Natural Resources
Conservation Service
Ecological site F026XY063NV
Shallow Sandy Pediment 13-15 P.Z. JUOS/ARTRW8/ACHY-HECO26
Last updated: 4/10/2024
Accessed: 02/28/2026
General information
Provisional. A provisional ecological site description has undergone quality control and quality assurance review. It contains a working state and transition model and enough information to identify the ecological site.
MLRA notes
Major Land Resource Area (MLRA): 026X–Carson Basin and Mountains
MLRA 26 is in western Nevada and eastern California; approximately 69 percent is in Nevada, and 31 percent in California. The area is predominantly in the Great Basin Section of the Basin and Range Province of the Intermontane Plateaus. Isolated north- south trending mountain ranges are separated by aggraded desert plains. The mountains are uplifted fault-blocks with steep side slopes. The valleys are drained by three major rivers flowing east across MLRA 26; the Truckee, Carson and Walker rivers. A narrow strip along the western border of MLRA 26 is in the Sierra Nevada Section of the Cascade-Sierra Mountains Province of the Pacific Mountain System. The Sierra Nevada Mountains are primarily a large fault-block that has been uplifted with a dominant tilt to the west. The structure creates an impressive wall of mountains directly west of the area creating a rain shadow affect to MLRA 26. Parts of the eastern face; the foothills, mark the western boundary of the area. Elevations range from near 3,806 feet (1,160 meters) on the west shore of Pyramid Lake to 11,653 feet (3,552 meters) on the summit of Mount Patterson in the Sweetwater Mountains.
In MLRA 26, the valleys are composed dominantly of Quaternary alluvial deposits. Quaternary playa or alluvial flat deposits typically occupy the lowest valley bottoms in the internally drained valleys. Tertiary andesitic flows, breccias, ash flow tuffs, rhyolite tuffs or granodioritic rocks dominate the hills and mountains. Quaternary basalt flows are present in lesser amounts. Jurassic and Triassic limestone and shale, and Precambrian limestone and dolomite are also present in very limited amounts. Glacial till deposits, of limited extent are along the east flank of the Sierra Nevada Mountains; the result of alpine glaciation.
The average annual precipitation in MLRA 26 is 5 to 36 inches (125 to 915 millimeters), increasing with elevation. Most of the rainfall occurs as high-intensity, convective storms in spring and autumn. Precipitation is mostly snow in winter. Summers are dry. The average annual temperature is 37 to 54 degrees F (3 to 12 degrees C). The freeze-free period averages 115 days and ranges from 40 to 195 days, decreasing in length with elevation.
The dominant soil orders in MLRA 26 are Aridisols and Mollisols. The soils in the area typically have a mesic soil temperature regime, an aridic or xeric soil moisture regime, and mixed or smectitic mineralogy. The soils are generally well drained, clayey or loamy and are commonly skeletal. The soils depths are typically very shallow to moderately deep.
This area supports shrub-grass vegetation characterized by big sagebrush. Low sagebrush and Lahontan sagebrush are on some soils. Antelope bitterbrush, squirreltail, desert needlegrass, Thurber needlegrass, and Indian ricegrass are important associated plants. Green ephedra, Sandberg bluegrass, desert peach, and several forb species are also common. Juniper-pinyon woodland is typical on mountain slopes. Jeffrey pine, lodgepole pine, white fir, and manzanita grow on the highest mountain slopes. Shadscale is the typical plant in the drier parts of the area. Sedges, rushes, and moisture-loving grasses grow on the wettest parts of the wet flood plains and terraces. Basin wildrye, alkali sacaton, saltgrass, buffaloberry, black greasewood, and rubber rabbitbrush grow on the drier sites that have a high concentration of salts.
Wildlife species in the area are mule deer, coyote, beaver, muskrat, jackrabbit, cottontail, raptors, pheasant, chukar, blue grouse, mountain quail, and mourning dove, amongst other species. The species of fish in the area include trout and catfish. The Lahontan cutthroat trout in the Truckee River is a threatened and endangered species.
LRU notes
The Sierra Influenced Ranges LRU is characterized by wooded great basin mountains and climatic and biotic affinities to the Sierra Nevada Mountain range. The Sierra Influenced Ranges LRU receives greater precipitation than the mountain ranges of central Nevada.
Amount of precipitation varies in relation to the local strength of the Sierra Nevada rain shadow, characterized by pinyon and juniper trees. The White, Sweetwater, Pine Nut, Wassuk, and Virginia ranges of Nevada support varying amounts of Sierra Nevada flora, like ponderosa pine. Elevations range from 1610 to 2420 meters and slopes range from 5 to 49 percent, with a median value of 22 percent.
Frost free days (FFD) ranges from 92 to 163.
Ecological site concept
This forestland site is on sand sheets that cover rock pediments. Slopes range from 2 to over 15 percent, but slopes are typically 2 to 8 percent. Elevations are 6800 to 7400 feet. The soils are typically shallow and well drained. The soil surface is covered with a mantle of aeolian sand that strongly influences understory vegetation. The dominant plants are Utah juniper (Juniperus osteosperma), Wyoming big sagebrush (Artemisia tridentata ssp. wyomingensis), Indian ricegrass (Achnatherum hymenoides), and needle and thread (Hesperostipa comata).
Similar sites
| F026XY064NV |
Shallow Clayey Summit 11-14 P.Z. PIMO-JUOS/ARAR8/ACTH7 Surface soil texture is sandy loam. |
|---|
Table 1. Dominant plant species
| Tree |
(1) Juniperus osteosperma |
|---|---|
| Shrub |
(1) Artemisia tridentata ssp. wyomingensis |
| Herbaceous |
(1) Achnatherum hymenoides |
Physiographic features
This forestland site is on sand sheets that cover summits and side slopes of rock pediments. Slopes range from 2 to over 15 percent, but slopes are typically 2 to 8 percent. Elevations are 6800 to 7400 feet.
Table 2. Representative physiographic features
| Landforms |
(1)
Pediment
|
|---|---|
| Runoff class | Very high |
| Elevation | 6,800 – 7,400 ft |
| Slope | 2 – 15% |
| Aspect | Aspect is not a significant factor |
Climatic features
Average annual precipitation is about 8 to 12 inches (20 to 30 cm). Mean annual air temperature is 47 to 51 degrees F. The average growing season is 90 to 140 days.
Nevada’s climate is predominantly arid, and has large daily ranges of temperature, infrequent severe storms, heavy snowfall in the higher mountains, and significant variations with elevation. Three basic geographical factors largely influence Nevada’s climate (1) continentality, (2) latitude, and (3) elevation. Continentality is the most important factor. The strong continental effect is expressed in the form of both dryness and large temperature variations. Nevada is on the eastern, lee side of the Sierra Nevada Range, a massive mountain barrier that markedly influences the climate of the State. The prevailing winds are from the west, and as the warm moist air from the Pacific Ocean ascend the western slopes of the Sierra Range, the air cools, condensation occurs and most of the moisture falls as precipitation. As the air descends the eastern slope, it is warmed by compression, and very little precipitation occurs. The effects of this mountain barrier are felt, not only in the west, but throughout the state. As a result, the lowlands of Nevada are largely deserts or steppes. The temperature regime is also affected by the blocking of the inland-moving maritime air. Nevada sheltered from maritime winds, has a continental climate with well-developed seasons. The terrain responds quickly to changes in solar heating.
Nevada is within the mid-latitude belt of prevailing westerly winds which occur most of the year. These winds bring frequent changes in weather during the late fall, winter, and spring months when most of the precipitation occurs. To the south of the mid-latitude westerlies, is a zone of high pressure in subtropical latitudes, with a center over the Pacific Ocean. In the summer, this high-pressure belt shifts northward over the latitudes of Nevada, blocking storms from the ocean. The resulting weather is mostly clear and dry during the summer and early fall, with scattered thundershowers. The eastern portion of the state receives significant summer thunderstorms generated from monsoonal moisture pushed up from the Gulf of California, known as the North American monsoon. The monsoon system peaks in August and by October the monsoon high over the Western U.S. begins to weaken and the precipitation retreats southward towards the tropics (NOAA 2004).
Mean annual precipitation at the Bear Creek, Nevada SNOTEL station (170501020301) is 37.69 inches. monthly mean precipitation in inches is:
January 3.84 (9.75 cm); February 3.75 (9.53 cm); March 4.38 (11.13 cm); April 4.9 (12.45 cm); May 3.99 (10.13 cm); June 2.82 (7.16 cm);
July .95 (2.41 cm); August 1.66 (4.22 cm); September 1.22 (3.10 cm); October 2.12 (5.38 cm); November 3.67 (9.32 cm); December 4.38 (11.13 cm).
Table 3. Representative climatic features
| Frost-free period (characteristic range) | 60-110 days |
|---|---|
| Freeze-free period (characteristic range) | |
| Precipitation total (characteristic range) | 8-12 in |
| Frost-free period (average) | 90 days |
| Freeze-free period (average) | |
| Precipitation total (average) | 10 in |
Figure 1. Monthly average minimum and maximum temperature
Figure 2. Annual precipitation pattern
Figure 3. Annual average temperature pattern
Influencing water features
No influencing water features are associated with this site.
Soil features
The soils associated with this site are typically shallow and well drained. The soil surface is covered with a mantle of aeolian sand that strongly influences understory vegetation. The soils are typically skeletal with 35 to over 50 percent gravels, cobbles, or stones, by volume, distributed throughout the soil profile. Available water capacity is low, but trees and shrubs extend their roots into fractures in the underlying material allowing them to utilize deep moisture. Some soils have high amounts of gravel on the soil surface that can provide a stabilizing effect on surface erosion conditions. Runoff is slow to medium to rapid and the potential for sheet and rill erosion is low. Potential for wind erosion is high. The soil associated with this site includes Bregar and Karpp families.
Table 4. Representative soil features
| Parent material |
(1)
Residuum
–
volcanic rock
(2) Colluvium – volcanic rock |
|---|---|
| Surface texture |
(1) Very gravelly sand |
| Drainage class | Well drained |
| Soil depth | 8 – 16 in |
| Surface fragment cover <=3" | 26% |
| Surface fragment cover >3" | 10% |
| Available water capacity (0-40in) |
0.6 – 0.8 in |
| Calcium carbonate equivalent (0-40in) |
Not specified |
| Electrical conductivity (0-40in) |
Not specified |
| Sodium adsorption ratio (0-40in) |
Not specified |
| Soil reaction (1:1 water) (0-40in) |
6.6 – 7.3 |
| Subsurface fragment volume <=3" (Depth not specified) |
35% |
| Subsurface fragment volume >3" (Depth not specified) |
Not specified |
Ecological dynamics
Description of MLRA 26 Disturbance Response Group 17 (Stringham et al. 2021):
Disturbance Response Group (DRG) 17 consists of one ecological site, JUOS WSG: 0S0402 (026XY063NV). This woodland site is on sand sheets that cover summits and side slopes of upper fan piedmonts and rock pediments. This site is dominated by old growth Utah juniper (Juniperus osteosperma) with Wyoming big sagebrush (Artemisia tridentata ssp. wyomingensis) as the principal understory shrub. Other shrubs on the site include currant (Ribes ssp.), green ephedra (Ephedra viridis), and Douglas rabbitbrush (Chrysothamnus viscidiflorus). The dominant understory grasses are Indian ricegrass (Achnatherum hymenoides) and needle and thread (Hesperostipa comata). Other understory grasses include desert needlegrass (Achnatherum speciosum), bottlebrush squirreltail (Elymus elymoides), and Sandberg bluegrass (Poa secunda). An overstory canopy cover of 10 to 20 percent was assumed to be representative of tree dominance for a mature forest in the Reference State for this model. Wildfire is recognized as a natural disturbance that strongly influenced the structure and composition of the Reference State. The Reference plant community is dominated by Utah juniper with Wyoming big sagebrush and Indian ricegrass dominant in the understory. Few tree seedling and saplings would be present in the Reference State.
Under medium canopy cover (11-20 percent), understory production (plants under 4.5 feet in height) ranges from 100 to 350 lbs/ac on this site. This range of elevation for this site is 6,500 to 7,500 feet elevation. Slopes range from 2 to 15 percent, but are typically 2 to 8 percent. Average annual precipitation is about 8 to 12 inches. The soils on this site are shallow and well drained. The surface is covered with a mantle of aeolian sand that strongly influences the understory vegetation. The soils are typically skeletal with 35 to over 50 percent gravels, cobbles, or stones, by volume, distributed throughout the soil profile. Available water capacity is low, but trees and shrubs extend their roots into fractures in the underlying material, allowing them to utilize deep moisture. Some soils have high amounts of gravel on the soil surface that can provide a stabilizing effect on surface erosion conditions. Runoff is slow to medium to rapid and the potential for sheet and rill erosion is moderate to severe depending on the slope. Potential for wind erosion is high.
Ecological Dynamics and Disturbance Response:
An ecological site is the product of all the environmental factors responsible for its development, and it has a set of key characteristics that influence a site’s resilience to disturbance and resistance to invasive species. Key characteristics include: (1) climate (precipitation, temperature), (2) topography (aspect, slope, elevation, and landform), (3) hydrology (infiltration, runoff), (4) soils (depth, texture, structure, organic matter), (5) plant communities (functional groups, productivity), and (6) natural disturbance regimes (fire, herbivory, etc.) (Caudle et al. 2013). Biotic factors that influence resilience include: (1) site productivity, (2) species composition and structure, and (3) population regulation and regeneration (Chambers et al. 2013).
Pinyon and juniper dominated plant communities in the cold desert of the Intermountain West occupy over 18 million ha (44,600,000 acres) (Miller and Tausch 2001). In the mid to late 1900’s, the number of pinyon and juniper trees establishing per decade began to increase compared to the previous several hundred years. The substantial increase in conifer establishment is attributed to several factors. These factors include: (1) cessation of the aboriginal burning (Tausch 1999), (2) change in climate with rising temperatures (Heyerdahl et al. 2008), (3) the reduced frequency of fire likely driven by the introduction of domestic livestock, (4) a decrease in wildfire frequency along with improved wildfire suppression efforts, and (5) potentially increased CO2 levels favoring woody plant establishment (Tausch 1999, Bunting 1994). Miller et al. (2008) found pre-settlement tree densities averaged 2 to 11 trees per acre in six woodlands studied across the Intermountain West. Current stand densities range from 80 to 358 trees per acre. In Utah, Nevada, and Oregon, trees establishing prior to 1860 account for only two percent or less of the total population of pinyon and juniper (R. Miller et al. 1999, Miller and Tausch 2001, Miller et al. 2008). The research strongly suggests that for over 200 years prior to settlement, woodlands in the Great Basin were relatively low density with limited rates of establishment (Miller and Tausch 2001, Miller et al. 2008). Tree canopy cover of 10 to 20 percent might be more representative of these sites in pristine condition (USDA 1997). Increases in pinyon and juniper densities post-settlement were the result of both infill in mixed age tree communities and expansion into shrub-steppe communities. However, the proportion of old-growth can vary depending on disturbance regimes, soils, and climate. Some ecological sites are capable of supporting persistent woodlands, likely due to specific soils and climate resulting in infrequent stand-replacing disturbances. In the Great Basin, old-growth trees typically grow on rocky shallow or sandy soils that support little understory vegetation to carry a fire (Burkhardt and Tisdale 1976, Holmes et al. 1986, West et al. 1998, Miller and Rose 1995, USDA 1997).
Utah juniper is a long-lived tree species with wide ecological amplitudes (Tausch et al. 1981, West et al. 1998, Weisberg and Ko 2012). Maximum ages of pinyon and juniper exceed 1000 years, and stands with maximum age classes are only on steep rocky slopes with no evidence of fire (West et al. 1975). Juniper growth is dependent mostly upon soil moisture stored from winter precipitation, mainly snow. Much of the summer precipitation is ineffective, being lost in runoff after summer convection storms or by evaporation and interception (Tueller and Clark 1975). Juniper is highly resistant to drought, which is common in the Great Basin. Taproots of juniper have a relatively rapid rate of root elongation and are thus able to persist until precipitation conditions are more favorable (Emerson 1932).
Infilling by younger trees increases canopy cover and causes a decline in understory perennial vegetation because of increased competition for water and sunlight. Evidence suggests that phenolic compounds in juniper litter might have allelopathic effects on grass (Jameson 1970). Infilling shifts stand level biomass from ground fuels to canopy fuels, which has the potential to significantly impact fire behavior. The more tree-dominated pinyon and juniper woodlands become, the less likely they are to burn under moderate conditions, resulting in infrequent high intensity fires (Gruell 1999, Miller et al. 2008). As the understory vegetation declines in vigor, the ability of native perennial plants to recover after fire is reduced (Urza et al. 2017). The increase in bare ground allows for the invasion of non-native annual species such as cheatgrass (Bromus tectorum), and with intensive wildfire, the potential for conversion to annual exotics is a serious threat (Tausch 1999, Miller et al. 2008).
Specific successional pathways after disturbance in juniper stands are dependent on a number of variables such as plant species present at the time of disturbance and their individual responses to disturbance, past management, type and size of disturbance, available seed sources in the soil or adjacent areas, and site and climatic conditions throughout the successional process.
Insects and diseases of Western juniper are not well understood or studied (Eddleman et al. 1994). A fungus called juniper pocket rot (Pyrofomes demidoffi), also known as white trunk rot (Eddleman et al. 1994, Durham 2014) can kill Utah juniper. Pocket rot enters the tree through any wound or opening that exposes the heartwood. In an advanced stage, this fungus can cause high mortality (Durham 2014). Dwarf mistletoe (Phorandendron spp.), a parasitic plant, might also affect Utah juniper and without treatment or pruning, might kill the tree 10-15 years after infection. Seedlings and saplings are most susceptible to the parasite (Christopherson 2014). Other diseases affecting juniper are: dwarf mistletoe (Arceuthobium spp.) that might weaken trees; leaf rust (Gymnosporangium sp.) on leaves and young branches; and juniper blight (Phomopsis sp.). Flat-head borers (Chrysobothris sp.) attack the wood; long-horned beetles (Methia juniper, Styloxus bicolor) and round-head borers (Callidium spp.) girdle branches and can kill branches or entire trees (Tueller and Clark 1975).
The understory is dominated by deep-rooted, cool season, perennial bunchgrasses and long-lived shrubs (50+ years) with high root to shoot ratios. The dominant shrubs typically root to the full depth of the winter-spring soil moisture recharge, which ranges from 1.0 to over 3.0 m. (Comstock and Ehleringer 1992). Root length of mature sagebrush plants was measured to a depth of 2 meters in alluvial soils in Utah (Richards and Caldwell 1987). These shrubs have a flexible generalized root system with development of both deep taproots and laterals near the surface (Dobrowolski et al. 1990).
The dominant perennial bunchgrass on this site is Indian ricegrass. This and other perennial bunchgrasses generally have somewhat shallower root systems than the shrubs, but root densities are often as high as or higher than those of shrubs in the upper 0.5 m of the soil profile. General differences in root depth distributions between grasses, shrubs, and trees results in resource partitioning in these shrub/grass systems.
In the Great Basin, the majority of annual precipitation is received during the winter and early spring. This continental semiarid climate regime favors growth and development of deep-rooted shrubs and herbaceous cool season plants using the C3 photosynthetic pathway (Comstock and Ehleringer 1992). Winter precipitation and slow melting of snow results in deeper percolation of moisture into the soil profile. Herbaceous plants, more shallow-rooted than shrubs, grow earlier in the growing season and thrive on spring rains, while the deeper rooted shrubs lag in phenological development because they draw from deeply infiltrating moisture from snowmelt the previous winter. Periodic drought regularly influences sagebrush ecosystems and drought duration and severity has increased throughout the 20th century in much of the Intermountain West. Major shifts away from historical precipitation patterns have the greatest potential to alter ecosystem function and productivity. Species composition and productivity can be altered by the timing of precipitation and water availability within the soil profile (Bates et al. 2006).
The ecological site in this DRG has low to moderate resilience to disturbance and resistance to invasion. Resilience increases with higher elevation, northerly aspect, increased precipitation, and nutrient availability. Three possible states have been identified for this DRG.
Annual Invasive Grasses:
The species most likely to invade these sites is cheatgrass, however the sandy surface decreases the probability of cheatgrass dominance. Cheatgrass is a cool season annual grass that maintains an advantage over native plants in part because it is a prolific seed producer, can germinate in the autumn or spring, tolerates grazing, and increases with frequent fire (Klemmedson and Smith 1964, Miller et al. 1999). Cheatgrass originated from Eurasia and was first reported in North America in the late 1800s (Mack and Pyke 1983, Furbush 1953). Pellant and Hall (1994) found 3.3 million acres of public lands dominated by cheatgrass and suggested that another 76 million acres were susceptible to invasion by winter annuals including cheatgrass and medusahead. Bradley and Mustard (2005) use Landsat and Advanced Very High Resolution Radiometer to estimate the areal extent of cheatgrass dominance in the Great Basin. Their results suggest cheatgrass dominated over 4.9 million acres in 2005. In addition, cheatgrass was 26 percent more likely to be found within 450 feet of areas occupied by cheatgrass in 1973, with cultivation, power lines and roads identified as primary vectors of spread (Bradley and Mustard 2006).
Recent modeling and empirical work by Bradford and Lauenroth (2006) suggests that seasonal patterns of precipitation input and temperature are also key factors determining regional variation in the growth, seed production, and spread of invasive annual grasses. The phenomenon of cheatgrass “die-off” provides opportunities for restoration of perennial and native species (Baughman et al. 2016, Baughman et al. 2017). The causes of these events are not fully understood, but there is ongoing work to try to predict where they occur, in the hopes of aiding conservation planning (Weisberg et al. 2017, Brehm 2019).
Methods to control cheatgrass include herbicide, fire, targeted grazing, and seeding. Mapping potential or current invasion vectors is a management method designed to increase the cost effectiveness of control methods. Spraying with herbicide (Imazapic or Imazapic + glyphosate) and seeding with crested wheatgrass and Sandberg bluegrass might be more successful at combating cheatgrass (and medusahead) than spraying alone (Sheley et al. 2012). To date, most seeding success has occurred with non-native wheatgrass species.
Perennial grasses, especially crested wheatgrass, can suppress cheatgrass growth when mature (Blank et al. 2020). Where native bunchgrasses are missing from the site, revegetation of annual grass invaded rangelands has been shown to have a higher likelihood of success when using introduced perennial bunchgrasses such as crested wheatgrass (Clements et al. 2017, Davies et al. 2015). Butler et al. (2011) tested four herbicides (Imazapic, Imazapic + glyphosate, rimsulfuron, and sulfometuron + Chlorsulfuron) for suppression of cheatgrass, medusahead and ventenata (North Africa grass, Ventenata dubia) within residual stands of native bunchgrass. Additionally, they tested the same four herbicides followed by seeding of six bunchgrasses (native and non-native) with varying success (Butler et al. 2011). Herbicide-only treatments appeared to remove competition for established bluebunch wheatgrass by providing 100 percent control of ventenata and medusahead and greater than 95 percent control of cheatgrass (Butler et al. 2011). Caution in using these results is advised, as only one year of data was reported.
In considering the combination of pre-emergent herbicide and prescribed fire for invasive annual grass control, it is important to assess the tolerance of desirable brush species to the herbicide being applied. Vollmer and Vollmer (2008) tested the tolerance of mountain mahogany (Cercocarpus montanus), antelope bitterbrush, and multiple sagebrush species to three rates of Imazapic with and without methylated seed oil as a surfactant. They discovered a cheatgrass control program in an antelope bitterbrush community should not exceed Imazapic at 8 ounces per acre with or without surfactant. Sagebrush, regardless of species or rate of application, was not affected. However, many environmental variables were not reported in this study and managers should install test plots before broad scale herbicide application is initiated.
Fire Ecology:
Utah juniper is typically killed by fire, and is most vulnerable to fire when it is under four feet tall (Bradley et al. 1992). Larger trees, because they have foliage farther from the ground and thicker bark, can survive low severity fires but mortality occurs when 60 percent or more of the crown is scorched (Jameson 1966). With the low production of the understory vegetation, high severity fires within this plant community were not likely and rarely became crown fires (Bradley et al. 1992, Miller and Tausch 2001). Tree density on this site increases with grazing management that favors the removal of fine fuels and management focused on fire suppression. With an increase of cheatgrass in the understory, fire severity is likely to increase. Utah juniper reestablishes by seed from nearby seed source or surviving seeds. Utah juniper begins to produce seed at about 30 years old (Bradley et al. 1992). Seeds establish best using a nurse plant such as sagebrush and rabbitbrush (Chrysothamnus spp. or Ericameria spp). (Everett and Ward 1984, Tausch and West 1988, Bradley et al. 1992). Utah juniper woodlands reach mature stage between 85 to 150 years after fire (Barney and Frischknecht 1974, Tausch and West 1988).
Large fires were and continue to be rare on this site due to large interspaces and low levels of fine fuels (Miller and Heyerdahl 2008). Lightning-ignited fires were likely common but typically did not affect more than a few individual trees. Replacement fires were uncommon to rare (100-600 years) and occurred primarily during extreme fire behavior conditions. Spreading, low-intensity surface fires had a very limited role in molding stand structure and dynamics (Miller at al. 2019). Surface spread was more likely to occur in more productive areas with moderately deep to deep soils, which favors the dominance of herbaceous vegetation and sagebrush (Miller and Heyerdahl 2008, Romme et al. 2009, Miller et al. 2019). The open structure of woodlands is the result of limited seedling establishment, natural thinning processes such as drought and pets, or competition from herbaceous vegetation (Miller et al. 2019). Pre-settlement fire return intervals in the Great Basin National Park, Nevada were found to have a mean range between 50 to 100 years with north-facing slopes burning every 15 to 20 years and rocky landscapes with sparse understory very infrequently (Gruell 1999). Results were less conclusive in a similar study in the Bodie Hills, however it was apparent that old (300+ yr) pinyon primarily survived in protected, low-fuel areas. Woodland dynamics are largely attributed to long-term climatic shifts (temperature, amounts and distribution of precipitation) and the extent and return intervals of fire (Miller and Tausch 2001, Miller et al. 2019). Limited data exists that describes fire histories across woodlands in the Great Basin. Both the infilling of younger trees into old-growth stands and the expansion of trees into surrounding sagebrush communities has increased the risk of loss of pre-settlement trees through the increased landscape level continuity of fuels (Miller et al. 2008).
Wyoming big sagebrush communities historically had low fuel loads. Patchy fires that burned in a mosaic pattern were common at 10-to-70-year return intervals (Young et al. 1979, West and Hassan 1985, Bunting et al. 1987), however newer research suggests longer return intervals. Davies et al. (2006) suggest fire return intervals in Wyoming big sagebrush communities were around 50 to 100 years. More recently, Baker (2011) estimates fire rotation to be 200-350 years in Wyoming big sagebrush communities. Wyoming big sagebrush is killed by fire and only regenerates from seed. Recovery time for Wyoming big sagebrush might require 50-120 or more years (Baker 2006). However, the introduction and expansion of cheatgrass has dramatically altered the fire regime (Balch et al. 2013) and restoration potential of Wyoming big sagebrush communities.
The effect of fire on bunchgrasses relates to culm density, culm-leaf morphology, and the size of the plant. The initial condition of bunchgrasses within the site along with seasonality and intensity of the fire all factor into the individual species response. For most forbs and grasses, the growing points are located at or below the soil surface which provides relative protection from disturbances that decrease above ground biomass, such as grazing or fire. Thus, fire mortality is more correlated to duration and intensity of heat which is related to culm density, culm-leaf morphology, size of plant and abundance of old growth (Wright 1971, Young 1983).
Indian ricegrass is fairly fire tolerant (Wright 1985), which is likely due to its low culm density and below-ground root crowns. Vallentine (1989) cites several studies in the sagebrush zone that classified Indian ricegrass as being slightly damaged from late summer burning. Indian ricegrass has also been found to reestablish on burned sites through seed dispersed from adjacent unburned areas (Young 1983, West 1994). Thus, the presence of surviving, seed producing plants facilitates the reestablishment of Indian ricegrass. Grazing management following fire to promote seed production and establishment of seedlings is important.
Needle-and-thread, a fine-leaved grass, is considered sensitive to fire (Akinsoji 1988, Bradley et al. 1992, Miller et al. 2013). In a study by Wright and Klemmedson (1965), season of burn rather than fire intensity seemed to be the crucial factor in mortality for needle-and-thread grass. Early spring season burning was seen to kill the plants while August burning had no effect. Thus, under wildfire scenarios needle-and- thread is often present in the post-burn community.
Desert needlegrass might increase after burning. In a summation of 13 studies, Abella (2009) found that desert needlegrass increased in abundance (derived from cover, density, or frequency depending on the source of publication) on burned to unburned sites. Thatcher and Hart (1974) observed an increase in desert needlegrass in areas which appeared to have burned on a relict site, however they attributed this to soil type rather than species response.
Bottlebrush squirreltail is considered more fire tolerant than Indian ricegrass due to its small size, coarse stems, and sparse leafy material (Britton et al. 1990). Postfire regeneration occurs from surviving root crowns and from on- and off-site seed sources. Bottlebrush squirreltail has the ability to produce large numbers of highly germinable seeds with relatively rapid germination (Young and Evans 1977) when exposed to the correct environmental cues. Early spring growth and ability to grow at low temperatures contribute to the persistence of bottlebrush squirreltail among cheatgrass dominated ranges (Hironaka and Tisdale 1973).
The grasses likely to invade this site are cheatgrass and medusahead. These invasive grasses displace desirable perennial grasses, reduce livestock forage, and accumulate large fuel loads that foster frequent fires (Davies and Svejcar 2008). Invasion by annual grasses can alter the fire cycle by increasing fire size, fire season length, rate of spread, numbers of individual fires, and likelihood of fires spreading into native or managed ecosystems (D’Antonio and Vitousek 1992, Brooks et al. 2004). While historical fire return intervals are estimated at 15 to 100 years, areas dominated with cheatgrass are estimated to have a fire return interval of 3-5 years (Whisenant 1990). The mechanisms by which invasive annual grasses alter fire regimes likely interact with climate. For example, cheatgrass cover and biomass vary with climate (Chambers et al. 2007) and are promoted by wet and warm conditions during the fall and spring. Invasive annual species have been shown able to take advantage of high nitrogen availability following fire through higher growth rates and increased seedling established relative to native perennial grasses (Monaco et al. 2003).
Livestock/Wildlife Grazing Interpretations:
This ecological site is suitable for grazing. Grazing management considerations include timing, duration and intensity of grazing along with other disturbances that might have changed the resiliency and resistance of the ecological site. In addition, old growth juniper stands provide habitat for a variety of plant and animal species. Bird surveys indicate that the highest abundance and diversity of songbirds occur in shrub steppe communities adjacent to old-growth stands (Reinkensmeyer et al. 2007) but might decline when understory complexity is lost in canopy closure (Miller 2005).
The literature is unclear as to the palatability of Wyoming big sagebrush. Generally, Wyoming sagebrush is the least palatable of the big sagebrush taxa (Bray et al. 1991, Sheehy and Winward 1981), however, it might receive light or moderate use depending upon the amount of understory herbaceous cover (Tweit and Houston 1980). Personius et al. (1987) found Wyoming big sagebrush and basin big sagebrush to be intermediately palatable to mule deer when compared to mountain big sagebrush (most palatable) and black sagebrush (least palatable).
Bunchgrasses, in general, best tolerate light grazing after seed formation. Britton et al. (1990) observed the effects of clipping date on basal area of five bunchgrasses in eastern Oregon and found grazing from August to October (after seed set) has the least impact. Heavy grazing during the growing season will reduce perennial bunchgrasses and increase sagebrush. Abusive grazing by cattle or horses will likely increase cover of Wyoming big sagebrush, rabbitbrush and deep-rooted perennial forbs. Non-native weedy species such as cheatgrass and mustards, and potentially medusahead might invade.
Indian ricegrass is a preferred forage species for livestock and wildlife (Cook 1962, Booth et al. 2006). This species is often heavily utilized in winter because it cures well (Booth et al. 2006). It is also readily utilized in early spring, being a source of green feed before most other perennial grasses have produced new growth (Quinones 1981). Booth et al. (2006) note that the plant does well when utilized in winter and spring. Cook and Child (1971), however, found that repeated heavy grazing reduced crown cover, which might reduce seed production, density, and basal area of these plants. Additionally, heavy early spring grazing reduces plant vigor and stand density (Stubbendieck 1985). In eastern Idaho, productivity of Indian ricegrass was at least 10 times greater in undisturbed plots than in heavily grazed ones (Pearson 1965). Cook and Child (1971) found significant reduction in plant cover after 7 years of rest from heavy (90 percent) and moderate (60 percent) spring use. The seed crop might be reduced where grazing is heavy (Bich et al. 1995). Tolerance to grazing increases after May, thus spring deferment might be necessary for stand enhancement (Pearson 1964, Cook and Child 1971); however, utilization of less than 60 percent is recommended.
Bottlebrush squirreltail generally increases in abundance when moderately grazed or protected (Hutchings & Stewart, 1953). In addition, moderate trampling by livestock in big sagebrush rangelands of central Nevada enhanced bottlebrush squirreltail seedling emergence compared to untrampled conditions. Heavy trampling however was found to significantly reduce germination sites (Eckert, Peterson, & Emmerich, 1987). Squirreltail is more tolerant of grazing than Indian ricegrass, but all bunchgrasses are sensitive to over utilization within the growing season.
Needlegrasses in general are valuable forage for both livestock and wildlife. Needlegrasses are grazed closely when the leaves are green in early spring, but are typically avoided once seed has matured (Sampson et al. 1951). Desert needlegrass is a compact bunchgrass with considerable basal leafage. The young herbage is palatable to all classes of livestock. When mature the fine basal leaves, intermingled with the coarse stems and flowering stalks, are grazed some by cattle and horses, but little by sheep (Sampson et al. 1951). Desert needlegrass is palatable to wildlife such as bighorn sheep and feral burros when young. Desert needlegrass tolerates light grazing but overgrazing might eliminate it from an ecological site. It is best to graze it before seed develops because the seed has a sharp callus that can injure the eyes and mouths of grazing animals (Perkins and Ogle, 2008).
Needle-and-thread is not grazing tolerant and will be one of the first grasses to decrease cover under heavy grazing pressure (Smoliak et al. 1972, Tueller & Blackburn 1974). Heavy grazing is likely to reduce basal area of these plants (Smoliak et al. 1972). With the reduction in competition from deep rooted perennial bunchgrasses, shallower rooted grasses such as bottlebrush squirreltail might increase (Smoliak et al. 1972).
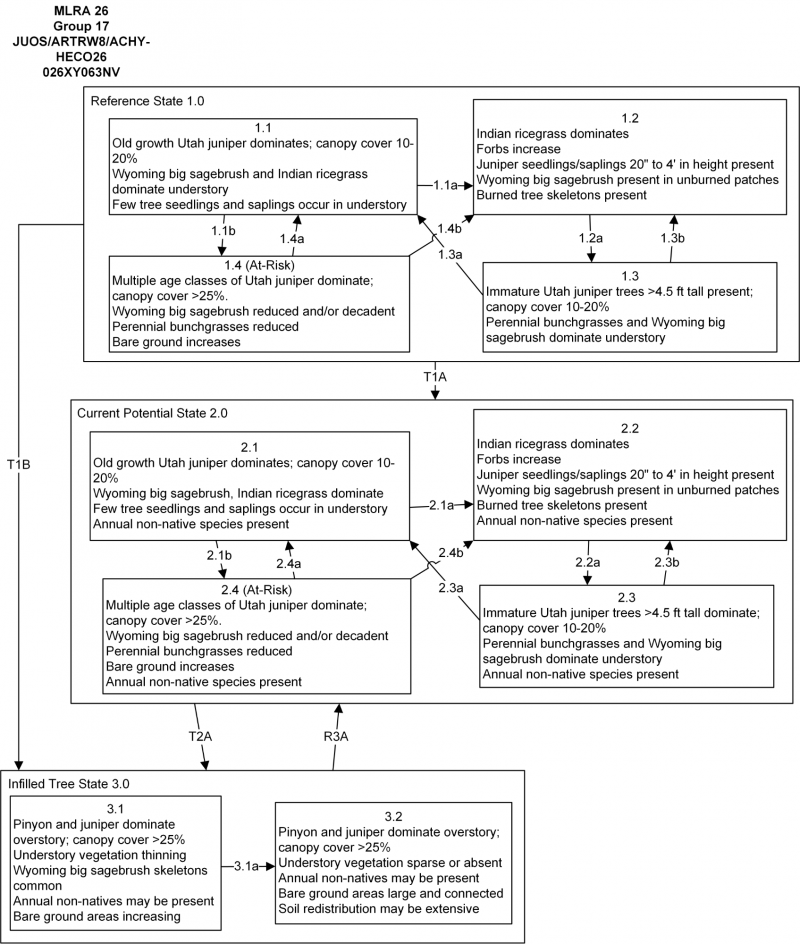
State and Transition Model Narrative Group 17:
This is a text description of the states, phases, transitions, and community pathways possible in the State and Transition model for the MLRA 26 Disturbance Response Group 17.
Reference State 1.0:
The Reference State 1.0 represents the natural range of variability of this site under pristine conditions. The reference state has four general community phases: an old-growth phase, a shrub-herbaceous phase, an immature tree phase, and an infilled tree phase. State dynamics are maintained by interactions between climatic patterns and disturbance regimes. Negative feedbacks enhance ecosystem resilience and contribute to the stability of the state. These include the presence of all structural and functional groups, low fine fuel loads, and retention of organic matter and nutrients. Plant community phase changes are primarily driven by: (a) fire, (b) periodic drought, or (3) insect or disease attack. Fires within this community are infrequent and likely small and patchy due to low fuel loads; for example, single tree death due to lightning strike. This fire type will create a plant community mosaic that will include all/most of the following community phases within this state.
Community Phase 1.1:
Widely dispersed old-growth juniper trees with a dominant understory of sagebrush and perennial bunchgrass, characterize this phase. The visual aspect is dominated by Utah juniper with canopy cover of 15 percent or more (USDA 1997). Trees have reached maximal or near maximal heights for the site and many tree crowns might be flat- or round-topped. Wyoming big sagebrush is the primary understory shrub along with Indian ricegrass and needle-and-thread as the most prevalent understory grasses. Forbs, such as lupine (Lupinus ssp.) and milkvetch (Astragalus ssp.) are minor components. Overall, the understory is sparse with production ranging between 100 to 350 pounds per acre.
Community Phase Pathway 1.1a, from Phase 1.1 to 1.2:
A high-severity crown fire will reduce or eliminate the Utah juniper overstory.
Community Phase Pathway 1.1b, from Phase 1.1 to 1.4:
Time without disturbances such as fire, drought, or disease will allow for the gradual infilling of juvenile Utah juniper.
Community Phase 1.2:
This phase is characterized by a post-fire shrub and herbaceous community. Indian ricegrass and other perennial grasses dominate. Forbs might increase after a fire but will likely return to pre-burn levels within a few years. Juniper seedlings/saplings up to 4 feet in height might be present. Sprouting shrubs, might increase. Wyoming big sagebrush might be present in unburned patches. Burned tree skeletons might be present; however, these have little or no effect on the understory vegetation.
Community Phase Pathway 1.2a, from Phase 1.2 to 1.3:
Time without disturbances such as fire, drought, or disease will allow for the gradual maturation of the Utah Juniper component. Wyoming big sagebrush reestablishes. Excessive herbivory might also reduce perennial grass understory.
Community Phase 1.3:
This community phase is characterized by an immature woodland, with juniper trees averaging over 4.5 feet in height. Tree canopy cover is between 10 to 20 percent. Tree crowns are typically cone- or pyramidal-shaped. Understory vegetation consists of smaller tree seedling and saplings, however perennial bunchgrasses and big sagebrush dominate.
Community Phase Pathway 1.3a, from Phase 1.3 to 1.4:
Time without disturbances such as fire, drought, or disease will allow for the gradual maturation of Utah juniper. Infilling by younger trees continues. Excessive herbivory might also reduce perennial bunchgrass understory.
Community Phase Pathway 1.3b, from Phase 1.3 to 1.2:
Fire reduces or eliminates tree canopy, allowing perennial grasses to dominate the site.
Community Phase 1.4 (at-risk):
This phase is dominated by Utah juniper. The stand exhibits mixed age classes and canopy cover exceeds 25 percent. The density and vigor of the Wyoming big sagebrush and perennial bunchgrass understory is decreased. Bare ground areas are likely to increase. This community is at risk of crossing a threshold; without proper management or natural disturbance this phase will transition to the Infilled Tree State 3.0. This community phase is typically described as early Phase II woodland (Miller et al. 2008).
Community Phase Pathway 1.4a, from Phase 1.4 to 1.1:
Low intensity fire, insect infestation, or disease kills individual trees within the stand, reducing canopy cover to less than 20 percent. Over time, young trees mature to replace and maintain the old-growth woodland. The big sagebrush and perennial bunchgrass community increases in density and vigor because of increased availability of light and water resources.
Community Phase Pathway 1.4b, from Phase 1.4 to 1.2:
A high-severity crown fire will eliminate or reduce the Utah juniper overstory and the shrub component which will allow for the perennial bunchgrasses to dominate the site.
T1A: Transition from Reference State 1.0 to Current Potential State 2.0:
Trigger: Introduction of non-native annual species.
Slow variables: Over time the annual non-native plants will increase within the community.
Threshold: Any amount of introduced non-native species causes an immediate decrease in the resilience of the site. Annual non-native species cannot be easily removed from the system and have the potential to significantly alter disturbance regimes from their historic range of variation.
T1B: Transition from Reference State 1.0 to Infilled Tree State 3.0:
Trigger: Time and a lack of disturbance allow trees to dominate site resources; might be coupled with inappropriate herbivory that favors shrub and tree dominance.
Slow variables: Over time the abundance and size of trees will increase.
Threshold: Juniper canopy cover is greater than 25 percent. Little understory vegetation remains due to competition with trees for site resources.
Current Potential State 2.0:
This state is similar to the Reference State 1.0, with four general community phases: an old-growth tree phase, a shrub-herbaceous phase, an immature tree phase, and an infilled tree phase. Ecological function has not changed, however the resiliency of the state has been reduced by the presence of non-native species. These non-natives, particularly cheatgrass, can be highly flammable and promote fire where historically fire had been infrequent. Negative feedbacks enhance ecosystem resilience and contribute to the stability of the state. These include the presence of all structural and functional groups, low fine fuel loads and retention of organic matter and nutrients. Positive feedbacks decrease ecosystem resilience and stability of the state. These include the non-natives’ high seed output, persistent seed bank, rapid growth rate, ability
to cross pollinate, and adaptations for seed dispersal. Fires within this community with the small amount of non-native annual species present are likely still small and patchy due to low fuel loads. This fire type will create a plant community mosaic that will include all/most of the following community phases within this state.
Community Phase 2.1:
This phase is characterized by a widely dispersed old-growth juniper trees with a big sagebrush and perennial bunchgrass understory. The visual aspect is dominated by Utah juniper with canopy cover of 15 percent or more (USDA 1997). Trees have reached maximal or near maximal heights for the site and many tree crowns might be flat- or round-topped. Wyoming big sagebrush is the primary understory shrub. Indian ricegrass is the most prevalent perennial understory grass. Forbs such as lupin and milkvetch are minor components. Overall, the understory is sparse with production ranging between 100 to 350 lbs/ac.
Community Phase Pathway 2.1a, from Phase 2.1 to 2.2:
A high-severity crown fire will eliminate or reduce the Utah juniper overstory and the shrub component. This allows for the perennial bunchgrasses to dominate the site.
Community Phase Pathway 2.1b, from Phase 2.1 to 2.4:
Time without disturbances such as fire, drought, or disease will allow for the gradual infilling of Utah juniper.
Community Phase 2.2:
This community phase is characterized by a post-fire shrub and herbaceous community. Indian ricegrass and other perennial grasses dominate. Forbs might increase post-fire but will likely return to pre-burn levels within a few years. Juniper seedlings up to 4 feet in height might be present. Wyoming big sagebrush might be present in unburned patches. Burned tree skeletons might be present; however, these have little or no effect on the understory vegetation. Annual non-native species generally respond well after fire and might be stable or increasing within the community.
Community Phase Pathway 2.2a, from Phase 2.2 to 2.3:
Time without disturbances such as fire, drought, or disease will allow for the gradual maturation of the Utah Juniper component. Big sagebrush reestablishes. Excessive herbivory might also reduce perennial grass understory.
Community Phase 2.3:
This community phase is characterized by an immature woodland, with juniper trees averaging over 4.5 feet in height. Tree canopy cover is between 10 to 20 percent. Tree crowns are typically cone- or pyramidal-shaped. Understory vegetation consists of smaller tree seedling and saplings, however perennial bunchgrasses and big sagebrush dominate. Annual non-native species are present.
Community Phase Pathway 2.3a, from Phase 2.3 to 2.4:
Time without disturbances such as fire, drought, or disease will allow for the gradual maturation of Utah juniper. Infilling by younger trees continues. Excessive herbivory might also reduce perennial grass understory.
Community Phase Pathway 2.3b, from Phase 2.3 to 2.2:
Fire reduces or eliminates tree canopy, allowing perennial grasses to dominate the site.
Community Phase 2.4 (at-risk):
This phase is dominated by Utah juniper. The stand exhibits mixed age classes and canopy cover exceeds 25 percent. The density and vigor of the big sagebrush and perennial bunchgrass understory is decreased. Bare ground areas are likely to increase. Mat-forming forbs might increase. Annual non-native species are present, primarily under tree canopies. This community is at risk of crossing a threshold, without proper management this phase will transition to the Infilled Tree State 3.0. This community phase is typically described as early Phase II woodland (Miller et al. 2008).
Community Phase Pathway 2.4a, from Phase 2.4 to 2.1:
Low intensity fire, insect infestation, or disease kills individual trees within the stand reducing canopy cover to less than 20 percent. Over time young trees mature to replace and maintain the old-growth woodland. The big sagebrush and perennial bunchgrass community increases in density and vigor. Annual non-natives present in trace amounts.
Community Phase Pathway 2.4b, from Phase 2.4 to 2.2:
A high-severity crown fire will eliminate or reduce the Utah juniper overstory and the shrub component which will allow for the perennial bunchgrasses to dominate the site. Annual non-native grasses typically respond positively to fire and might increase in the post-fire community.
T2A: Transition from Current Potential State 2.0 to Infilled Tree State 3.0:
Trigger: Time and a lack of disturbance allow trees to dominate site resources; might be coupled with inappropriate grazing management that favors shrub and tree dominance.
Slow variables: Over time the abundance and size of trees will increase.
Threshold: Utah juniper canopy cover is greater than 25 percent. Little understory vegetation remains due to competition with trees for site resources.
Infilled Tree State 3.0:
This state has two community phases that are characterized by the dominance of Utah juniper in the overstory. This state is identifiable by greater than 25 percent cover of Utah juniper. This stand exhibits a mixed age class. Older trees are at maximal height and upper crowns might be flat-topped or rounded. Younger trees are typically cone- or pyramidal-shaped. Understory vegetation is sparse due to increasing shade and nutrient competition from trees.
Community Phase 3.1:
Utah juniper dominate the aspect. Understory vegetation is thinning. Perennial bunchgrasses are sparse and big sagebrush skeletons are as common as live shrubs due to tree competition for soil water, overstory shading, and duff accumulation. Tree canopy cover is greater than 25 percent. Annual non-native species are present or co-dominate in the understory. Bare ground areas are prevalent and increasing. This community phase is typically described as a Phase II woodland (Miller et al. 2008).
Community Phase Pathway 3.1a, from Phase 3.1 to 3.2:
Time without disturbances such as fire, drought, or disease will allow for the gradual maturation of Utah juniper. Infilling by younger trees continues.
Community Phase 3.2 (at risk):
Utah juniper dominates the visual aspect. Tree canopy cover exceeds 25 percent and might be as high as 50 percent. Understory vegetation is sparse to absent. Perennial bunchgrasses, if present, exist in the drip line or under the canopy of trees. Wyoming big sagebrush skeletons are common or the sagebrush has been extinct long enough that only scattered limbs remain. Mat-forming forbs or Sandberg bluegrass might dominate interspaces. Annual non-native species are present and are typically found under the trees. Bare ground areas are large and interconnected. Soil redistribution might be extensive. This community phase is typically described as a Phase III woodland (Miller et al.
2008).
R3A: Restoration from Infilled Tree state 3.0 to Current Potential State 2.0:
Manual or mechanical thinning of trees coupled with seeding. Probability of success is highest from community phase 3.1.
State and transition model
More interactive model formats are also available.
View Interactive Models
Click on state and transition labels to scroll to the respective text
| T1A | - | Trigger: Introduction of non-native annual species. Slow variables: Over time the annual non-native plants will increase within the community. Threshold: Any amount of introduced non-native species causes an immediate decrease in the resilience of the site. Annual non-native species cannot be easily removed from the system and have the potential to significantly alter disturbance regimes from their historic range of variation. |
|---|---|---|
| T1B | - | Trigger: Time and a lack of disturbance allow trees to dominate site resources; might be coupled with inappropriate herbivory that favors shrub and tree dominance. Slow variables: Over time the abundance and size of trees will increase. Threshold: Juniper canopy cover is greater than 25 percent. Little understory vegetation remains due to competition with trees for site resources. |
| T2A | - | Trigger: Time and a lack of disturbance allow trees to dominate site resources; might be coupled with inappropriate grazing management that favors shrub and tree dominance. Slow variables: Over time the abundance and size of trees will increase. Threshold: Utah juniper canopy cover is greater than 25 percent. Little understory vegetation remains due to competition with trees for site resources. |
| R3A | - | This restoration is a result of manual or mechanical thinning of trees coupled with seeding. Probability of success is highest from community phase 3.1. |
State 1 submodel, plant communities
| 1.1a | - | This community phase pathway is a result of a high-severity crown fire which reduces or eliminates the Utah juniper overstory. |
|---|---|---|
| 1.1b | - | This community phase pathway is a result of time without disturbances such as fire, drought, or disease which will allow for the gradual infilling of juvenile Utah juniper. |
| 1.2a | - | This community phase pathway is a result of time without disturbances such as fire, drought, or disease which will allow for the gradual maturation of the Utah Juniper component. Wyoming big sagebrush reestablishes. Excessive herbivory might also reduce perennial grass understory. |
| 1.3a | - | This community phase pathway is a result of time without disturbances such as fire, drought, or disease which will allow for the gradual maturation of Utah juniper. Infilling by younger trees continues. Excessive herbivory might also reduce perennial bunchgrass understory. |
| 1.3b | - | This community phase occurs when a fire reduces or eliminates tree canopy, allowing perennial grasses to dominate the site. |
| 1.4a | - | This community phase pathway is a result of low intensity fire, insect infestation, or disease that kills individual trees within the stand, reducing canopy cover to less than 20 percent. Over time, young trees mature to replace and maintain the old-growth woodland. The big sagebrush and perennial bunchgrass community increases in density and vigor because of increased availability of light and water resources. |
State 2 submodel, plant communities
| 2.1a | - | This community phase pathway is a result of a high-severity crown fire which will eliminate or reduce the Utah juniper overstory and the shrub component. This allows for the perennial bunchgrasses to dominate the site. |
|---|---|---|
| 2.1b | - | This community phase pathway is a result of time without disturbances such as fire, drought, or disease which will allow for the gradual infilling of Utah juniper. |
| 2.2a | - | This community phase pathway is a result of time without disturbances such as fire, drought, or disease which will allow for the gradual maturation of the Utah Juniper component. Big sagebrush reestablishes. Excessive herbivory might also reduce perennial grass understory. |
| 2.3a | - | This community phase pathway is a result of time without disturbances such as fire, drought, or disease which will allow for the gradual maturation of Utah juniper. Infilling by younger trees continues. Excessive herbivory might also reduce perennial grass understory. |
| 2.3b | - | This community phase pathway occurs when fire reduces or eliminates tree canopy, allowing perennial grasses to dominate the site. |
| 2.4a | - | This community phase pathway is a result of low intensity fire, insect infestation, or disease which kills individual trees within the stand reducing canopy cover to less than 20 percent. Over time young trees mature to replace and maintain the old-growth woodland. The big sagebrush and perennial bunchgrass community increases in density and vigor. Annual non-natives present in trace amounts. |
| 2.4b | - | This community phase pathway occurs when a high-severity crown fire eliminates or reduces the Utah juniper overstory and the shrub component which will allow for the perennial bunchgrasses to dominate the site. Annual non-native grasses typically respond positively to fire and might increase in the post-fire community. |
State 3 submodel, plant communities
| 3.1a | - | This community phase pathway is a result of time without disturbances such as fire, drought, or disease which will allow for the gradual maturation of Utah juniper. Infilling by younger trees continues. |
|---|
State 1
Reference State
The Reference State 1.0 represents the natural range of variability of this site under pristine conditions. The reference state has four general community phases: an old-growth phase, a shrub-herbaceous phase, an immature tree phase, and an infilled tree phase. State dynamics are maintained by interactions between climatic patterns and disturbance regimes. Negative feedbacks enhance ecosystem resilience and contribute to the stability of the state. These include the presence of all structural and functional groups, low fine fuel loads, and retention of organic matter and nutrients. Plant community phase changes are primarily driven by: (a) fire, (b) periodic drought, or (3) insect or disease attack. Fires within this community are infrequent and likely small and patchy due to low fuel loads; for example, single tree death due to lightning strike. This fire type will create a plant community mosaic that will include all/most of the following community phases within this state.
Community 1.1
Widely dispersed old-growth juniper trees with a dominant understory of sagebrush and perennial bunchgrass, characterize this phase. The visual aspect is dominated by Utah juniper with canopy cover of 15 percent or more (USDA 1997). Trees have reached maximal or near maximal heights for the site and many tree crowns might be flat- or round-topped. Wyoming big sagebrush is the primary understory shrub along with Indian ricegrass and needle-and-thread as the most prevalent understory grasses. Forbs, such as lupine (Lupinus ssp.) and milkvetch (Astragalus ssp.) are minor components. Overall, the understory is sparse with production ranging between 100 to 350 pounds per acre.
Forest overstory. MATURE FORESTLAND: The visual aspect and vegetal structure are dominated by Utah juniper that have reached or are near maximal heights for the site. Dominant trees average greater than five inches in diameter at one-foot stump height. Upper crowns of Utah juniper are typically either irregularly or smoothly flat-topped or rounded. Tree canopy cover ranges from 10 to 20 percent. Understory vegetation is strongly influenced by tree competition, overstory shading, duff accumulation, etc. Few tree seedlings and/or saplings occur in the understory. Infrequent, yet periodic, wildfire is presumed to be a natural factor influencing the understory of mature juniper forestlands. This stage of community development is assumed to be representative of this forestland site in the natural environment.
Forest understory. Understory vegetative composition is about 50 percent grasses, 5 percent forbs and 45 percent shrubs and young trees when the average overstory canopy is medium (10 to 20 percent). Average understory production ranges from 100 to 350 pounds per acre with a medium canopy cover. Understory production includes the total annual production of all species within 4½ feet of the ground surface.
Figure 4. Annual production by plant type (representative values) or group (midpoint values)
Table 5. Annual production by plant type
| Plant type | Low (lb/acre) |
Representative value (lb/acre) |
High (lb/acre) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grass/Grasslike | 50 | 125 | 175 |
| Shrub/Vine | 38 | 95 | 133 |
| Tree | 7 | 18 | 25 |
| Forb | 5 | 12 | 17 |
| Total | 100 | 250 | 350 |
Community 1.2
This phase is characterized by a post-fire shrub and herbaceous community. Indian ricegrass and other perennial grasses dominate. Forbs might increase after a fire but will likely return to pre-burn levels within a few years. Juniper seedlings/saplings up to 4 feet in height might be present. Sprouting shrubs, might increase. Wyoming big sagebrush might be present in unburned patches. Burned tree skeletons might be present; however, these have little or no effect on the understory vegetation.
Community 1.3
This community phase is characterized by an immature woodland, with juniper trees averaging over 4.5 feet in height. Tree canopy cover is between 10 to 20 percent. Tree crowns are typically cone- or pyramidal-shaped. Understory vegetation consists of smaller tree seedling and saplings, however perennial bunchgrasses and big sagebrush dominate.
Community 1.4
(at-risk)
This phase is dominated by Utah juniper. The stand exhibits mixed age classes and canopy cover exceeds 25 percent. The density and vigor of the Wyoming big sagebrush and perennial bunchgrass understory is decreased. Bare ground areas are likely to increase. This community is at risk of crossing a threshold; without proper management or natural disturbance this phase will transition to the Infilled Tree State 3.0. This community phase is typically described as early Phase II woodland (Miller et al. 2008).
Pathway 1.1a
Community 1.1 to 1.2
This community phase pathway is a result of a high-severity crown fire which reduces or eliminates the Utah juniper overstory.
Pathway 1.1b
Community 1.1 to 1.4
This community phase pathway is a result of time without disturbances such as fire, drought, or disease which will allow for the gradual infilling of juvenile Utah juniper.
Pathway 1.2a
Community 1.2 to 1.3
This community phase pathway is a result of time without disturbances such as fire, drought, or disease which will allow for the gradual maturation of the Utah Juniper component. Wyoming big sagebrush reestablishes. Excessive herbivory might also reduce perennial grass understory.
Pathway 1.3a
Community 1.3 to 1.1
This community phase pathway is a result of time without disturbances such as fire, drought, or disease which will allow for the gradual maturation of Utah juniper. Infilling by younger trees continues. Excessive herbivory might also reduce perennial bunchgrass understory.
Pathway 1.3b
Community 1.3 to 1.2
This community phase occurs when a fire reduces or eliminates tree canopy, allowing perennial grasses to dominate the site.
Pathway 1.4a
Community 1.4 to 1.1
This community phase pathway is a result of low intensity fire, insect infestation, or disease that kills individual trees within the stand, reducing canopy cover to less than 20 percent. Over time, young trees mature to replace and maintain the old-growth woodland. The big sagebrush and perennial bunchgrass community increases in density and vigor because of increased availability of light and water resources.
Pathway 1.4b
Community 1.4 to 1.2
This community phase pathway is a result of a high-severity crown fire which will eliminate or reduce the Utah juniper overstory and the shrub component which will allow for the perennial bunchgrasses to dominate the site.
State 2
Current Potential State
This state is similar to the Reference State 1.0, with four general community phases: an old-growth tree phase, a shrub-herbaceous phase, an immature tree phase, and an infilled tree phase. Ecological function has not changed, however the resiliency of the state has been reduced by the presence of non-native species. These non-natives, particularly cheatgrass, can be highly flammable and promote fire where historically fire had been infrequent. Negative feedbacks enhance ecosystem resilience and contribute to the stability of the state. These include the presence of all structural and functional groups, low fine fuel loads and retention of organic matter and nutrients. Positive feedbacks decrease ecosystem resilience and stability of the state. These include the non-natives’ high seed output, persistent seed bank, rapid growth rate, ability to cross pollinate, and adaptations for seed dispersal. Fires within this community with the small amount of non-native annual species present are likely still small and patchy due to low fuel loads. This fire type will create a plant community mosaic that will include all/most of the following community phases within this state.
Community 2.1
This phase is characterized by a widely dispersed old-growth juniper trees with a big sagebrush and perennial bunchgrass understory. The visual aspect is dominated by Utah juniper with canopy cover of 15 percent or more (USDA 1997). Trees have reached maximal or near maximal heights for the site and many tree crowns might be flat- or round-topped. Wyoming big sagebrush is the primary understory shrub. Indian ricegrass is the most prevalent perennial understory grass. Forbs such as lupin and milkvetch are minor components. Overall, the understory is sparse with production ranging between 100 to 350 pounds per acre.
Community 2.2
This community phase is characterized by a post-fire shrub and herbaceous community. Indian ricegrass and other perennial grasses dominate. Forbs might increase post-fire but will likely return to pre-burn levels within a few years. Juniper seedlings up to 4 feet in height might be present. Wyoming big sagebrush might be present in unburned patches. Burned tree skeletons might be present; however, these have little or no effect on the understory vegetation. Annual non-native species generally respond well after fire and might be stable or increasing within the community.
Community 2.3
This community phase is characterized by an immature woodland, with juniper trees averaging over 4.5 feet in height. Tree canopy cover is between 10 to 20 percent. Tree crowns are typically cone- or pyramidal-shaped. Understory vegetation consists of smaller tree seedling and saplings, however perennial bunchgrasses and big sagebrush dominate. Annual non-native species are present.
Community 2.4
(at-risk)
This phase is dominated by Utah juniper. The stand exhibits mixed age classes and canopy cover exceeds 25 percent. The density and vigor of the big sagebrush and perennial bunchgrass understory is decreased. Bare ground areas are likely to increase. Mat-forming forbs might increase. Annual non-native species are present, primarily under tree canopies. This community is at risk of crossing a threshold, without proper management this phase will transition to the Infilled Tree State 3.0. This community phase is typically described as early Phase II woodland (Miller et al. 2008).
Pathway 2.1a
Community 2.1 to 2.2
This community phase pathway is a result of a high-severity crown fire which will eliminate or reduce the Utah juniper overstory and the shrub component. This allows for the perennial bunchgrasses to dominate the site.
Pathway 2.1b
Community 2.1 to 2.4
This community phase pathway is a result of time without disturbances such as fire, drought, or disease which will allow for the gradual infilling of Utah juniper.
Pathway 2.2a
Community 2.2 to 2.3
This community phase pathway is a result of time without disturbances such as fire, drought, or disease which will allow for the gradual maturation of the Utah Juniper component. Big sagebrush reestablishes. Excessive herbivory might also reduce perennial grass understory.
Pathway 2.3a
Community 2.3 to 2.1
This community phase pathway is a result of time without disturbances such as fire, drought, or disease which will allow for the gradual maturation of Utah juniper. Infilling by younger trees continues. Excessive herbivory might also reduce perennial grass understory.
Pathway 2.3b
Community 2.3 to 2.2
This community phase pathway occurs when fire reduces or eliminates tree canopy, allowing perennial grasses to dominate the site.
Pathway 2.4a
Community 2.4 to 2.1
This community phase pathway is a result of low intensity fire, insect infestation, or disease which kills individual trees within the stand reducing canopy cover to less than 20 percent. Over time young trees mature to replace and maintain the old-growth woodland. The big sagebrush and perennial bunchgrass community increases in density and vigor. Annual non-natives present in trace amounts.
Pathway 2.4b
Community 2.4 to 2.2
This community phase pathway occurs when a high-severity crown fire eliminates or reduces the Utah juniper overstory and the shrub component which will allow for the perennial bunchgrasses to dominate the site. Annual non-native grasses typically respond positively to fire and might increase in the post-fire community.
State 3
Infilled Tree State
This state has two community phases that are characterized by the dominance of Utah juniper in the overstory. This state is identifiable by greater than 25 percent cover of Utah juniper. This stand exhibits a mixed age class. Older trees are at maximal height and upper crowns might be flat-topped or rounded. Younger trees are typically cone- or pyramidal-shaped. Understory vegetation is sparse due to increasing shade and nutrient competition from trees.
Community 3.1
Utah juniper dominate the aspect. Understory vegetation is thinning. Perennial bunchgrasses are sparse and big sagebrush skeletons are as common as live shrubs due to tree competition for soil water, overstory shading, and duff accumulation. Tree canopy cover is greater than 25 percent. Annual non-native species are present or co-dominate in the understory. Bare ground areas are prevalent and increasing. This community phase is typically described as a Phase II woodland (Miller et al. 2008).
Community 3.2
(at-risk)
Utah juniper dominates the visual aspect. Tree canopy cover exceeds 25 percent and might be as high as 50 percent. Understory vegetation is sparse to absent. Perennial bunchgrasses, if present, exist in the drip line or under the canopy of trees. Wyoming big sagebrush skeletons are common or the sagebrush has been extinct long enough that only scattered limbs remain. Mat-forming forbs or Sandberg bluegrass might dominate interspaces. Annual non-native species are present and are typically found under the trees. Bare ground areas are large and interconnected. Soil redistribution might be extensive. This community phase is typically described as a Phase III woodland (Miller et al. 2008).
Pathway 3.1a
Community 3.1 to 3.2
This community phase pathway is a result of time without disturbances such as fire, drought, or disease which will allow for the gradual maturation of Utah juniper. Infilling by younger trees continues.
Transition T1A
State 1 to 2
Trigger: Introduction of non-native annual species. Slow variables: Over time the annual non-native plants will increase within the community. Threshold: Any amount of introduced non-native species causes an immediate decrease in the resilience of the site. Annual non-native species cannot be easily removed from the system and have the potential to significantly alter disturbance regimes from their historic range of variation.
Transition T1B
State 1 to 3
Trigger: Time and a lack of disturbance allow trees to dominate site resources; might be coupled with inappropriate herbivory that favors shrub and tree dominance. Slow variables: Over time the abundance and size of trees will increase. Threshold: Juniper canopy cover is greater than 25 percent. Little understory vegetation remains due to competition with trees for site resources.
Transition T2A
State 2 to 3
Trigger: Time and a lack of disturbance allow trees to dominate site resources; might be coupled with inappropriate grazing management that favors shrub and tree dominance. Slow variables: Over time the abundance and size of trees will increase. Threshold: Utah juniper canopy cover is greater than 25 percent. Little understory vegetation remains due to competition with trees for site resources.
Restoration pathway R3A
State 3 to 2
This restoration is a result of manual or mechanical thinning of trees coupled with seeding. Probability of success is highest from community phase 3.1.
Additional community tables
Table 6. Community 1.1 plant community composition
| Group | Common name | Symbol | Scientific name | Annual production (lb/acre) | Foliar cover (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Grass/Grasslike
|
||||||
| 1 | Primary Perennial Grasses | 62–142 | ||||
| needle and thread | HECO26 | Hesperostipa comata | 25–60 | – | ||
| Indian ricegrass | ACHY | Achnatherum hymenoides | 25–60 | – | ||
| desert needlegrass | ACSP12 | Achnatherum speciosum | 12–22 | – | ||
| 2 | Secondary Perennial Grasses | 4–24 | ||||
| squirreltail | ELEL5 | Elymus elymoides | 2–12 | – | ||
| Sandberg bluegrass | POSE | Poa secunda | 2–12 | – | ||
|
Forb
|
||||||
| 3 | Perennial | 1–17 | ||||
|
Shrub/Vine
|
||||||
| 4 | Primary Shrubs | 37–82 | ||||
| Wyoming big sagebrush | ARTRW8 | Artemisia tridentata ssp. wyomingensis | 25–60 | – | ||
| currant | RIBES | Ribes | 12–22 | – | ||
| 5 | Secondary Shrubs | 4–24 | ||||
| yellow rabbitbrush | CHVI8 | Chrysothamnus viscidiflorus | 2–12 | – | ||
| mormon tea | EPVI | Ephedra viridis | 2–12 | – | ||
|
Tree
|
||||||
| 6 | Evergreen | 12–22 | ||||
| Utah juniper | JUOS | Juniperus osteosperma | 12–22 | – | ||
Table 7. Community 1.1 forest overstory composition
| Common name | Symbol | Scientific name | Nativity | Height (ft) | Canopy cover (%) | Diameter (in) | Basal area (square ft/acre) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Tree
|
|||||||
| Utah juniper | JUOS | Juniperus osteosperma | Native | – | 100 | – | – |
Interpretations
Animal community
Livestock Interpretations:
This site is suited to cattle and sheep grazing during the early spring, fall, and winter. Grazing management should be keyed to Indian ricegrass and Needle and thread grass production. This grass furnishes palatable, highly nutritious, forage during the spring. It supplies a source of green feed before most other native grasses have produced much new growth. New plants are established entirely from seed and grazing practices should allow for ample seed production and seedling establishment. Repeated, severe, spring grazing reduces plant vigor. Needle and thread grass is important to livestock, especially in the spring before fruits have developed. Needlegrasses are grazed in the fall only if the fruits are softened by rain. Livestock browse Wyoming big sagebrush, but might use it only lightly when palatable herbaceous species are available. Livestock will often concentrate on this site taking advantage of the shade and shelter offered by the tree overstory. Many areas are not used due to lack of adequate water.
Stocking rates vary with such factors as kind and class of grazing animal, season of use and fluctuations in climate. Actual use records for individual sites, a determination of the degree to which the sites have been grazed, and an evaluation of trend in site condition offer the most reliable basis for developing initial stocking rates.
The forage value rating is not an ecological evaluation of the understory as is the range condition rating for rangeland. The forage value rating is a utilitarian rating of the existing understory plants for use by specific kinds of grazing animals.
The amount and nature of the understory vegetation in a forestland is highly responsive to the amount and duration of shade provided by the overstory canopy. Significant changes in kinds and abundance of plants occur as the canopy changes, often regardless of grazing use.
Wildlife Interpretations:
This site has high value for mule deer during the summer, fall and winter. Pinyon trees provide shelter from winter storms. Sites where water is available offer good quail habitat and are visited seasonally by mourning dove. It is also used by various songbirds, rodents, reptiles and associated predators natural to area. Feral horses will use this site in the late spring, summer and fall. This site is used by mule deer in the summer and fall. The trees provide protection from winter storms. The pinyon jay is dependent on sites supporting pinyon pine trees. This site is also used by upland game species and various song birds, rodents, reptiles and associated predators natural to the area. Feral horses will use this site in the late spring, summer and fall. Wyoming big sagebrush is preferred browse for wild ungulates. Pronghorn typically browse Wyoming big sagebrush heavily. Needle and thread is a moderately important spring forage for mule deer, but use declines considerably as more preferred forages become available. Indian Ricegrass is also an important forage species for several wildlife species.
Hydrological functions
The hydrologic cover condition of this site is fair in a representative stand with a sparse canopy cover. The average runoff curve is about 80 for group C soils.
Recreational uses
The trees on this site provide a welcome break in an otherwise open landscape. Steep slopes and stony surfaces inhibit many forms of recreation. It has potential for hiking, cross-country skiing, camping, and for big game as well as upland game hunting.
Wood products
Utah juniper wood is very durable. Its primary uses have been for posts and fuelwood. It probably has considerable potential in the charcoal industry and in wood fiber products.
PRODUCTIVE CAPACITY
This forestland community is of very low site quality for tree production. Site index ranges from about 20 to 35 (Howell, 1940). Productivity Class: 0.1 to 0.2
CMAI*: 1.3 to 2.7 cubic feet per acre per year;
0.10 to 0.20 cubic meters per hectare per year.
Culmination is estimated to be greater than 100 years.
*CMAI: is the Culmination of Mean Annual Increment or highest average growth rate of the stand in the units specified. Fuelwood Production: 2 to 4 cords per acre for stands averaging 5 inches in diameter at 1 foot height with a medium canopy cover. Approximately 274,000 gross BTUs heat content exist per cubic foot of Utah juniper. Solid wood volume in a cord varies but typically ranges from 65 to 90 cubic feet. Assuming an average of 75 cubic feet of solid wood per cord, there are about 20.6 million BTUs of heat value in a cord of Utah juniper firewood.
Posts (7 foot or 2.13 meters): About 5 to 15 posts per acre in stands of medium canopy. MANAGEMENT GUIDES AND INTERPRETATIONS
1. LIMITATIONS AND CONSIDERATIONS
a. Potential for sheet and rill erosion is moderate to severe depending on slope.
b. Moderate equipment limitations on steeper slopes and moderate to severe equipment limitations on sites having extreme surface stoniness.
c. Proper spacing is the key to a well-managed, multiple use and multi-product juniper forestland.
2. ESSENTIAL REQUIREMENTS
a. Adequately protect from wildfire.
b. Protect soils from accelerated erosion.
c. Apply proper grazing management.
3. SILVICULTURAL PRACTICES
Silvicultural treatments are not reasonably applied on this site due to poor site quality and severe limitations for equipment and tree harvest.
Other products
Native Americans make tea from big sagebrush leaves. The tea is used as a tonic, an antiseptic, for treating colds, diarrhea, and sore eyes and as a rinse to ward off ticks. Big sagebrush seeds are eaten raw or made into meal. The fruit of wax currant is used for making jam, jelly, or pie. Some western Indian tribes use currants for making pemmican. Wax currant is cultivated as an ornamental. Indian ricegrass has been traditionally eaten by some Native Americans. The Paiutes use the seed as a reserve food source.
Other information
Wyoming big sagebrush is used for stabilizing slopes and gullies and for restoring degraded wildlife habitat, rangelands, mine spoils and other disturbed sites. It is particularly recommended on dry upland sites where other shrubs are difficult to establish. Needle and thread is useful for stabilizing eroded or degraded sites.
Table 8. Representative site productivity
| Common name | Symbol | Site index low | Site index high | CMAI low | CMAI high | Age of CMAI | Site index curve code | Site index curve basis | Citation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Utah juniper | JUOS | 20 | 35 | 1 | 3 | 100 | – | – |
Supporting information
Inventory data references
NASIS data for soil survey area NV774.
Type locality
| Location 1: Mineral County, NV | |
|---|---|
| Township/Range/Section | T4N R29E S33 |
| UTM zone | N |
| UTM northing | 346654 |
| UTM easting | 4225048 |
| Latitude | 38° 9′ 37″ |
| Longitude | 118° 45′ 1″ |
| General legal description | South of NvHwy 31, northeast side of Mono Lake, Anchorite Hills area, Mineral County, Nevada. |
References
-
. 1998. NRCS National Forestry Manual.
-
Stringham, T.K., D. Snyder, P. Novak-Echenique, K. O'Neill, A. Lyons, and M. Johns. 2021. Great Basin Ecological Site Development Project: State-and-Transition Models for Major Land Resource Area 26, Nevada and Portions of California..
-
USDA, N. 2018 (Date accessed). The PLANTS Database. http://plants.usda.gov.
Other references
Howell, J. 1940. Pinyon and juniper: a preliminary study of volume, growth, and yield. Regional Bulletin 71. Albuquerque, NM: USDA, NRCS; 90p.
Jordan, M. 1974. An inventory of two selected woodland sites in the Pine Nut Hills of Western Nevada. Master's Thesis, UNReno.
USDA-NRCS. 2004 National forestry handbook, title 190. Washington, D. C.
Contributors
DK/FR
Tamzen Stringham
Approval
Kendra Moseley, 4/10/2024
Rangeland health reference sheet
Interpreting Indicators of Rangeland Health is a qualitative assessment protocol used to determine ecosystem condition based on benchmark characteristics described in the Reference Sheet. A suite of 17 (or more) indicators are typically considered in an assessment. The ecological site(s) representative of an assessment location must be known prior to applying the protocol and must be verified based on soils and climate. Current plant community cannot be used to identify the ecological site.
| Author(s)/participant(s) | |
|---|---|
| Contact for lead author | |
| Date | 04/11/2024 |
| Approved by | Kendra Moseley |
| Approval date | |
| Composition (Indicators 10 and 12) based on | Annual Production |
Indicators
-
Number and extent of rills:
-
Presence of water flow patterns:
-
Number and height of erosional pedestals or terracettes:
-
Bare ground from Ecological Site Description or other studies (rock, litter, lichen, moss, plant canopy are not bare ground):
-
Number of gullies and erosion associated with gullies:
-
Extent of wind scoured, blowouts and/or depositional areas:
-
Amount of litter movement (describe size and distance expected to travel):
-
Soil surface (top few mm) resistance to erosion (stability values are averages - most sites will show a range of values):
-
Soil surface structure and SOM content (include type of structure and A-horizon color and thickness):
-
Effect of community phase composition (relative proportion of different functional groups) and spatial distribution on infiltration and runoff:
-
Presence and thickness of compaction layer (usually none; describe soil profile features which may be mistaken for compaction on this site):
-
Functional/Structural Groups (list in order of descending dominance by above-ground annual-production or live foliar cover using symbols: >>, >, = to indicate much greater than, greater than, and equal to):
Dominant:
Sub-dominant:
Other:
Additional:
-
Amount of plant mortality and decadence (include which functional groups are expected to show mortality or decadence):
-
Average percent litter cover (%) and depth ( in):
-
Expected annual annual-production (this is TOTAL above-ground annual-production, not just forage annual-production):
-
Potential invasive (including noxious) species (native and non-native). List species which BOTH characterize degraded states and have the potential to become a dominant or co-dominant species on the ecological site if their future establishment and growth is not actively controlled by management interventions. Species that become dominant for only one to several years (e.g., short-term response to drought or wildfire) are not invasive plants. Note that unlike other indicators, we are describing what is NOT expected in the reference state for the ecological site:
-
Perennial plant reproductive capability:
Print Options
Sections
Font
Other
The Ecosystem Dynamics Interpretive Tool is an information system framework developed by the USDA-ARS Jornada Experimental Range, USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service, and New Mexico State University.
Click on box and path labels to scroll to the respective text.
| T1A | - | Trigger: Introduction of non-native annual species. Slow variables: Over time the annual non-native plants will increase within the community. Threshold: Any amount of introduced non-native species causes an immediate decrease in the resilience of the site. Annual non-native species cannot be easily removed from the system and have the potential to significantly alter disturbance regimes from their historic range of variation. |
|---|---|---|
| T1B | - | Trigger: Time and a lack of disturbance allow trees to dominate site resources; might be coupled with inappropriate herbivory that favors shrub and tree dominance. Slow variables: Over time the abundance and size of trees will increase. Threshold: Juniper canopy cover is greater than 25 percent. Little understory vegetation remains due to competition with trees for site resources. |
| T2A | - | Trigger: Time and a lack of disturbance allow trees to dominate site resources; might be coupled with inappropriate grazing management that favors shrub and tree dominance. Slow variables: Over time the abundance and size of trees will increase. Threshold: Utah juniper canopy cover is greater than 25 percent. Little understory vegetation remains due to competition with trees for site resources. |
| R3A | - | This restoration is a result of manual or mechanical thinning of trees coupled with seeding. Probability of success is highest from community phase 3.1. |
State 1 submodel, plant communities
| 1.1a | - | This community phase pathway is a result of a high-severity crown fire which reduces or eliminates the Utah juniper overstory. |
|---|---|---|
| 1.1b | - | This community phase pathway is a result of time without disturbances such as fire, drought, or disease which will allow for the gradual infilling of juvenile Utah juniper. |
| 1.2a | - | This community phase pathway is a result of time without disturbances such as fire, drought, or disease which will allow for the gradual maturation of the Utah Juniper component. Wyoming big sagebrush reestablishes. Excessive herbivory might also reduce perennial grass understory. |
| 1.3a | - | This community phase pathway is a result of time without disturbances such as fire, drought, or disease which will allow for the gradual maturation of Utah juniper. Infilling by younger trees continues. Excessive herbivory might also reduce perennial bunchgrass understory. |
| 1.3b | - | This community phase occurs when a fire reduces or eliminates tree canopy, allowing perennial grasses to dominate the site. |
| 1.4a | - | This community phase pathway is a result of low intensity fire, insect infestation, or disease that kills individual trees within the stand, reducing canopy cover to less than 20 percent. Over time, young trees mature to replace and maintain the old-growth woodland. The big sagebrush and perennial bunchgrass community increases in density and vigor because of increased availability of light and water resources. |
State 2 submodel, plant communities
| 2.1a | - | This community phase pathway is a result of a high-severity crown fire which will eliminate or reduce the Utah juniper overstory and the shrub component. This allows for the perennial bunchgrasses to dominate the site. |
|---|---|---|
| 2.1b | - | This community phase pathway is a result of time without disturbances such as fire, drought, or disease which will allow for the gradual infilling of Utah juniper. |
| 2.2a | - | This community phase pathway is a result of time without disturbances such as fire, drought, or disease which will allow for the gradual maturation of the Utah Juniper component. Big sagebrush reestablishes. Excessive herbivory might also reduce perennial grass understory. |
| 2.3a | - | This community phase pathway is a result of time without disturbances such as fire, drought, or disease which will allow for the gradual maturation of Utah juniper. Infilling by younger trees continues. Excessive herbivory might also reduce perennial grass understory. |
| 2.3b | - | This community phase pathway occurs when fire reduces or eliminates tree canopy, allowing perennial grasses to dominate the site. |
| 2.4a | - | This community phase pathway is a result of low intensity fire, insect infestation, or disease which kills individual trees within the stand reducing canopy cover to less than 20 percent. Over time young trees mature to replace and maintain the old-growth woodland. The big sagebrush and perennial bunchgrass community increases in density and vigor. Annual non-natives present in trace amounts. |
| 2.4b | - | This community phase pathway occurs when a high-severity crown fire eliminates or reduces the Utah juniper overstory and the shrub component which will allow for the perennial bunchgrasses to dominate the site. Annual non-native grasses typically respond positively to fire and might increase in the post-fire community. |
State 3 submodel, plant communities
| 3.1a | - | This community phase pathway is a result of time without disturbances such as fire, drought, or disease which will allow for the gradual maturation of Utah juniper. Infilling by younger trees continues. |
|---|