, and urbanized.
As this landscape was de-watered and houses and agriculture took over, the water table for many of these habitats moved deeper and deeper, creating soils that would no longer offer the available soil moisture for many of the plants that had evolved with the hydrologic function of the natural system that no longer existed. These clayey basins may have remained wetter than many of the surrounding soils, due to their high water-holding capacity and their depressional location on the landscape. The clays of this ESG are high shrink-swell clays that dry out in the summer when the water table recedes and develop cracks and low soil pores spaces making them less hospitable for many of the native perennial grasses that existed within the drier surrounding grasslands.
Historically, this site may have looked similar to the CWHR wet meadow classification, however with the introduction of non-native annual grasses and the impacts from fragmentation, continued de-watering, and human alterations such as homes and roads, this site now reflects a lower producing, dry, annual grassland.
Major Land Resource Area
MLRA 014X
Central California Coastal Valleys
Stage
Provisional
Click on box and path labels to scroll to the respective text.