
Natural Resources
Conservation Service
Ecological site R010XY011ID
South Slope Stony 12-16 PZ ARTRT/PSSPS
Last updated: 9/23/2020
Accessed: 03/14/2025
General information
Provisional. A provisional ecological site description has undergone quality control and quality assurance review. It contains a working state and transition model and enough information to identify the ecological site.
Associated sites
| R010XY001ID |
North Slope Loamy 12-16 PZ FEID-PSSPS |
|---|---|
| R010XY007ID |
Loamy 12-16 PZ |
| R010XY019ID |
South Slope Loamy 12-16 PZ ARTRX/PSSPS |
Similar sites
| R010XY009ID |
Stony Loam 12-16 PZ ARTRT/PSSPS |
|---|
Table 1. Dominant plant species
| Tree |
Not specified |
|---|---|
| Shrub |
Not specified |
| Herbaceous |
Not specified |
Physiographic features
This site occurs on rolling to very steep slopes that range from 8 to 75 percent with south and west facing exposures. Slopes are generally greater than 30 percent. Elevation ranges from 2000 to 3500 feet (600-1050 m).
Table 2. Representative physiographic features
| Landforms |
(1)
Mountain slope
(2) Hill (3) Terrace |
|---|---|
| Flooding frequency | None |
| Elevation | 610 – 1,067 m |
| Slope | 30% |
| Water table depth | 152 cm |
| Aspect | S, W |
Climatic features
The elevation of MLRA 10 ranges from 1791 feet to 9236 feet, with a mean of 4602 feet. Overall, elevation increases from west to east. However, average annual precipitation decreases from west to east, ranging from 16.59 inches to 22.17 inches, with a mean of 19.56 inches, based on 7 long term climate stations throughout the MLRA. In general, precipitation peaks in December and January, with a steady decline to a low in July and August, then a steep increase during the autumn months. Most of the winter precipitation falls as snow, and maximum annual snowfalls of up to 82 inches have been recorded.
There is considerable variation in temperature throughout the year. Temperatures as low as -52° Fahrenheit and as high as 117° Fahrenheit are on record. Some areas have recorded the occurrence of more than 50 days with temperatures above 90° Fahrenheit. The average maximum annual temperature is 63 degrees F, while the average minimum temperature is 36.2 degrees F.The frost-free period can range from 128 to 152 days, while the freeze-free period can be from 164 to 189 days.
Both the average morning and average afternoon relative humidity values are lowest in July and August, and are below the national average. The number of clear, sunny days peaks during this same period, and is higher then the national average. During the Spring and Summer months high-intensity convective thunderstorms are not unusual.
Table 3. Representative climatic features
| Frost-free period (average) | 152 days |
|---|---|
| Freeze-free period (average) | 189 days |
| Precipitation total (average) | 559 mm |
Figure 1. Monthly precipitation range
Figure 2. Monthly average minimum and maximum temperature
Influencing water features
This site is not influenced by adjacent wetlands, streams or run on.
Soil features
The soils on this site are shallow to moderately deep over bedrock. The soils are well drained, with predominately moderately slow permeability. Runoff is high to very high. The erosion hazard is moderate to severe by water. The available water capacity is very low to low. The surface texture is extremely stony loam. Stones are present on the surface and throughout the profile. These soils are characterized by a xeric soil moisture regime. Soil temperature regime is mesic.
Soil Series Correlated to this Ecological Site
Crawley
Deshler
Duco
Elmore
Gem
Lorella
Reywat
Riggins
Searles
Table 4. Representative soil features
| Surface texture |
(1) Extremely stony loam (2) Stony clay loam (3) Very stony sandy loam |
|---|---|
| Drainage class | Well drained |
| Permeability class | Slow to moderate |
| Soil depth | 25 – 102 cm |
| Surface fragment cover <=3" | 0 – 35% |
| Surface fragment cover >3" | 0 – 60% |
| Available water capacity (0-101.6cm) |
2.03 – 11.18 cm |
| Soil reaction (1:1 water) (0-101.6cm) |
6.1 – 7.8 |
| Subsurface fragment volume <=3" (Depth not specified) |
5 – 70% |
| Subsurface fragment volume >3" (Depth not specified) |
5 – 70% |
Ecological dynamics
The dominant visual aspect is bluebunch wheatgrass and basin big sagebrush. Some antelope bitterbrush is present on the site. Composition by weight is approximately 55-65 percent grass, 15-25 percent forbs and 15-25 percent shrubs.
The Reference State (State 1), moves through many phases depending on the natural and man-made forces that impact the community over time. State 1, described later, indicates some of these phases. The Reference Plant Community Phase is Phase A. The plant species composition of Phase A is listed later under “Reference Plant Community Phase Plant Species Composition”.
In the last few thousand years, this site has evolved in a semi-arid climate characterized by dry summers and cold, wet winters. Herbivory has historically occurred on this site at low levels of utilization. Herbivores include Rocky Mountain elk, mule deer, lagomorphs, and small rodents. Fire has historically occurred on the site at intervals of 50-70 years. The Reference Plant Community Phase of this site is dominated by bluebunch wheatgrass and basin big sagebrush. Subdominant species include Sandberg bluegrass, Nevada bluegrass, arrowleaf balsamroot, tapertip hawksbeard, lupine, antelope bitterbrush, and tall green rabbitbrush.
Total annual production is 600 pounds per acre (666 kilograms per hectare) in a normal year. Production in a favorable year is 1000 pounds per acre (1120 kilograms per hectare). Production in an unfavorable year is 300 pounds per acre (333 kilograms per hectare). Structurally, cool season deep-rooted perennial bunchgrasses are very dominant, followed by tall shrubs and perennial forbs being equal while shallow rooted bunchgrasses are subdominant.
This site is best suited for livestock grazing as spring range. Green-up occurs occasionally following fall rain. The site can be used as early spring and winter range for big game in moderate winters.
The site has limited value for recreation except for hunting.
Due to the rainfall, elevation and steep topography on this site, it is susceptible to degradation from erosion. This is caused by improper grazing management or frequent fire. Infiltration is good where the community is in mid to late seral status. Runoff, when it does occur can be erosive on steeper slopes particularly during high intensity convection storms. A mixed stand of shrubs and perennial grasses is necessary to reach the potential of the site.
Impacts on the Plant Community.
Influence of fire:
In the absence of normal fire frequency, basin big sagebrush and antelope bitterbrush can gradually increase on the site. Grasses and forbs decrease as shrubs increase. With the continued absence of fire, basin big sagebrush can displace most of the primary understory species.
When fires become more frequent than historic levels (50-70 years), basin big sagebrush and bitterbrush are reduced significantly. Rabbitbrush can increase slightly. With continued short fire frequency, basin big sagebrush and bitterbrush can be completely eliminated along with many of the desirable understory species such as bluebunch wheatgrass, Nevada bluegrass and Thurber’s needlegrass. These species may be replaced by Fendler threeawn, Sandberg bluegrass, and bulbous bluegrass along with a variety of annual and perennial forbs including noxious and invasive species. Cheatgrass and medusahead will invade the site. These fine fuels will increase the fire frequency.
Influence of improper grazing management:
Season-long grazing and/or excessive utilization can be very detrimental to this site. This type of management leads to reduced vigor of the bunchgrasses. With reduced vigor, recruitment of these species declines. As these species decline, the plant community becomes susceptible to increase in basin big sagebrush and noxious and invasive plants.
Continued improper grazing management influences fire frequency by increasing fine fuels that carry fires. If cheatgrass and/or medusahead increase and become co-dominant with Sandberg bluegrass and other annuals, fires become more frequent.
Proper grazing management that addresses frequency, duration, and intensity of grazing over time, can also keep fine fuels from developing, thereby reducing fire frequency. This can lead to gradual increases in basin big sagebrush. A planned grazing system can be developed to intentionally accumulate fine fuels in preparation for a prescribed burn. Any brush management should be carefully planned, as a reduction in shrubs without a suitable understory of perennial grasses can increase cheatgrass which will lead to more frequent fire intervals.
Weather influences:
Above normal precipitation in March, April and May can dramatically increase total annual production of the plant community. These weather patterns can also increase viable seed production of desirable species to provide for recruitment. Likewise, below normal precipitation during these spring months can significantly reduce total annual production and be detrimental to viable seed production. Overall plant composition is normally not affected when perennials have good vigor.
Below normal temperatures in the spring can have an adverse impact on total production regardless of the precipitation. An early, hard freeze can occasionally kill some plants.
Prolonged drought adversely affects this plant community in several ways. Vigor, recruitment, and production are usually reduced. Mortality can occur. Prolonged drought can lead to a reduction in fire frequency.
Influence of Insects and disease:
Outbreaks can affect vegetation health. Bitterbrush can be severely affected by the western tent caterpillar (Malacosoma fragilis). Two consecutive years of defoliation by the tent caterpillar can cause mortality in bitterbrush. Mormon cricket and grasshopper outbreaks occur periodically. Outbreaks seldom cause plant mortality since defoliation of the plant occurs only once during the year of the outbreak.
Influence of noxious and invasive plants:
Many of these species add to the fine-fuel component and lead to increased fire frequency.
Perennial and annual invasive species compete with desirable plants for moisture and nutrients. The result is reduced production and change in composition of the understory.
Influence of wildlife:
Big game use this site in the spring, fall and in moderate winters. Their numbers are seldom high enough to adversely affect the plant community. Herbivory can be detrimental to bitterbrush when livestock grazing and browsing by big game occurs at the same time and season. This will occur when both kinds of animal are using the plant in the late summer or fall. The adverse impact is excessive use of the current year’s leader growth.
The deer mouse is beneficial to this site as it is the principal vector for planting bitterbrush seed.
Watershed:
Decreased infiltration and increased runoff occur with an increase in basin big sagebrush. Desired understory species can be reduced. This composition change can affect nutrient and water cycles. Increased runoff also causes sheet and rill erosion. Abnormally short fire frequency also gives the same results, but to a lesser degree. The long-term effect is a transition to a different state.
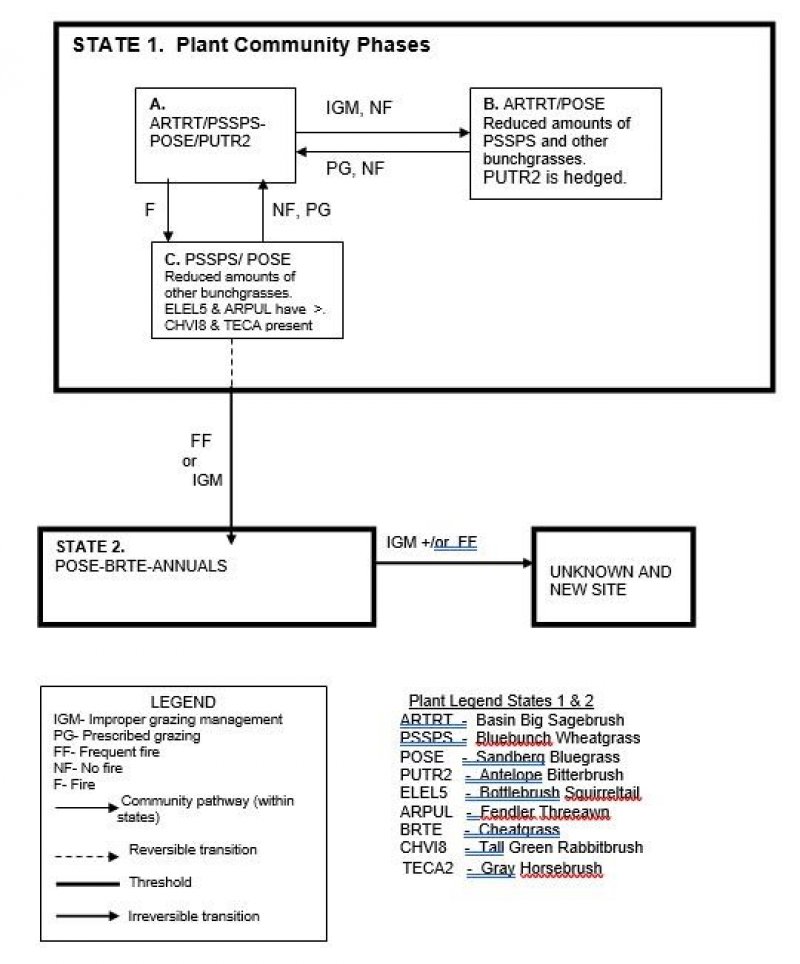
Plant Community and Sequence:
Transition pathways between common vegetation states and phases:
State 1.
Phase A to B. Develops with improper grazing management and in the absence of fire.
Phase A to C. Develops with fire.
Phase B to A. Develops with prescribed grazing and no fire.
Phase C to A. Develops with prescribed grazing and no fire.
State 1 Phase C to State 2. Develops through frequent fire or improper grazing management. This state has crossed the threshold. It is not economically feasible to move it back towards State 1.
State 2 to unknown site. Excessive soil loss and changes in the hydrologic cycle caused by continued improper grazing management and/or frequent fire cause this state to cross a threshold and retrogress to a new site with reduced potential. It is not economically feasible to move this state back towards State 1.
Practice Limitations.
Usually this site will not be a key area for livestock management due to slope and stoniness. Moderate to severe limitations exist on this site for facilitating practices for livestock management. The steep slopes, stoniness, and limited soil depths will make construction of fences, pipelines, troughs and trails difficult. Stony soils and steep slopes present severe limitations for the use of ground travel equipment for seeding.
State and transition model
More interactive model formats are also available.
View Interactive Models
More interactive model formats are also available.
View Interactive Models
Click on state and transition labels to scroll to the respective text
State 1 submodel, plant communities
State 2 submodel, plant communities
State 3 submodel, plant communities
State 4 submodel, plant communities
State 5 submodel, plant communities
State 1
State 1 Phase A
Community 1.1
State 1 Phase A
This plant community has basin big sagebrush in the overstory with bluebunch wheatgrass dominating the understory. Nevada bluegrass, Sandberg bluegrass, antelope bitterbrush and arrowleaf balsamroot are sub-dominant species. Other significant species in the plant community can include Thurber’s needlegrass, bottlebrush squirreltail, longleaf phlox, tapertip hawksbeard and tall green rabbitbrush. Natural fire frequency is 50-70 years.
Table 5. Ground cover
| Tree foliar cover | 0% |
|---|---|
| Shrub/vine/liana foliar cover | 0% |
| Grass/grasslike foliar cover | 0% |
| Forb foliar cover | 0% |
| Non-vascular plants | 0% |
| Biological crusts | 0% |
| Litter | 60-70% |
| Surface fragments >0.25" and <=3" | 0% |
| Surface fragments >3" | 0% |
| Bedrock | 0% |
| Water | 0% |
| Bare ground | 0% |
Figure 3. Plant community growth curve (percent production by month). ID0207, ARTRX/PSSPS. State 1.
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| J | F | M | A | M | J | J | A | S | O | N | D |
| 0 | 0 | 15 | 35 | 35 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 0 |
State 2
State 1 Phase B
Community 2.1
State 1 Phase B
This plant community is dominated by basin big sagebrush with reduced amounts of bluebunch wheatgrass. Sandberg bluegrass, Fendler threeawn and bottlebrush squirreltail have increased in the understory. There is a reduced amount of Nevada bluegrass, Thurber’s needlegrass, and prairie junegrass. All deep-rooted perennial bunchgrasses are typically in low vigor. Basin big sagebrush has increased. Antelope bitterbrush is usually hedged. This state has developed due to improper grazing management and lack of fire. Some cheatgrass and medusahead may have invaded the site.
Table 6. Ground cover
| Tree foliar cover | 0% |
|---|---|
| Shrub/vine/liana foliar cover | 0% |
| Grass/grasslike foliar cover | 0% |
| Forb foliar cover | 0% |
| Non-vascular plants | 0% |
| Biological crusts | 0% |
| Litter | 60-70% |
| Surface fragments >0.25" and <=3" | 0% |
| Surface fragments >3" | 0% |
| Bedrock | 0% |
| Water | 0% |
| Bare ground | 0% |
Figure 4. Plant community growth curve (percent production by month). ID0207, ARTRX/PSSPS. State 1.
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| J | F | M | A | M | J | J | A | S | O | N | D |
| 0 | 0 | 15 | 35 | 35 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 0 |
State 3
State 1 Phase C
Community 3.1
State 1 Phase C
This plant community is dominated by bluebunch wheatgrass and Sandberg bluegrass. Thurber’s needlegrass and Nevada bluegrass can be lost due to fire. Bottlebrush squirreltail and Fendler threeawn have increased. Forbs remain about in the same proportion as Phase A. Very little basin sagebrush is present due to wildfire, but some rabbitbrush and horsebrush are present due to sprouting. Some cheatgrass may have invaded the site. This plant community is the result of wildfire.
Table 7. Ground cover
| Tree foliar cover | 0% |
|---|---|
| Shrub/vine/liana foliar cover | 0% |
| Grass/grasslike foliar cover | 0% |
| Forb foliar cover | 0% |
| Non-vascular plants | 0% |
| Biological crusts | 0% |
| Litter | 60-70% |
| Surface fragments >0.25" and <=3" | 0% |
| Surface fragments >3" | 0% |
| Bedrock | 0% |
| Water | 0% |
| Bare ground | 0% |
Figure 5. Plant community growth curve (percent production by month). ID0207, ARTRX/PSSPS. State 1.
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| J | F | M | A | M | J | J | A | S | O | N | D |
| 0 | 0 | 15 | 35 | 35 | 10 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 0 |
State 4
State 2
Community 4.1
State 2
This plant community is dominated by Sandberg bluegrass, cheatgrass and other annuals. Root sprouting shrubs such as rabbitbrush and horsebrush can be present, dependent upon, how frequent, fire has occurred. Some soil loss has occurred. This state has developed due to frequent fires or improper grazing management. This state has crossed the threshold. It is not economically feasible to move this site back across the threshold with accelerated practices.
Table 8. Ground cover
| Tree foliar cover | 0% |
|---|---|
| Shrub/vine/liana foliar cover | 0% |
| Grass/grasslike foliar cover | 0% |
| Forb foliar cover | 0% |
| Non-vascular plants | 0% |
| Biological crusts | 0% |
| Litter | 60-70% |
| Surface fragments >0.25" and <=3" | 0% |
| Surface fragments >3" | 0% |
| Bedrock | 0% |
| Water | 0% |
| Bare ground | 0% |
Figure 6. Plant community growth curve (percent production by month). ID0211, POSE/BRTE-ANNUALS. State 2.
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| J | F | M | A | M | J | J | A | S | O | N | D |
| 0 | 0 | 15 | 25 | 40 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 0 |
State 5
State 3
Community 5.1
State 3
Table 9. Ground cover
| Tree foliar cover | 0% |
|---|---|
| Shrub/vine/liana foliar cover | 0% |
| Grass/grasslike foliar cover | 0% |
| Forb foliar cover | 0% |
| Non-vascular plants | 0% |
| Biological crusts | 0% |
| Litter | 60-70% |
| Surface fragments >0.25" and <=3" | 0% |
| Surface fragments >3" | 0% |
| Bedrock | 0% |
| Water | 0% |
| Bare ground | 0% |
Additional community tables
Interpretations
Animal community
Wildlife Interpretations.
Animal Community – Wildlife Interpretations
This rangeland ecological site provides diverse habitat for many native wildlife species. The plant community exhibits a diverse mixture of forbs throughout the growing season offering excellent habitat for invertebrates. Mule deer and elk are the large herbivores using the site. The plant community provides important spring, fall and winter forage and cover for mule deer and elk. The site provides seasonal habitat for resident and migratory animals including western toad, sagebrush lizard, shrews, ground squirrels, mice, coyote, red fox, badger, sage-grouse, Ferruginous hawk, prairie falcon, horned lark and western meadowlark. Sagebrush obligate avian species include sage-grouse, Brewer’s sparrow and sage thrasher. Sage-grouse, an area sensitive species, may utilize the sagebrush plant community as nesting, winter and brood-rearing habitat. Encroachment of noxious and invasive plant species (cheatgrass and medusahead) in isolated areas can replace native plant species which provide critical feed, brood-rearing and nesting cover for a variety of native wildlife. Water features are sparse provided by seasonal streams, artificial water catchments and springs.
State 1 Phase 1.1 – Basin Big Sagebrush/ Bluebunch Wheatgrass/ Sandberg Bluegrass/ Antelope Bitterbrush Reference Plant Community (RPC): This plant community provides a diversity of grasses, forbs and shrubs, used throughout the growing season by native insect communities that assist in pollination. Many avian and mammal species utilize this habitat based on the availability of invertebrate prey species. The reptile and amphibian community is represented by leopard lizard, short horned lizard, sagebrush lizard, western skink, western toad, boreal chorus frog and northern leopard frog. Amphibians are associated with springs and isolated water bodies adjacent to this plant community. Development of spring sites that collect all available water would exclude amphibian use on these sites. Native shrub-steppe obligate avian species utilizing the habitat include the Brewer’s sparrow, sage sparrow, sage thrasher and sage-grouse. Sage-grouse may utilize this plant community for nesting, winter and brood-rearing habitat. The plant community provides forage and cover for large mammals including mule deer and elk. The site can be an important wintering area for mule deer and elk where bitterbrush is present. A diverse small mammal population including golden-mantled ground squirrels, kangaroo rats, chipmunks and yellow-bellied marmots utilize this community. Habitat for the pygmy rabbit would be marginal due to stoney soils and steepness of slopes. The deer mouse is beneficial to this site as it is the principal vector for planting bitterbrush seed.
State 1 Phase 1.2 - Basin Big Sagebrush/ Sandberg Bluegrass Plant Community: This plant community is the result of improper grazing management and no fire. An increase in canopy cover of sagebrush contributes to a sparse herbaceous understory. The reduced herbaceous understory results in lower diversity and numbers of insects. The reptile and amphibian community is represented by leopard lizard, short horned lizard, sagebrush lizard, western skink and western toad. The reduction of grasses and forbs in the plant community would reduce the available prey species and cover for these resident reptile species. Amphibian habitat would be tied to permanent spring sites in the area. Development of spring sites that collect all available water would exclude amphibian use on these sites. Key shrub-steppe obligate avians include Brewer’s sparrow, sage sparrow, sage thrasher and sage-grouse. Winter cover and winter food for sage-grouse is available. Quality of nesting and brood-rearing habitat for sage-grouse would decline due to poor plant vigor and lower amounts of herbaceous cover. Loss of understory vegetation, increased sagebrush density and decline of bitterbrush, reduces forage value for mule deer and elk. Antelope bitterbrush has decreased reducing quality of winter habitat for mule deer. A small mammal population including golden-mantled ground squirrels, kangaroo rats, chipmunks, badger and yellow-bellied marmots utilize these areas. The deer mouse is beneficial to this site as it is the principal vector for planting bitterbrush seed.
State 1 Phase 1.3 – Bluebunch Wheatgrass/ Sandberg Bluegrass/ Bottlebrush Squirreltail/ Rabbitbrush Plant Community: This plant community is the result of fire. The plant community, dominated by herbaceous vegetation with little to no sagebrush or antelope bitterbrush would provide less vertical structure for animals. Patches of root sprouting shrubs including rabbitbrush may be present to provide limited vertical structure for wildlife. Insect diversity would be reduced but a diverse native forb plant community would still support select pollinators. Reptiles including leopard lizard, short horned lizard and sagebrush lizard would be limited or excluded due to the loss of sagebrush and antelope bitterbrush. Amphibian habitat would be tied to permanent spring sites in the area. Development of spring sites that collected all available water would exclude use on this site by amphibians. The loss of sagebrush and antelope bitterbrush canopy cover would reduce the quality of this area as nesting habitat for Brewer’s sparrow, sage sparrow, sage thrasher, and sage-grouse. This plant community provides limited brood-rearing habitat for sage-grouse when adjacent sagebrush cover is present. Winter habitat for sage-grouse is eliminated. The dominant herbaceous vegetation improves habitat for grassland avian species (horned lark and western meadowlark). Mule deer and elk forage use would be seasonal (spring and fall) and the site would offer little thermal cover and young of year cover. The populations of small mammals would be dominated by open grassland species like the Columbian ground squirrel.
State 2 – Sandberg Bluegrass/ Cheatgrass / Annuals Plant Community:
This plant community is the result of continued improper grazing management and/or frequent fire. Invasive herbaceous plants and patches of root sprouting shrubs like rabbitbrushes can be present. The reduced forb and shrub component in the plant community would support a very limited population of pollinators. Most reptilian species are not supported with food, water or cover. This plant community does not support the habitat requirements for sage-grouse, sage thrasher, Brewer’s sparrow or sage sparrow. Diversity of grassland avian species is reduced due to poor cover and available food. Birds of prey including hawks and falcons may range throughout these areas looking for prey species. Large mammals may utilize the herbaceous vegetation in the early part of the year when the invasive annuals (cheatgrass) are more palatable. At other times of the year large mammals would not regularly utilize these areas due to poor food and cover conditions. The populations of small mammals would be dominated by open grassland species like the Columbian ground squirrel.
Grazing Interpretations.
This site is best used as spring range for domestic livestock. Some fall use can be made when fall
rains provide green-up.
Estimated initial stocking rate will be determined with the landowner or decision-maker. They will be based on the inventory which includes species, composition, similarity index, production, past use history, season of use and seasonal preference. Calculations used to determine estimated initial stocking rate will be based on forage preference ratings.
Hydrological functions
Soils on this site are in hydrologic group C.
Recreational uses
This site has limited value for recreation except that it does provide some hunting opportunities for upland game birds.
Wood products
None
Other products
None
Other information
Field Offices
Weiser, ID
Emmett, ID
Mountain Home, ID
Meridian, ID
Cascade, ID
Supporting information
Inventory data references
Information presented here has been derived from NRCS clipping and other inventory data. Also, field knowledge of range-trained personnel was used. Those involved in developing this site description include:
Dave Franzen, co-owner, Intermountain Rangeland Consultants, LLC
Jacy Gibbs, co-owner, Intermountain Rangeland Consultants, LLC
Jim Cornwell, Range Management Specialist, IASCD
Brendan Brazee, State Rangeland Management Specialist, NRCS, Idaho
Leah Juarros, Resource Soil Scientist, NRCS, Idaho
Lee Brooks, Range Management Specialist, IASCD
Type locality
| Location 1: Gem County, ID |
|---|
Other references
Hironaka, M., M.A. Fosberg, A. H. Winward. 1983. Sagebrush- Grass Habitat Types of Southern Idaho. University of Idaho. Moscow, Idaho. Bulletin Number 35
USDA Forest Service, Rocky Mountain Research Station. 2004. Restoring Western Ranges and Wildlands. General Technical Report RMRS-GTR-136-vols. 1-3.
USDA, NRCS.2001. The PLANTS Database, Version 3.1 (http://plants.usda.gov.). National Plant Data Center, Baton Rouge, LA 70874-4490 USA
USDA, Forest Service, Fire Effects Information Database. 2004. www.fs.fed.us/database.
USDI Bureau of Land Management, US Geological Survey; USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service, Agricultural Research Service; Interpreting Indicators of Rangeland Health. Technical Reference 1734-6; version 4-2005.
Approval
Kendra Moseley, 9/23/2020
Rangeland health reference sheet
Interpreting Indicators of Rangeland Health is a qualitative assessment protocol used to determine ecosystem condition based on benchmark characteristics described in the Reference Sheet. A suite of 17 (or more) indicators are typically considered in an assessment. The ecological site(s) representative of an assessment location must be known prior to applying the protocol and must be verified based on soils and climate. Current plant community cannot be used to identify the ecological site.
| Author(s)/participant(s) | Dave Franzen and Jacy Gibbs Intermountain Range Consultants 17700 Fargo Rd. Wilder, ID 83676 |
|---|---|
| Contact for lead author | Brendan Brazee, State Rangeland Management Specialist USDA-NRCS 9173 W. Barnes Drive, Suite C, Boise, ID 83709 |
| Date | 03/26/2008 |
| Approved by | Kendra Moseley |
| Approval date | |
| Composition (Indicators 10 and 12) based on | Annual Production |
Indicators
-
Number and extent of rills:
can occur on this site due to steep slopes, limited water-holding capacity and percent bare ground. Gravel and stones on the surface reduces erosion. -
Presence of water flow patterns:
are common on this site. When they occur they may be short and not extensive. -
Number and height of erosional pedestals or terracettes:
are common on this site. Terracettes develop uphill from the large bunchgrasses and shrubs.
-
Bare ground from Ecological Site Description or other studies (rock, litter, lichen, moss, plant canopy are not bare ground):
ranges from 30-40 percent. -
Number of gullies and erosion associated with gullies:
do not occur on this site. -
Extent of wind scoured, blowouts and/or depositional areas:
usually does not occur. -
Amount of litter movement (describe size and distance expected to travel):
fine litter in the interspaces may move up to 5 feet or further following a significant run-off event. Terracettes and rocks can trap fine litter. Coarse litter generally does not move. -
Soil surface (top few mm) resistance to erosion (stability values are averages - most sites will show a range of values):
values should range from 4 to 6, but needs to be tested. -
Soil surface structure and SOM content (include type of structure and A-horizon color and thickness):
the A or A1 horizon is typically 3 to 11 inches thick. Structure ranges from weak very fine granular to moderate coarse granular. Soil organic matter (SOM) ranges from 1 to 4 percent. -
Effect of community phase composition (relative proportion of different functional groups) and spatial distribution on infiltration and runoff:
bunchgrasses, especially deep-rooted perennials, slow run-off and increase infiltration. Tall shrubs accumulate snow in the interspaces. Terracettes provide a favorable micro-site for vegetative establishment which further increases infiltration. -
Presence and thickness of compaction layer (usually none; describe soil profile features which may be mistaken for compaction on this site):
not present. -
Functional/Structural Groups (list in order of descending dominance by above-ground annual-production or live foliar cover using symbols: >>, >, = to indicate much greater than, greater than, and equal to):
Dominant:
cool season deep-rooted perennial bunchgrassesSub-dominant:
tall shrubs= perennial forbsOther:
Additional:
-
Amount of plant mortality and decadence (include which functional groups are expected to show mortality or decadence):
basin big sagebrush and antelope bitterbrush will become decadent in the absence of fire and ungulate grazing. Grass and forb mortality will occur as tall shrubs increase. -
Average percent litter cover (%) and depth ( in):
annual litter cover in the interspaces will be 5-10 percent to a depth of <0.1 inch. Under the mature shrubs litter is greater than 0.5 inches. Fine litter can accumulate on the terracettes and behind surface stones. -
Expected annual annual-production (this is TOTAL above-ground annual-production, not just forage annual-production):
600 lbs. per acre in a year with normal precipitation and temperatures. Production is normally low due to low infiltration, steep south aspect and moderate water capacity. Perennial grasses produce 55-65 percent of the total, forbs 15-25 percent, and shrubs 15-25 percent. -
Potential invasive (including noxious) species (native and non-native). List species which BOTH characterize degraded states and have the potential to become a dominant or co-dominant species on the ecological site if their future establishment and growth is not actively controlled by management interventions. Species that become dominant for only one to several years (e.g., short-term response to drought or wildfire) are not invasive plants. Note that unlike other indicators, we are describing what is NOT expected in the reference state for the ecological site:
cheatgrass, medusahead, bulbous bluegrass, rush skeletonweed, scotch thistle, spotted and diffuse knapweed. -
Perennial plant reproductive capability:
all functional groups have the potential to reproduce in favorable years.
Print Options
Sections
Font
Other
The Ecosystem Dynamics Interpretive Tool is an information system framework developed by the USDA-ARS Jornada Experimental Range, USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service, and New Mexico State University.
Click on box and path labels to scroll to the respective text.