Natural Resources
Conservation Service
Ecological site R030XD015CA
Hyper-Arid Fans
Last updated: 10/21/2024
Accessed: 03/17/2025
General information
Provisional. A provisional ecological site description has undergone quality control and quality assurance review. It contains a working state and transition model and enough information to identify the ecological site.
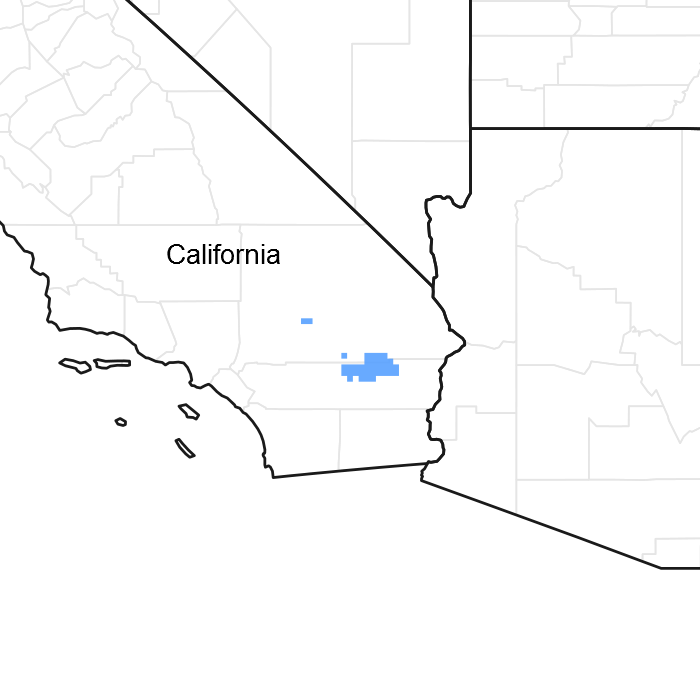
Figure 1. Mapped extent
Areas shown in blue indicate the maximum mapped extent of this ecological site. Other ecological sites likely occur within the highlighted areas. It is also possible for this ecological site to occur outside of highlighted areas if detailed soil survey has not been completed or recently updated.
MLRA notes
Major Land Resource Area (MLRA): 030X–Mojave Basin and Range
MLRA Description:
Major Land Resource Area (MLRA) 30, Mojave Desert, is found in southern California, southern Nevada, the extreme southwest corner of Utah and northwestern Arizona within the Basin and Range Province of the Intermontane Plateaus. The climate of the area is hot (primarily hyperthermic and thermic; however at higher elevations, generally above 5000 feet, mesic, cryic and frigid) and dry (aridic). Elevations range from below sea level to over 12,000 feet in the higher mountain areas found within the MLRA. Due to the extreme elevational range found within this MLRA, Land Resource Units (LRUs) were designated to group the MLRA into similar land units.
LRU notes
This Land Resource Unit (designated by ‘XD’) is found on the eastern side of California. Elevations range from 400 to 2200 feet on average, but may be found up to 4000 feet on southern exposures. Precipitation ranges from 1 to 6 inches per year, but averages between 2-4 inches. This LRU is characterized primarily by the extreme aridity, hot temperatures, hyperthermic soil temperatures and low stature of widely spaced vegetation. Temperatures can reach over 110 degrees Fahrenheit for several weeks in July and August. Summer precipitation falls between July and September, ranging from 20-33% in the form of rain, and winter precipitation falls starting in November and ends between February and March, ranging from 56-70%, also mostly in the form of rain. Vegetation is primarily small, widely-spaced, low-producing creosote bush (Larrea tridentata), burrobush (Ambrosia dumosa), and brittlebush (Encelia farinosa).
Classification relationships
Mojave Creosote Bush (Holland 1986).
Larrea tridentata Shrubland Alliance (Sawyer et al. 2009).
Ecological site concept
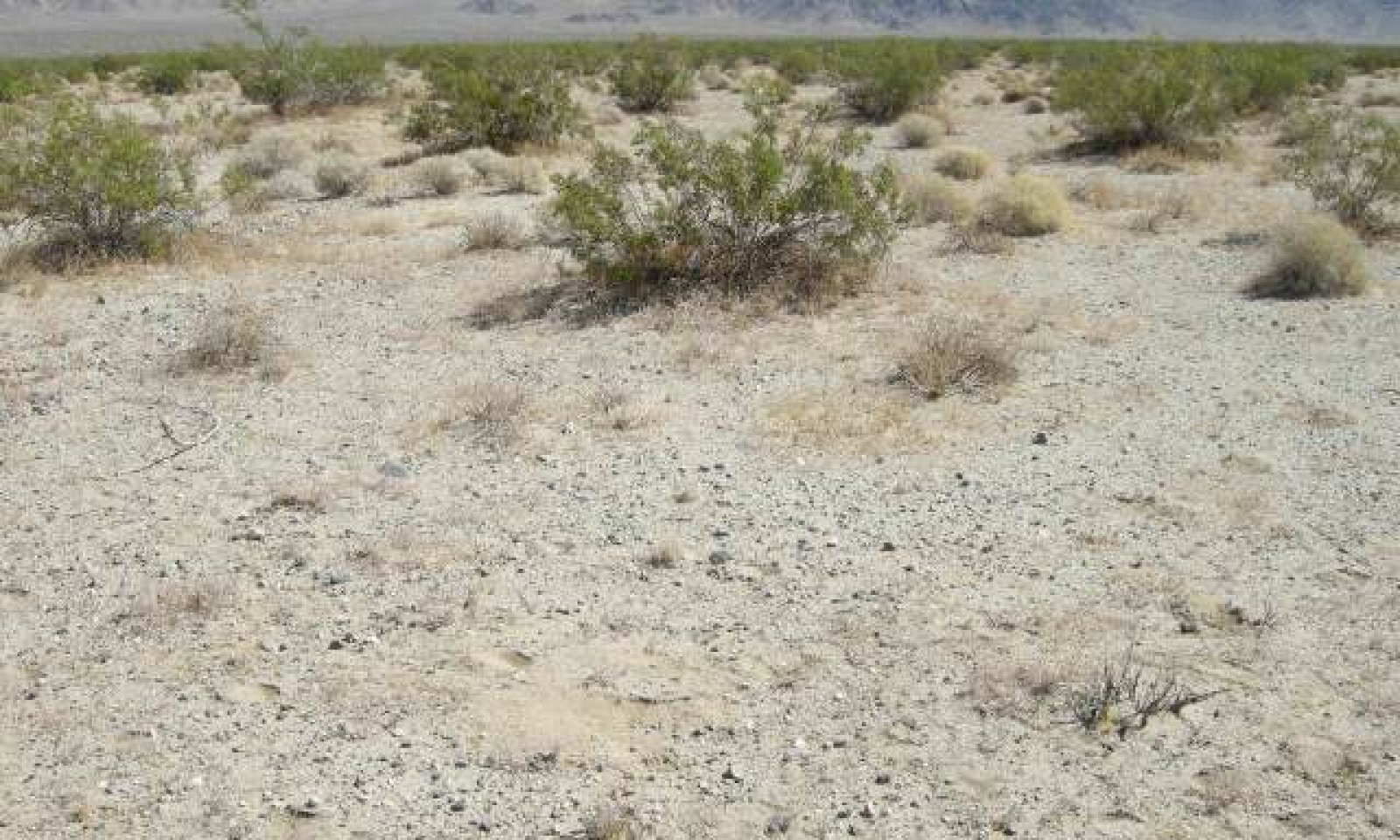
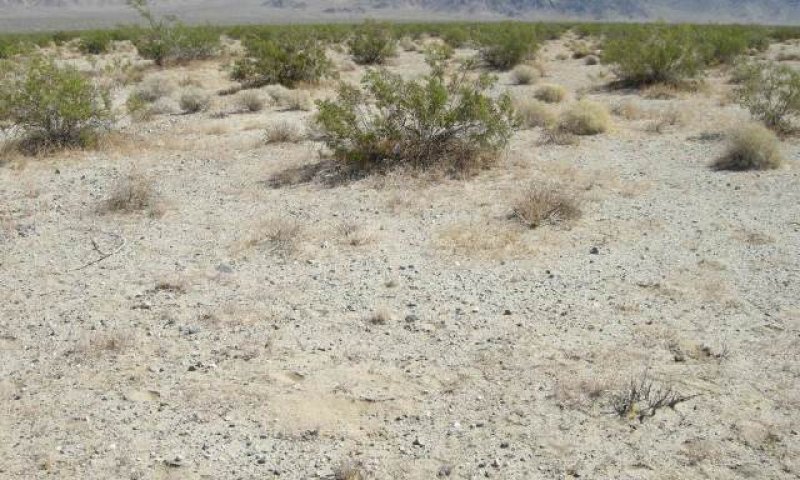
This ecological site occurs on gently sloping alluvial fans, fan aprons, and fan remnants at elevations of 960 to 2810 feet. Soils are typically very deep, but may be moderately deep to deep over a duripan. This site typically has rare sheet-flow due to flash-flooding events.
Production reference value (RV) is 139 pounds per acre, and ranges from 75 to 291 pounds per acre depending on annual precipitation. The site is co-dominated by creosote bush (Larrea tridentata) and burrobush (Ambrosia dumosa). A hyperthermic climate with rare additional run-on from sheet flooding drives the vegetation community of this ecological site. Creosote bush and burrobush are widespread dominants across the fan piedmont landscape of the Mojave Desert. Production, cover, density and diversity in this site are lower than the thermic equivalent of this site; however they are higher than on sites receiving no additional run-on.
The data in the following sections is from major (15% of map unit or greater) components only.
This is a group concept and provisional STM that also covers R030XB141NV.
Associated sites
| R030XD001CA |
Hyperthermic Dry Hills This ecological site is found on north-facing hill and mountain slopes. Creosote bush (Larrea tridentata) and burrobush (Ambrosia dumosa) are dominant. |
|---|---|
| R030XD003CA |
Hyperthermic Steep South Slopes This ecological site is found on adjacent south-facing mountain slopes. Brittlebush (Encelia farinosa) is dominant. |
| R030XD004CA |
Low-Production Hyperthermic Hills This ecological site is found on adjacent steep sideslopes of fan remnants. Sparse vegetation is dominated by creosote bush (Larrea tridentata). |
| R030XD006CA |
Abandoned Fan This ecological site occurs on adjacent fan aprons with no surface flooding. Creosote bush (Larrea tridentata) is dominant. |
| R030XD014CA |
Hyperthermic Sandy Plains This ecological site is found on adjacent semi-active sandsheets. Big galleta (Pleuraphis rigida) is dominant. |
| R030XD025CA |
Hyperthermic Sandsheets This ecological site is found on adjacent sandsheets. Creosote bush (Larrea tridentata) and big galleta (Pleuraphis rigida) dominate. |
| R030XD041CA |
Channeled Warm Alluvial Fans This ecological site occurs on adjacent channeled, rarely flooded fan aprons. Creosote bush (Larrea tridentata), burrobush (Ambrosia dumosa) and brittlebush (Encelia farinosa) are co-dominant. |
| R030XD042CA |
Hyperthermic Shallow To Moderately Deep Fan Remnants This ecological site is found on adjacent stable fan remnants with a high degree of soil horizon development. Vegetation is sparse and dominated by creosote bush (Larrea tridentata). |
| R030XY001CA |
Occasionally Flooded, Hyperthermic, Diffuse Ephemeral Stream This ecological site occurs on adjacent occasionally flooded drainageways. Creosote bush (Larrea tridentata) and Schott's dalea (Psorothamnus schottii) dominate. |
| R030XY038CA |
Flooded Gravelly Fans This ecological site is found on adjacent channeled inset fans. Vegetation is diverse and co-dominated by creosote bush (Larrea tridentata), desertsenna (Senna armata), and Schott's dalea (Psorothamnus schottii). |
| R030XY092NV |
DESERT PATINA This ecological site occurs on adjacent very stable fan remnants with desert pavement surfaces. Vegetation is very sparse, and dominated by creosote bush (Larrea tridentata). |
Similar sites
| R030XB005NV |
Arid Active Alluvial Fans This ecological site occurs on thermic soils at higher elevations. Shrub production, cover, density and diversity are higher. |
|---|---|
| R030XD041CA |
Channeled Warm Alluvial Fans This ecological site occurs on rarely flooded, channeled, typically upper, fan aprons. Production is higher, shrub diversity is higher, and brittlebush (Encelia farinosa) is co-dominant with creosote bush (Larrea tridentata) and burrobush (Ambrosia dumosa). |
| R030XD042CA |
Hyperthermic Shallow To Moderately Deep Fan Remnants This ecological site occurs on very stable fan remnants with a high degree of soil horizon development. Shrub production, cover and density are lower. Creosote bush (Larrea tridentata) is strongly dominant. |
| R030XD006CA |
Abandoned Fan This ecological site occurs on landform positions receiving no additional sheet flooding, and/or in otherwise drier, hotter environments. Production, shrub cover, density and diversity are lower. Creosote bush (Larrea tridentata) is strongly dominant, and burrobush (Ambrosia dumosa) is trace if present. |
Table 1. Dominant plant species
| Tree |
Not specified |
|---|---|
| Shrub |
(1) Larrea tridentata |
| Herbaceous |
Not specified |
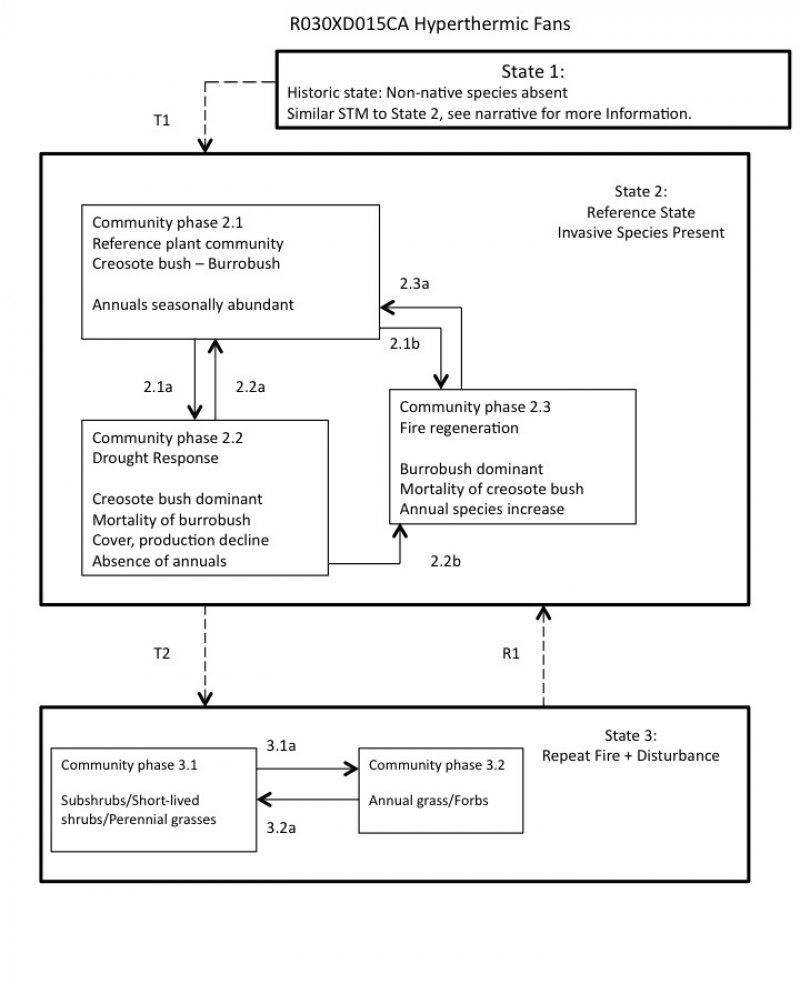
Click on box and path labels to scroll to the respective text.