Natural Resources
Conservation Service
Ecological site R030XB164CA
Steep South Slopes
Last updated: 10/21/2024
Accessed: 11/23/2024
General information
Provisional. A provisional ecological site description has undergone quality control and quality assurance review. It contains a working state and transition model and enough information to identify the ecological site.
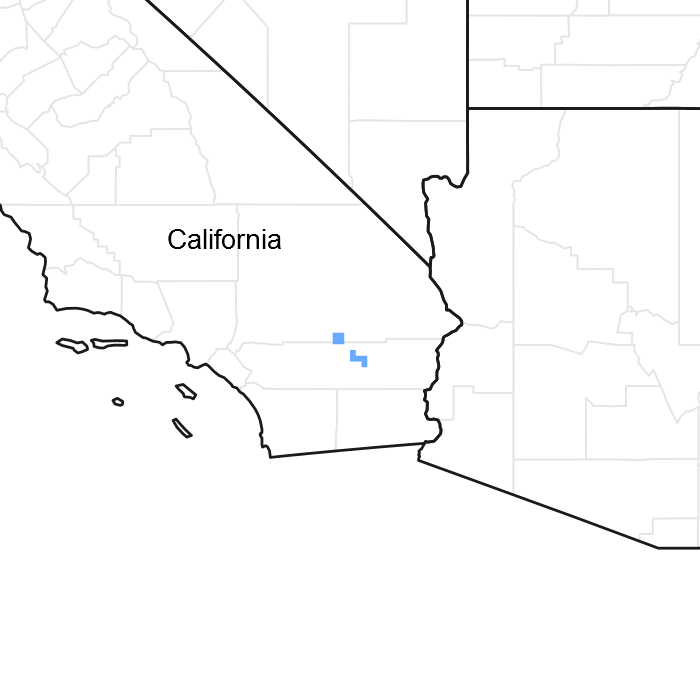
Figure 1. Mapped extent
Areas shown in blue indicate the maximum mapped extent of this ecological site. Other ecological sites likely occur within the highlighted areas. It is also possible for this ecological site to occur outside of highlighted areas if detailed soil survey has not been completed or recently updated.
MLRA notes
Major Land Resource Area (MLRA): 030X–Mojave Basin and Range
MLRA Description:
Major Land Resource Area (MLRA) 30, Mojave Desert, is found in southern California, southern Nevada, the extreme southwest corner of Utah and northwestern Arizona within the Basin and Range Province of the Intermontane Plateaus. The climate of the area is hot (primarily hyperthermic and thermic; however at higher elevations, generally above 5000 feet, mesic, cryic and frigid) and dry (aridic). Elevations range from below sea level to over 12,000 feet in the higher mountain areas found within the MLRA. Due to the extreme elevational range found within this MLRA, Land Resource Units (LRUs) were designated to group the MLRA into similar land units.
LRU Description:
This LRU (designated by ’XB’) is found across the eastern half of California, much of the mid-elevations of Nevada, the southernmost portions of western Utah, and the mid-elevations of northwestern Arizona. Elevations range from 1800 to 5000 feet and precipitation ranges from 4 to 9 inches per year, but is generally between 5-6 inches. This LRU is characterized primarily by the summer precipitation it receives, ranging from 18 – 35% but averages 25%. Summer precipitation falls between July and September in the form of rain, and winter precipitation falls starting in November and ends between February and March, also mostly in the form of rain; however it does receive between 0 and 3 inches of snow, with an average of 1 inch. The soil temperature regime is thermic and the soil moisture regime is typic-aridic. Vegetation includes creosote bush, burrobush, Nevada jointfir, ratany, Mojave yucca, Joshua tree, chollas, cactus, big galleta grass and several other warm season grasses. At the upper portions of the LRU, plant production and diversity are greater and blackbrush is a common dominant shrub.
Classification relationships
The Encelia farinosa Association of the Encelia farinosa shrubland alliance (Sawyer et al. 2009) is found within this ecological site.
Ecological site concept
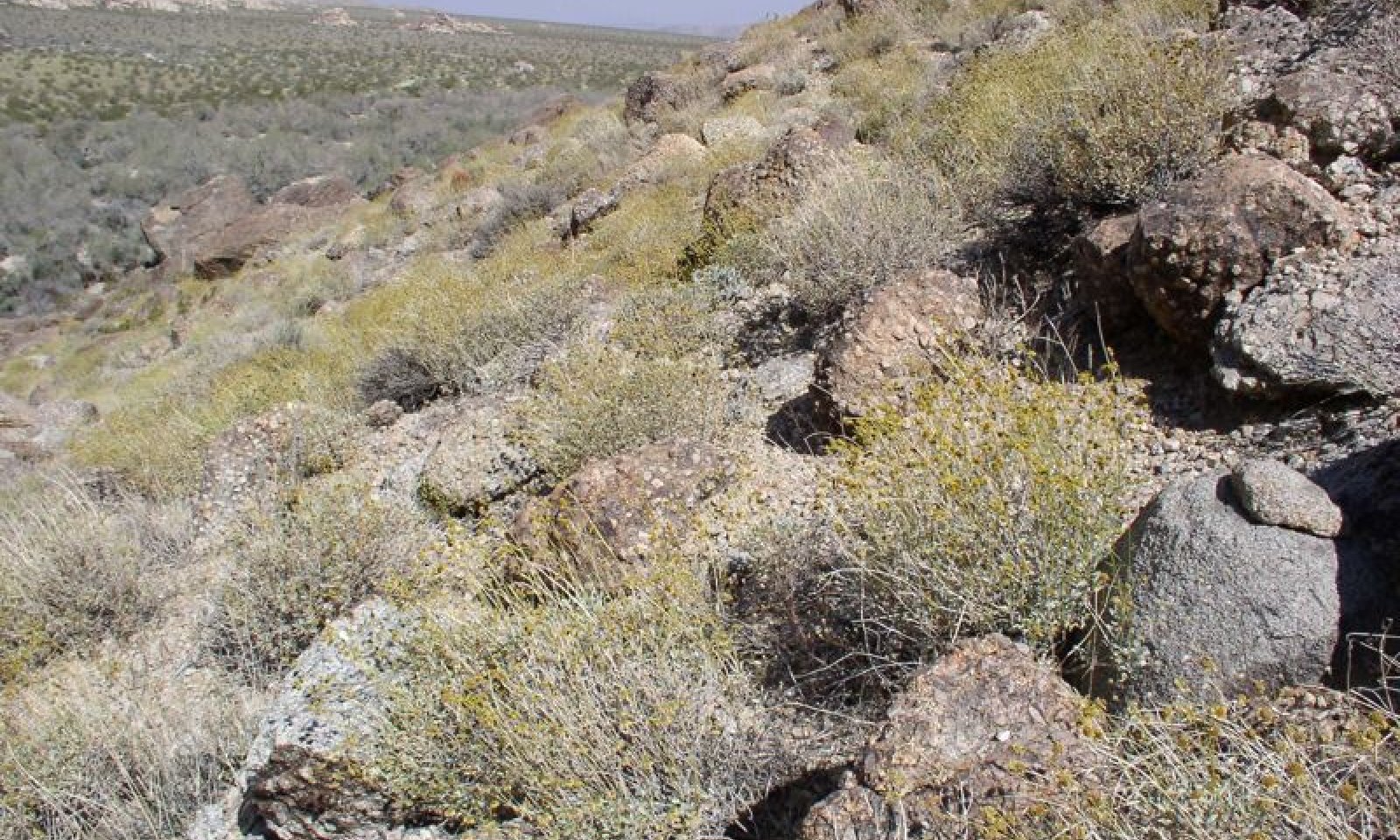
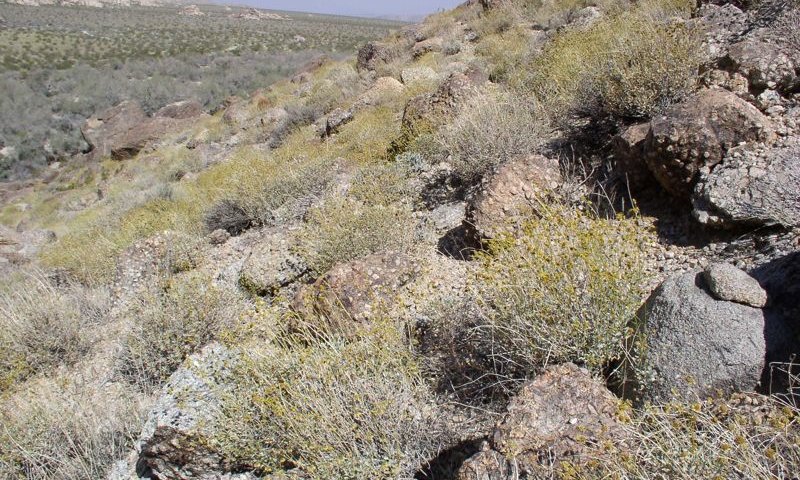
This ecological site occurs on steep south-facing slopes at elevations of approximately 2100 to 3950 feet. Soils have a warm thermic temperature regime, and are shallow gravelly sands over bedrock.
Annual production reference value (RV) is 273 pounds per acre, and ranges from 145 to 370 pounds per acre, depending on precipitation. The site is strongly dominated by brittlebush (Encelia farinosa). Arid topographic positions and shallow soils favor dominance by this drought-tolerant and cold-intolerant shrub.
Data ranges in the physiographic data, climate data, water features, and soil data sections of this Ecological Site Description are based on all components (major and minor) correlated with this ecological site.
This is a group concept and provisional STM that also covers R030XB077NV.
Associated sites
| R030XB139CA |
Shallow Dry Hill 4-6 P.Z. R030XB139CA is found on adjacent extremely gravelly slopes. Creosote bush (Larrea tridentata) is the dominant species. |
|---|---|
| R030XB171CA |
Dissected Pediment R030XB171CA Dissected Pediment, Warm 3-5 |
| R030XB170CA |
Bouldery Very Shallow To Shallow Gravelly Slopes R030XB170CA occurs on cool thermic slopes at higher elevations. The site has a high percentage of rock outcrops. Blackbrush (Coleogyne ramosissima), single-leaf pinyon pine (Pinus monophylla), California juniper (Juniperus californica), and Muller's oak (Quercus cornelius-mulleri) are dominant species. |
| R030XB193CA |
Very Shallow To Moderately Deep Gravelly Slopes R030XB193CA is found on adjacent slopes with moderately deep soils and an argillic horizon. Burrobush (Ambrosia dumosa), Parish's goldeneye (Viguiera parishi), jojoba (Simmondsia chinensis) and waterjacket (Lycium andersonii) are important species. |
| R030XE196CA |
Sandy Xeric-Intergrade Slopes R030XE196CA is found on adjacent slopes with a xeric soil moisture regime. Single-leaf pinyon pine (Pinus monophylla) and Muller's oak (Quercus cornelius-mulleri) dominate over a diverse shrub understory. |
Similar sites
| R030XD003CA |
Hyperthermic Steep South Slopes R030XD003CA occurs on hyperthermic soils. The dominant species are brittlebush (Encelia farinosa) and creosote bush (Larrea tridentata). Site diversity and productivity is generally lower than in this site, and Schott's dahlia (Psorothamnus schottii) is often present. |
|---|
Table 1. Dominant plant species
| Tree |
Not specified |
|---|---|
| Shrub |
(1) Encelia farinosa |
| Herbaceous |
Not specified |
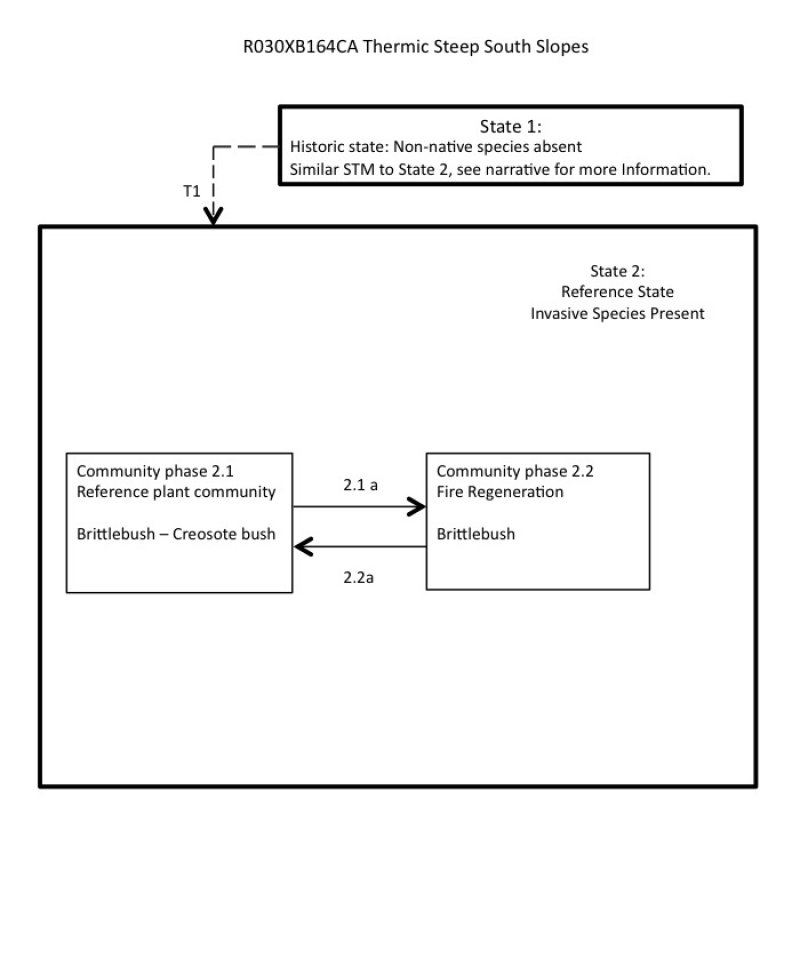
Click on box and path labels to scroll to the respective text.