Natural Resources
Conservation Service
Ecological site R102AY024SD
Shallow Loamy
Last updated: 8/20/2024
Accessed: 04/24/2025
General information
Provisional. A provisional ecological site description has undergone quality control and quality assurance review. It contains a working state and transition model and enough information to identify the ecological site.
MLRA notes
Major Land Resource Area (MLRA): 102A–Rolling Till Prairie
The Rolling Till Prairie (102A) is located within the Central Feed Grains and Livestock Land Resource Region. It spans 3 states (Minnesota 58 percent, South Dakota 42 percent, and small part in North Dakota), encompassing over 16,000 square miles (Figure 1). The elevation ranges from approximately over 2,000 feet above sea level (ASL) on the Prairie Coteau in Northeastern South Dakota to about 1,000 feet ASL on lowlands. The dominate landform in this area are stagnation moraines, end moraines, glacial outwash plains, terraces, and flood plains. The area is dominated by till covered moraines. The stagnation moraines are gently undulating to steep and have many depressions and poorly defined drainages. Small outwash areas are adjacent to the watercourses. The Cretaceous Pierre Shale underlies the till in the most of the area. Precambrian rocks also occur at depth. Granite is quarried near Milbank, South Dakota and outcrops of Sioux Quartzite are common. (USDA-NRCS 2006).
The dominant soil order in this MLRA is Mollisols. The soils in the area dominantly have a frigid soil temperature regime, an aquic or udic soil moisture regime, and mixed mineralogy. They generally are very deep, well drained to very poorly drained. This area supports true prairie vegetation characterized by big bluestem (Andropogon gerardii), little bluestem (Schizachyrium scoparium), porcupinegrass (Hesperostipa spartea), and green needlegrass (Nassella viridula). Prairie cordgrass (Spartina pectinata) commonly grows in wet areas. (USDA-NRCS 2006).
Classification relationships
Major Land Resource Area (MLRA): Rolling Till Prairie (102A) (USDA-NRCS 2006)
USFS Subregions: North Central Glaciated Plains Section (251B); Upper Minnesota River-Des Moines Lobe Subsection (251Ba); Outer Coteau des Prairies Subsection (251Bb); Northwest Iowa Plains Subsection (251Bd); Minnesota and Northeast Iowa Morainal-Oak Savannah Section (222M); Alexandria Moraine-Hardwood Hills Subsection (222Ma) (Cleland et al. 2007).
US EPA Level IV Ecoregion: Tewaukon/Big Stone Stagnation Moraine (46e), Prairie Coteau (46k), Prairie Coteau Escarpment (46l), Big Sioux Basin (46m), Minnesota River Prairie (46o), Des Moines Lobe (47b) , Lake Agassiz Plains (48d), Alexandria Moraines and Detroit Lakes Outwash Plain (51j) (USEPA 2013)
Ecological site concept
The Shallow Loamy ecological site typically occurs on upland areas. Soils are well drained to somewhat excessively drained and have a root restricting layer of bedrock, such as shale or granite within 10 to 20 inches of the soil surface. Surface texture is typically loam and slopes can range from 0 to 25 percent. Vegetation in the Reference State includes little bluestem, porcupine grass, and sideoats grama. Forbs include goldenrods, white sagebrush (cudweed sagewort), heath aster, western yarrow. Non-native grasses such as Kentucky bluegrass, smooth bromegrass may invade the site due to changes in disturbance regime.
Associated sites
| R102AY010SD |
Loamy These sites occur on upland areas. The soils are well drained and have less than 40 percent clay in the surface and subsoil. The central concept soil series is Barnes, Forman, and Poinsett, but other series are included. |
|---|---|
| R102AY012SD |
Thin Upland These sites occur on uplands. Soils are well drained and will effervesce with acid at or near the surface. The central concept soil series is Buse, Langhei, and Zell, but other series are included. |
| R102AY020SD |
Loamy Overflow These sites occur in upland swales. Soils are moderately well drained which have water flow into and over/through the site. The central concept soil series is Aastad, Brookings, Svea, and Waubay but other series are included. |
Similar sites
| R102AY012SD |
Thin Upland The thin upland site occurs on shoulders in uplands. Soils are well drained and will effervesce with acid at or near the surface. Soils do not have a root restricting layer. The Thin Upland site will have more big bluestem, less needlegrasses and higher production than the Shallow Loamy site. |
|---|
Table 1. Dominant plant species
| Tree |
Not specified |
|---|---|
| Shrub |
Not specified |
| Herbaceous |
(1) Schizachyrium scoparium |
Physiographic features
The Shallow Loamy ecological site typically occurs on upland terraces and moraines.
Table 2. Representative physiographic features
| Landforms |
(1)
Upland
> Terrace
(2) Moraine |
|---|---|
| Runoff class | Low to very high |
| Flooding frequency | None |
| Ponding frequency | None |
| Elevation | 305 – 610 m |
| Slope | 0 – 25% |
| Ponding depth | 0 cm |
| Water table depth | 203 cm |
| Aspect | Aspect is not a significant factor |
Climatic features
MLRA 102A is considered to have a continental climate – cold winters and relatively hot summers, low to moderate humidity, light rainfall, and much sunshine. Extremes in temperature may also abound. The climate is the result of this MLRA’s location near the geographic center of North America. There are few natural barriers on the Northern Great Plains and air masses move freely across the plains and account for rapid changes in temperature.
Annual precipitation typically ranges from 21 to 27 inches per year. The average annual temperature is about 43°F. January is the coldest month with average temperatures ranging from about 5°F (Mahnomen 1 W, Minnesota (MN)), to about 14°F (Tracy, MN). July is the warmest month with temperatures averaging from about 69°F (Mahnomen 1 W, MN), to about 73°F (Tracy, MN). The range of normal average monthly temperatures between the coldest and warmest months is about 62°F. This large annual range attests to the continental nature of this area's climate. Hourly winds are estimated to average about 11 miles per hour (mph) annually, ranging from about 13 mph during the spring to about 10 mph during the summer. Daytime winds are generally stronger than nighttime and occasional strong storms may bring brief periods of high winds with gusts to more than 50 mph.
Growth of cool-season plants begins in early to mid-March, slowing or ceasing in late June. Warm-season plants begin growth about mid-May and continue to early or mid-September. Greenup of cool-season plants may occur in September and October when adequate soil moisture is present.
Table 3. Representative climatic features
| Frost-free period (characteristic range) | 124-127 days |
|---|---|
| Freeze-free period (characteristic range) | 141-152 days |
| Precipitation total (characteristic range) | 610-635 mm |
| Frost-free period (actual range) | 112-130 days |
| Freeze-free period (actual range) | 131-153 days |
| Precipitation total (actual range) | 610-635 mm |
| Frost-free period (average) | 124 days |
| Freeze-free period (average) | 143 days |
| Precipitation total (average) | 635 mm |
Figure 1. Monthly precipitation range
Figure 2. Monthly minimum temperature range
Figure 3. Monthly maximum temperature range
Figure 4. Monthly average minimum and maximum temperature
Figure 5. Annual precipitation pattern
Figure 6. Annual average temperature pattern
Climate stations used
-
(1) ARTICHOKE LAKE [USC00210287], Correll, MN
-
(2) BROWNS VALLEY [USC00211063], Beardsley, MN
-
(3) CASTLEWOOD [USC00391519], Castlewood, SD
-
(4) MILBANK 4 NW [USC00395536], Milbank, SD
-
(5) ROY LAKE [USC00397326], Lake City, SD
-
(6) SISSETON [USC00397742], Sisseton, SD
Influencing water features
No riparian areas or wetland features are directly associated with this site.
Wetland description
Not Applicable.
Soil features
The Shallow Loamy ecological site occurs on upland areas. Soils are well drained to somewhat excessively drained and have a root restricting layer of bedrock, such as shale or granite within 10 to 20 inches of the soil surface. The central concept soil series are Kloten, and Yellowbank, but other series could be included as well.
Table 4. Representative soil features
| Parent material |
(1)
Alluvium
(2) Till |
|---|---|
| Surface texture |
(1) Silt loam (2) Clay loam |
| Family particle size |
(1) Loamy |
| Drainage class | Well drained to somewhat excessively drained |
| Permeability class | Moderate to moderately rapid |
| Depth to restrictive layer | 28 – 51 cm |
| Soil depth | 25 – 51 cm |
| Surface fragment cover <=3" | 4 – 6% |
| Surface fragment cover >3" | 2 – 4% |
| Available water capacity (0-101.6cm) |
5.08 cm |
| Calcium carbonate equivalent (0-101.6cm) |
0 – 10% |
| Electrical conductivity (0-101.6cm) |
0 mmhos/cm |
| Sodium adsorption ratio (0-101.6cm) |
0 |
| Soil reaction (1:1 water) (0-101.6cm) |
6.1 – 8.4 |
| Subsurface fragment volume <=3" (0-101.6cm) |
6 – 9% |
| Subsurface fragment volume >3" (0-101.6cm) |
2 – 4% |
Ecological dynamics
The site which is located in the Prairie Pothole Region developed under Northern Great Plains climatic conditions and included natural influence of large herding herbivores and occasional fire. Changes will occur in the plant communities due to weather fluctuations and/or management actions. Under adverse impacts, a relatively rapid decline in vegetative vigor and composition can occur. Under favorable conditions the site has the potential to resemble the Reference State. Interpretations for this site are based primarily on the 1.1 Little Bluestem-Porcupine Grass-Sideoats Grama Plant Community Phase. This community phase and the Reference State have been determined by study of rangeland relic areas, areas protected from excessive disturbance, and areas under long-term rotational grazing regimes. Trends in plant community dynamics ranging from heavily grazed to lightly grazed areas, seasonal use pastures, and historical accounts also have been considered.
This ecological site (ES) has been grazed by domestic livestock since they have been introduced into the area. The introduction of domestic livestock and the use of fencing and reliable water sources have changed the ecological dynamics of this site. Continuous season-long grazing (during the typical growing season of May through October) and/or repeated seasonal grazing (e.g., every spring, every summer) without adequate recovery periods following grazing events causes departure from the 2.1 Little Bluestem-Porcupine Grass-Sideoats Grama Plant Community Phase. Little bluestem, western wheatgrass (Pascopyrum smithii), sideoats grama, and blue grama (Bouteloua gracilis) will increase. Eventually, blue grama, quackgrass (Elymus repens), and Kentucky bluegrass (Poa pratensis) may develop into a sod. Indiangrass (Sorghastrum nutans), big bluestem (Andropogon gerardii), porcupine grass (Hesperostipa spartea), green needlegrass (Nassella viridula), sideoats grama, and little bluestem will decrease in frequency and production. Extended periods of nonuse and/or lack of fire will result in excessive litter and a plant community dominated by cool-season grasses such as Kentucky bluegrass, smooth bromegrass (Bromus inermis), and green needlegrass.
Following the state and transition diagram are narratives for each of the described states and community phases. These may not represent every possibility, but they are the most prevalent and repeatable states/community phases. The plant composition tables shown below have been developed from the best available knowledge at the time of this revision. As more data are collected, some of these community phases and/or states may be revised or removed, and new ones may be added. The main purpose for including the descriptions here is to capture the current knowledge and experience at the time of this revision.
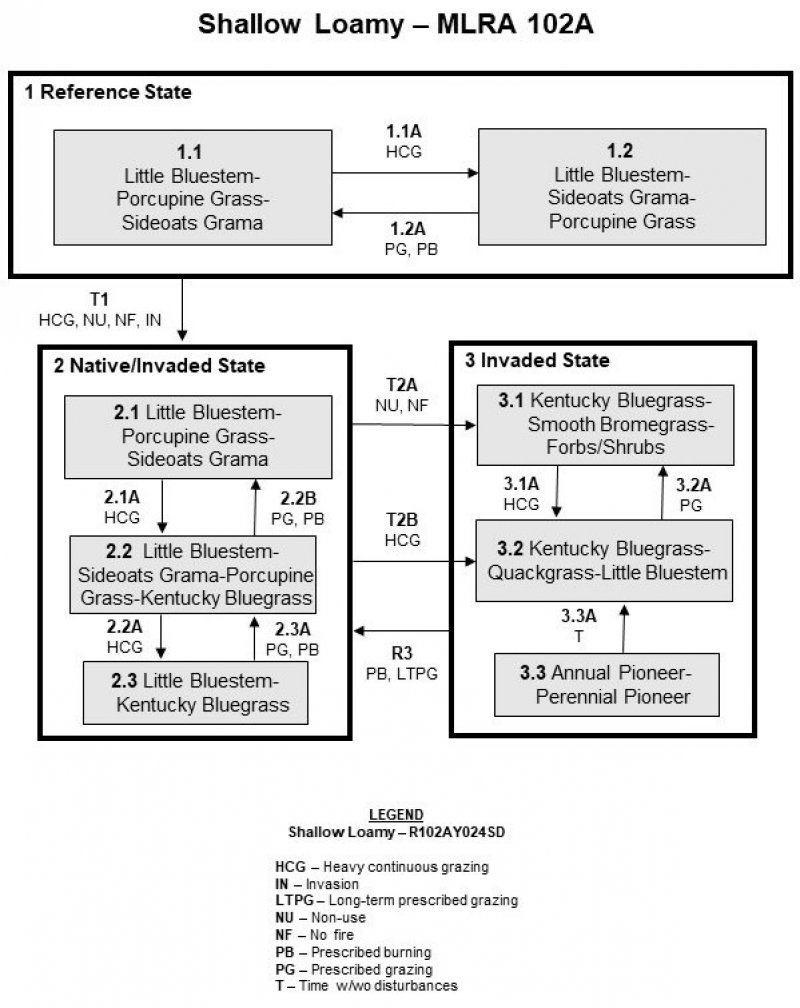
State and transition model
More interactive model formats are also available.
View Interactive Models
Click on state and transition labels to scroll to the respective text
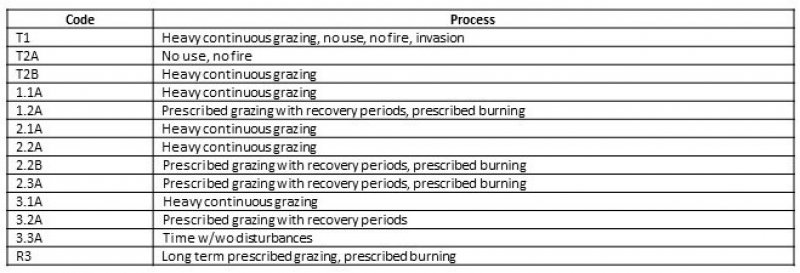
Ecosystem states
| T1 | - | Heavy continuous grazing, no use, no fire, invasion |
|---|---|---|
| T2A | - | No use, no fire, heavy continuous grazing |
| R3 | - | Long term prescribed grazing, prescribed burning |
State 1 submodel, plant communities
| 1.1A | - | Heavy continuous grazing |
|---|---|---|
| 1.2A | - | Prescribed grazing with recovery periods, prescribed burning |
State 2 submodel, plant communities
| 2.1A | - | Heavy continuous grazing |
|---|---|---|
| 2.2B | - | Prescribed grazing with recovery periods, prescribed burning |
| 2.2A | - | Heavy continuous grazing |
| 2.3A | - | Prescribed grazing with recovery periods, prescribed burning |
State 3 submodel, plant communities
| 3.1A | - | Heavy continuous grazing |
|---|---|---|
| 3.2A | - | Prescribed grazing with recovery periods |
| 3.3A | - | Time w/wo disturbances |
State 1
Reference State
The Reference State represents the natural range of variability that dominates the dynamics of this ES. This state is typically dominated by cool-season grass and grass-like species. Before European settlement, the primary disturbance mechanisms for this site in the reference condition included periodic fire, grazing by large herding ungulates, and fluctuations in the water table and ponding frequency and duration. Frequent surface fires (3 to 5 years) and grazing coupled with weather events dictated the dynamics that occurred within the natural range of variability. Today, the primary disturbance is from a lack of fire, concentrated livestock grazing, and weather fluctuations. Species that are desirable for livestock and wildlife can decline and a corresponding increase in less desirable species will occur.
Dominant plant species
-
little bluestem (Schizachyrium scoparium), grass
-
porcupinegrass (Hesperostipa spartea), grass
-
sideoats grama (Bouteloua curtipendula), grass
-
big bluestem (Andropogon gerardii), grass
-
Indiangrass (Sorghastrum nutans), grass
-
green needlegrass (Nassella viridula), grass
-
plains muhly (Muhlenbergia cuspidata), grass
-
prairie sandreed (Calamovilfa longifolia), grass
-
Canada wildrye (Elymus canadensis), grass
-
slender wheatgrass (Elymus trachycaulus), grass
-
needle and thread (Hesperostipa comata), grass
-
western wheatgrass (Pascopyrum smithii), grass
-
blue grama (Bouteloua gracilis), grass
-
threadleaf sedge (Carex filifolia), grass
-
goldenrod (Oligoneuron), other herbaceous
-
white sagebrush (Artemisia ludoviciana), other herbaceous
-
common yarrow (Achillea millefolium), other herbaceous
-
white heath aster (Symphyotrichum ericoides), other herbaceous
-
Cuman ragweed (Ambrosia psilostachya), other herbaceous
Community 1.1
Little Bluestem-Porcupine Grass-Sideoats Grama
Interpretations are based primarily on the 1.1 Little Bluestem-Porcupine Grass-Sideoats Grama Plant Community Phase (this is also considered to be climax). The potential vegetation was about 80 percent grasses or grass-like plants, 10 percent forbs, and 8 percent shrubs. The community was dominated by warm-season grasses with cool-season grasses being subdominant. The major grasses included little bluestem, big bluestem, Indiangrass, sideoats grama, porcupine grass, and green needlegrass. Other grass or grass-like species included plains muhly (Muhlenbergia cuspidata), prairie sandreed (Calamovilfa longifolia), Canada wildrye (Elymus Canadensis), slender wheatgrass (Elymus trachycaulus), needleandthread (Hesperostipa comata), western wheatgrass, blue grama, and threadleaf sedge (Carex filifolia). This plant community was resilient and well adapted to the Northern Great Plains climatic conditions. The diversity in plant species allowed for high drought tolerance. This was a sustainable plant community in regards to site/soil stability, watershed function, and biologic integrity.
Figure 7. Annual production by plant type (representative values) or group (midpoint values)
Table 5. Annual production by plant type
| Plant type | Low (kg/hectare) |
Representative value (kg/hectare) |
High (kg/hectare) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grass/Grasslike | 1973 | 2571 | 3116 |
| Shrub/Vine | 135 | 228 | 347 |
| Forb | 135 | 228 | 347 |
| Total | 2243 | 3027 | 3810 |
Figure 8. Plant community growth curve (percent production by month). SD0204, Rolling Till Prairie, warm-season dominant, cool-season subdominant.. Warm-season dominant, cool-season subdominant..
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| J | F | M | A | M | J | J | A | S | O | N | D |
| 0 | 0 | 3 | 7 | 17 | 25 | 25 | 15 | 7 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
Community 1.2
Little Bluestem-Sideoats Grama-Porcupine Grass
This plant community evolved under heavy continuous grazing or from over utilization during extended drought periods. The potential plant community was made up of approximately 75 percent grasses and grass-like species, 15 percent forbs, and 10 percent shrubs. Dominant grasses included little bluestem, sideoats grama, and porcupine grass. Grasses of secondary importance included big bluestem, green needlegrass, blue grama, western wheatgrass, prairie dropseed (Sporobolus heterolepis), and threadleaf sedge. Forbs commonly found in this plant community included goldenrod (Oligoneuron), white sagebrush (local known as cudweed sagewort) (Artemisia ludoviciana), heath aster (Symphyotrichum ericoides), scurfpea (Psoralidium), western ragweed (Ambrosia psilostachya), and western yarrow (Achillea millefolium). This plant community had similar plant composition to the 2.2 Little Bluestem-Sideoats Grama-Porcupine Grass-Kentucky Bluegrass Plant Community Phase. The main difference is that this plant community phase did not have the presence of nonnative invasive species such as Kentucky bluegrass and smooth bromegrass. When compared to the 1.1 Little Bluestem-Porcupine Grass-Sideoats Grama Plant Community Phase, little bluestem and sideoats grama increased. Production of tall warm-season grasses was reduced. This plant community was moderately resistant to change. The herbaceous species present were well adapted to grazing; however, species composition could be altered through long-term overgrazing. If the herbaceous component was intact, it tended to be resilient if the disturbance was not long-term. Most of the components of the ecological processes would have been functioning at optimum levels. However, the vigor and reproductive capability of the tall warm-season grasses would have been reduced due to grazing pressure or a combination of stressors. A reduction of this dominant functional group allowed for an increase in shorter-statured (and shallower rooted) species.
Figure 9. Plant community growth curve (percent production by month). SD0204, Rolling Till Prairie, warm-season dominant, cool-season subdominant.. Warm-season dominant, cool-season subdominant..
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| J | F | M | A | M | J | J | A | S | O | N | D |
| 0 | 0 | 3 | 7 | 17 | 25 | 25 | 15 | 7 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
Pathway 1.1A
Community 1.1 to 1.2
Heavy continuous grazing which includes herbivory at moderate to heavy levels at the same time of year each year without adequate recovery periods, or during periods of below normal precipitation when grazing frequency and intensity increases on these sites due to limited forage availability on adjacent upland sites will shift this community to the 1.2 Little Bluestem-Sideoats Grama-Porcupine Grass Plant Community Phase.
Pathway 1.2A
Community 1.2 to 1.1
Prescribed Grazing, and/or prescribed burning returned to normal disturbance regime levels and frequencies or periodic light to moderate grazing possibly including periodic rest would have converted this plant community to the 1.1 Little Bluestem-Porcupine Grass-Sideoats Grama Plant Community Phase.
State 2
Native/Invaded State
This state represents the more common range of variability that exists with higher levels of grazing management but in the absence of periodic fire due to fire suppression. This state is dominated by cool- and warm-season grasses. It can be found on areas that are properly managed with grazing and/or prescribed burning and sometimes on areas receiving occasional short periods of rest. Taller warm-season species can decline and a corresponding increase in short-statured grass will occur.
Dominant plant species
-
Kentucky bluegrass (Poa pratensis), grass
-
smooth brome (Bromus inermis), grass
-
little bluestem (Schizachyrium scoparium), grass
-
porcupinegrass (Hesperostipa spartea), grass
-
sideoats grama (Bouteloua curtipendula), grass
-
big bluestem (Andropogon gerardii), grass
-
slender wheatgrass (Elymus trachycaulus), grass
-
needle and thread (Hesperostipa comata), grass
-
western wheatgrass (Pascopyrum smithii), grass
-
blue grama (Bouteloua gracilis), grass
-
threadleaf sedge (Carex filifolia), grass
-
prairie sandreed (Calamovilfa longifolia), grass
-
Canada wildrye (Elymus canadensis), grass
-
goldenrod (Oligoneuron), other herbaceous
-
white sagebrush (Artemisia ludoviciana), other herbaceous
-
white heath aster (Symphyotrichum ericoides), other herbaceous
-
Cuman ragweed (Ambrosia psilostachya), other herbaceous
-
common yarrow (Achillea millefolium), other herbaceous
Community 2.1
Little Bluestem-Porcupine Grass-Sideoats Grama
This plant community phase is similar to the 1.1 Little Bluestem-Porcupine Grass-Sideoats Grama Plant Community Phase, but it also contains minor amounts of nonnative invasive grass species such as Kentucky bluegrass and smooth bromegrass (up to about 10 percent by air-dry weight). The potential vegetation is about 80 percent grasses or grass-like plants, 10 percent forbs, and 8 percent shrubs. This community is dominated by warm-season grasses, with cool-season grasses being subdominant. The major grasses include little bluestem, big bluestem, porcupine grass, sideoats grama, Indiangrass plains muhly, and green needlegrass. Other grass or grass-like species include prairie dropseed, prairie sandreed, Canada wildrye, needleandthread, slender wheatgrass, western wheatgrass, blue grama, Kentucky bluegrass, and threadleaf sedge. This plant community is resilient and well adapted to the Northern Great Plains climatic conditions. The diversity in plant species allows for high drought tolerance. This is a sustainable plant community in regards to site/soil stability, watershed function, and biologic integrity.
Figure 10. Plant community growth curve (percent production by month). SD0204, Rolling Till Prairie, warm-season dominant, cool-season subdominant.. Warm-season dominant, cool-season subdominant..
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| J | F | M | A | M | J | J | A | S | O | N | D |
| 0 | 0 | 3 | 7 | 17 | 25 | 25 | 15 | 7 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
Community 2.2
Little Bluestem-Sideoats Grama-Porcupine Grass-Kentucky Bluegrass
This plant community is a result of heavy continuous grazing or from over utilization during extended drought periods. The potential plant community is made up of approximately 75 percent grasses and grass-like species, 15 percent forbs, and 10 percent shrubs. Dominant grasses include little bluestem, sideoats grama, and porcupine grass. Grasses of secondary importance include big bluestem, green needlegrass, blue grama, western wheatgrass, prairie dropseed, and threadleaf sedge. Forbs commonly found in this plant community include goldenrod, cudweed sagewort, heath aster, scurfpea, western ragweed, and western yarrow. When compared to the 1.1 Little Bluestem-Porcupine Grass-Sideoats Grama Plant Community Phase, little bluestem, sideoats grama, and Kentucky bluegrass have increased. Production of tall warm-season grasses is reduced. This plant community is moderately resistant to change. The herbaceous species present are well adapted to grazing; however, species composition can be altered through long-term overgrazing. If the herbaceous component is intact, it tends to be resilient if the disturbance is not long-term. Most of the components of the ecological processes are functioning at optimum levels. However, the vigor and reproductive capability of the tall warm-season grasses are reduced due to grazing pressure or a combination of stressors. A reduction of this dominant functional group allows for an increase in shorter-statured (and shallower rooted) species. The introduction of nonnative invasive species such as Kentucky bluegrass and smooth bromegrass results in alterations to the soil profile. Organic matter levels tend to decrease and begin to be concentrated more in the surface layers and the structure will begin to be modified. These changes favor the shallow-rooted species and hasten their eventual dominance if steps are not taken to reduce these species.
Figure 11. Annual production by plant type (representative values) or group (midpoint values)
Table 6. Annual production by plant type
| Plant type | Low (kg/hectare) |
Representative value (kg/hectare) |
High (kg/hectare) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grass/Grasslike | 1569 | 2034 | 2427 |
| Forb | 112 | 247 | 432 |
| Shrub/Vine | 112 | 185 | 280 |
| Total | 1793 | 2466 | 3139 |
Figure 12. Plant community growth curve (percent production by month). SD0203, Rolling Till Prairie, cool-season/warm-season codominant.. Cool-season, warm-season codominant..
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| J | F | M | A | M | J | J | A | S | O | N | D |
| 0 | 0 | 3 | 10 | 20 | 28 | 21 | 10 | 5 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
Community 2.3
Little Bluestem-Kentucky Bluegrass
This plant community is a result of heavy continuous grazing or from over utilization during extended drought periods. The potential plant community is made up of approximately 75 percent grasses and grass-like species, 15 percent forbs, and 10 percent shrubs. Dominant grasses include little bluestem and Kentucky bluegrass. Grass and grass-like species of secondary importance include sideoats grama, blue grama, western wheatgrass, threadleaf sedge, green needlegrass, big bluestem, and quackgrass. Forbs commonly found in this plant community include goldenrod, cudweed sagewort, heath aster, scurfpea, western ragweed, and western yarrow. When compared to the 1.1 Little Bluestem-Porcupine Grass-Sideoats Grama Plant Community Phase, little bluestem and Kentucky bluegrass have increased. Production of mid and tall warm- and cool-season grasses is reduced. This plant community is moderately resistant to change. The herbaceous species present are well adapted to grazing; however, species composition can be altered through long-term overgrazing. If the herbaceous component is intact, it tends to be resilient if the disturbance is not long-term. A reduction of the dominant functional groups as found in the interpretive plant community phase allows for an increase in shorter-statured (and shallower rooted) species. The introduction of nonnative invasive species such as Kentucky bluegrass and smooth bromegrass results in alterations to the soil profile. Organic matter levels tend to decrease and begin to be concentrated more in the surface layers and the structure will begin to be modified. These changes favor the shallow-rooted species and hasten their eventual dominance if steps are not taken to reduce these species.
Figure 13. Annual production by plant type (representative values) or group (midpoint values)
Table 7. Annual production by plant type
| Plant type | Low (kg/hectare) |
Representative value (kg/hectare) |
High (kg/hectare) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grass/Grasslike | 1356 | 1849 | 2275 |
| Forb | 106 | 224 | 387 |
| Shrub/Vine | 106 | 168 | 252 |
| Total | 1568 | 2241 | 2914 |
Figure 14. Plant community growth curve (percent production by month). SD0203, Rolling Till Prairie, cool-season/warm-season codominant.. Cool-season, warm-season codominant..
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| J | F | M | A | M | J | J | A | S | O | N | D |
| 0 | 0 | 3 | 10 | 20 | 28 | 21 | 10 | 5 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
Pathway 2.1A
Community 2.1 to 2.2
Heavy continuous grazing which includes herbivory at moderate to heavy levels at the same time of year each year without adequate recovery periods, or during periods of below normal precipitation when grazing frequency and intensity increases on these sites due to limited forage availability on adjacent upland sites and no surface fire for extended periods of time (typically for 10 years or more) causing litter levels to become high enough to reduce native grass vigor, diversity, and density will shift this community to the 2.2 Little Bluestem-Sideoats Grama-Porcupine Grass-Kentucky Bluegrass Plant Community Phase.
Pathway 2.2B
Community 2.2 to 2.1
Prescribed grazing (alternating season of use and providing adequate recovery periods) or periodic light to moderate grazing possibly including periodic rest and/or prescribed burning with late season fire or at infrequent intervals (greater than 5 years) will convert this plant community to the 2.1 Little Bluestem-Porcupine Grass-Sideoats Grama Plant Community Phase.
Conservation practices
| Prescribed Burning | |
|---|---|
| Prescribed Grazing |
Pathway 2.2A
Community 2.2 to 2.3
Heavy continuous grazing which includes herbivory at moderate to heavy levels at the same time of year each year without adequate recovery periods, or during periods of below normal precipitation when grazing frequency and intensity increases on these sites due to limited forage availability on adjacent upland sites and no surface fire for extended periods of time (typically for 10 years or more) causing litter levels to become high enough to reduce native grass vigor, diversity, and density will shift this community to the 2.3 Little Bluestem-Kentucky Bluegrass Plant Community Phase.
Pathway 2.3A
Community 2.3 to 2.2
Prescribed grazing (alternating season of use and providing adequate recovery periods) or periodic light to moderate grazing possibly including periodic rest and/or prescribed burning with late season fire or at infrequent intervals (greater than 5 years) will convert this plant community to the 2.2 Little Bluestem-Sideoats Grama-Porcupine Grass-Kentucky Bluegrass Plant Community Phase.
Conservation practices
| Prescribed Burning | |
|---|---|
| Prescribed Grazing |
State 3
Invaded State
This state is a result of encroachment mainly by invasive introduced cool-season grasses. The ecological processes are not functioning, especially the biotic processes and the hydrologic functions. The introduced cool-season grasses cause reduced infiltration and increased runoff. Preliminary studies would tend to indicate this threshold may exist when Kentucky bluegrass exceeds 30 percent of the plant community and native grasses represent less than 40 percent of the plant community composition. The opportunity for high intensity spring burns is severely reduced by early greenup and increased moisture and humidity at the soil surface and grazing pressure cannot cause a reduction in sodgrass dominance. Production is limited to the sod forming species. Infiltration continues to decrease and runoff increases and energy capture into the system is restricted to early season low producing species. Nutrient cycling is limited by root depth of the dominant species.
Dominant plant species
-
Kentucky bluegrass (Poa pratensis), grass
-
smooth brome (Bromus inermis), grass
-
quackgrass (Elymus repens), grass
-
little bluestem (Schizachyrium scoparium), grass
Community 3.1
Kentucky Bluegrass-Smooth Bromegrass-Forbs/Shrubs
This plant community phase is a result of extended periods of nonuse and no fire or occasionally light levels of grazing over several years. It is characterized by dominance of smooth bromegrass and Kentucky bluegrass. The dominance is at times so complete that other species are difficult to find on the site. A thick duff layer also accumulates at or above the soil surface and eventually a thatch-mat layer may develop at the surface. Nutrient cycling is greatly reduced and native plants have great difficulty becoming established. When dominated by smooth bromegrass, infiltration is moderately reduced and runoff is moderate. Production can be equal to or higher than the interpretive plant community. However, when dominated by Kentucky bluegrass, infiltration is greatly reduced and runoff is high. Production in this case will likely be significantly less. In either case, the period that palatability is high is relatively short as these cool-season species mature rapidly. Energy capture is also reduced. The dominance of these introduced species has been shown to alter the biotic component of the soil, as well as, organic matter levels and eventually the soil structure. These alterations perpetuate the dominance of Kentucky bluegrass and smooth bromegrass and tend to make establishment of native species extremely difficult.
Figure 15. Annual production by plant type (representative values) or group (midpoint values)
Table 8. Annual production by plant type
| Plant type | Low (kg/hectare) |
Representative value (kg/hectare) |
High (kg/hectare) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grass/Grasslike | 1771 | 2242 | 2589 |
| Shrub/Vine | 123 | 280 | 499 |
| Forb | 123 | 280 | 499 |
| Total | 2017 | 2802 | 3587 |
Figure 16. Plant community growth curve (percent production by month). SD0201, Rolling Till Prairie, cool-season dominant.. Cool-season dominant..
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| J | F | M | A | M | J | J | A | S | O | N | D |
| 0 | 0 | 4 | 12 | 25 | 36 | 10 | 5 | 4 | 4 | 0 | 0 |
Community 3.2
Kentucky Bluegrass-Quackgrass-Little Bluestem
This plant community phase is a result of heavy continuous grazing or a combination of disturbances such as extended periods of below-average precipitation combined with heavy continuous grazing. It is characterized by a dominance of Kentucky bluegrass and quackgrass and occasionally with significant levels of little bluestem. The dominance is at times so complete that other species are difficult to find on the site. A relatively thick duff layer can sometimes accumulate at or above the soil surface and a thatch-mat layer often develops at the surface. Nutrient cycling is greatly reduced and native plants have great difficulty becoming established. Infiltration is greatly reduced and runoff is high. Production will be significantly reduced when compared to the interpretive plant community. The period that palatability is high is relatively short as Kentucky bluegrass matures rapidly. Energy capture is also reduced. Biological activity in the soil is likely reduced significantly in this phase.
Figure 17. Annual production by plant type (representative values) or group (midpoint values)
Table 9. Annual production by plant type
| Plant type | Low (kg/hectare) |
Representative value (kg/hectare) |
High (kg/hectare) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grass/Grasslike | 1115 | 1506 | 1956 |
| Forb | 84 | 179 | 308 |
| Shrub/Vine | 34 | 108 | 202 |
| Total | 1233 | 1793 | 2466 |
Figure 18. Plant community growth curve (percent production by month). SD0201, Rolling Till Prairie, cool-season dominant.. Cool-season dominant..
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| J | F | M | A | M | J | J | A | S | O | N | D |
| 0 | 0 | 4 | 12 | 25 | 36 | 10 | 5 | 4 | 4 | 0 | 0 |
Community 3.3
Annual Pioneer-Perennial Pioneer
This plant community developed under continuous heavy grazing or other excessive disturbances. The potential plant community is made up of approximately 40 to 80 percent grasses and grass-like species, 20 to 60 percent forbs, and 0 to 5 percent shrubs. The species present in this phase are highly variable, but often include nonnative invasive and/or early seral species. Plant diversity is low (plant richness may be high but areas are often dominated by a few species). The ecological processes are difficult to restore because of the loss of plant diversity and overall soil disturbance. Soil erosion is potentially very high because of the bare ground and shallow rooted herbaceous plant community. Water runoff will increase and infiltration will decrease due to animal related soil compaction and loss of root mass due to low plant diversity and vigor. This plant community will require significant economic inputs and time to move towards another plant community. This movement is highly variable in its succession. This is due to the loss of diversity (including the loss of the seed bank), within the existing plant community, and the plant communities on adjacent sites.
Pathway 3.1A
Community 3.1 to 3.2
Heavy continuous grazing which includes herbivory at moderate to heavy levels at the same time of year each year without adequate recovery periods, or during periods of below normal precipitation when grazing frequency and intensity increases on these sites due to limited forage availability on adjacent upland sites and no surface fire for extended periods of time (typically for 10 years or more) causing litter levels to become high enough to reduce native grass vigor, diversity, and density will shift this community to the 3.2 Kentucky Bluegrass-Quackgrass-Little Bluestem Plant Community Phase.
Pathway 3.2A
Community 3.2 to 3.1
Prescribed grazing (alternating season of use and providing adequate recovery periods) or periodic light to moderate grazing possibly including periodic rest may convert this plant community to the 3.1 Kentucky Bluegrass-Smooth Bromegrass-Forbs/Shrubs Plant Community Phase.
Pathway 3.3A
Community 3.3 to 3.2
This community pathway occurs with the passage of time as successional processes take place and perennial plants gradually begin to establish on the site again. This pathway will lead to the 3.2 Kentucky Bluegrass-Quackgrass-Little Bluestem Plant Community Phase.
Transition T1
State 1 to 2
Non-use and/or no surface fire for extended periods of time (typically for 10 or more years) causing litter levels to become high enough to reduce native grass vigor, diversity, and density, and/or heavy continuous grazing or invasion of non-native plant species will likely lead this state over a threshold resulting in the Native/Invaded State (State 2).
Transition T2A
State 2 to 3
Non-use and/or no surface fire for extended periods of time (typically for 10 or more years) causing litter levels to become high enough to reduce native grass vigor, diversity, and density, will likely lead this state over a threshold leading to the 3.1 Smooth Bromegrass-Kentucky Bluegrass-Forbs/Shrubs Plant Community Phase within the Invaded State (State 3). Heavy continuous grazing (stocking levels well above carrying capacity for extended portions of the growing season and often at the same time of year each year), will likely lead this state over a threshold leading to the 3.2 Kentucky Bluegrass-Quackgrass-Little Bluestem Plant Community Phase within the Invaded State (State 3). Grazing repeatedly in the early growing season can expedite this shift by causing mechanical disturbance due to trampling.
Restoration pathway R3
State 3 to 2
Long-term prescribed grazing (moderate stocking levels coupled with adequate recovery periods, or other grazing systems such as high-density, low-frequency intended to treat specific species dominance, or periodic light to moderate stocking levels possibly including periodic rest) coupled with prescribed burning may lead this this Invaded State (State 3) over a threshold to the Native/Invaded State (State 2).
Conservation practices
| Prescribed Grazing | |
|---|---|
| Integrated Pest Management (IPM) |
Additional community tables
Table 10. Community 1.1 plant community composition
| Group | Common name | Symbol | Scientific name | Annual production (kg/hectare) | Foliar cover (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Grass/Grasslike
|
||||||
| 1 | Mid Warm-season Grasses | 605–1059 | ||||
| little bluestem | SCSC | Schizachyrium scoparium | 303–757 | – | ||
| sideoats grama | BOCU | Bouteloua curtipendula | 151–454 | – | ||
| plains muhly | MUCU3 | Muhlenbergia cuspidata | 61–303 | – | ||
| prairie dropseed | SPHE | Sporobolus heterolepis | 30–151 | – | ||
| 2 | Cool-season Bunchgrasses | 454–1059 | ||||
| porcupinegrass | HESP11 | Hesperostipa spartea | 303–757 | – | ||
| green needlegrass | NAVI4 | Nassella viridula | 61–303 | – | ||
| needle and thread | HECOC8 | Hesperostipa comata ssp. comata | 30–151 | – | ||
| Canada wildrye | ELCA4 | Elymus canadensis | 30–91 | – | ||
| 3 | Tall Warm-season Grasses | 303–605 | ||||
| big bluestem | ANGE | Andropogon gerardii | 151–454 | – | ||
| Indiangrass | SONU2 | Sorghastrum nutans | 61–303 | – | ||
| prairie sandreed | CALO | Calamovilfa longifolia | 30–151 | – | ||
| 4 | Wheatgrass | 61–151 | ||||
| slender wheatgrass | ELTR7 | Elymus trachycaulus | 30–151 | – | ||
| western wheatgrass | PASM | Pascopyrum smithii | 30–151 | – | ||
| 5 | Other Native Grasses | 61–151 | ||||
| Graminoid (grass or grass-like) | 2GRAM | Graminoid (grass or grass-like) | 0–151 | – | ||
| blue grama | BOGR2 | Bouteloua gracilis | 30–91 | – | ||
| prairie Junegrass | KOMA | Koeleria macrantha | 30–91 | – | ||
| Scribner's rosette grass | DIOLS | Dichanthelium oligosanthes var. scribnerianum | 0–61 | – | ||
| 6 | Grass-likes | 61–151 | ||||
| Grass-like (not a true grass) | 2GL | Grass-like (not a true grass) | 30–91 | – | ||
| sun sedge | CAINH2 | Carex inops ssp. heliophila | 30–91 | – | ||
|
Forb
|
||||||
| 7 | Forbs | 151–303 | ||||
| Forb, native | 2FN | Forb, native | 30–91 | – | ||
| blacksamson echinacea | ECAN2 | Echinacea angustifolia | 30–91 | – | ||
| stiff sunflower | HEPA19 | Helianthus pauciflorus | 30–61 | – | ||
| blazing star | LIATR | Liatris | 30–61 | – | ||
| Indian breadroot | PEDIO2 | Pediomelum | 0–61 | – | ||
| scurfpea | PSORA2 | Psoralidium | 30–61 | – | ||
| cutleaf anemone | PUPAM | Pulsatilla patens ssp. multifida | 30–61 | – | ||
| upright prairie coneflower | RACO3 | Ratibida columnifera | 30–61 | – | ||
| compassplant | SILA3 | Silphium laciniatum | 30–61 | – | ||
| goldenrod | SOLID | Solidago | 30–61 | – | ||
| white heath aster | SYER | Symphyotrichum ericoides | 30–61 | – | ||
| purple prairie clover | DAPU5 | Dalea purpurea | 30–61 | – | ||
| American vetch | VIAM | Vicia americana | 30–61 | – | ||
| white sagebrush | ARLU | Artemisia ludoviciana | 30–61 | – | ||
| Nuttall's sensitive-briar | MINU6 | Mimosa nuttallii | 30–61 | – | ||
| purple locoweed | OXLA3 | Oxytropis lambertii | 0–30 | – | ||
| milkvetch | ASTRA | Astragalus | 0–30 | – | ||
| wavyleaf thistle | CIUN | Cirsium undulatum | 0–30 | – | ||
| aromatic aster | SYOB | Symphyotrichum oblongifolium | 0–30 | – | ||
| lacy tansyaster | MAPI | Machaeranthera pinnatifida | 0–30 | – | ||
| western yarrow | ACMIO | Achillea millefolium var. occidentalis | 0–30 | – | ||
| onion | ALLIU | Allium | 0–30 | – | ||
| Cuman ragweed | AMPS | Ambrosia psilostachya | 0–30 | – | ||
| pussytoes | ANTEN | Antennaria | 0–30 | – | ||
| field sagewort | ARCA12 | Artemisia campestris | 0–30 | – | ||
|
Shrub/Vine
|
||||||
| 8 | Shrubs | 151–303 | ||||
| Shrub (>.5m) | 2SHRUB | Shrub (>.5m) | 0–121 | – | ||
| leadplant | AMCA6 | Amorpha canescens | 30–121 | – | ||
| prairie sagewort | ARFR4 | Artemisia frigida | 30–61 | – | ||
| American plum | PRAM | Prunus americana | 0–61 | – | ||
| chokecherry | PRVI | Prunus virginiana | 0–61 | – | ||
| smooth sumac | RHGL | Rhus glabra | 0–61 | – | ||
| rose | ROSA5 | Rosa | 30–61 | – | ||
| snowberry | SYMPH | Symphoricarpos | 30–61 | – | ||
Table 11. Community 2.2 plant community composition
| Group | Common name | Symbol | Scientific name | Annual production (kg/hectare) | Foliar cover (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Grass/Grasslike
|
||||||
| 1 | Mid Warm-Season Grasses | 616–1110 | ||||
| little bluestem | SCSC | Schizachyrium scoparium | 493–986 | – | ||
| sideoats grama | BOCU | Bouteloua curtipendula | 123–493 | – | ||
| plains muhly | MUCU3 | Muhlenbergia cuspidata | 0–74 | – | ||
| prairie dropseed | SPHE | Sporobolus heterolepis | 0–49 | – | ||
| 2 | Cool-Season Bunchgrasses | 123–370 | ||||
| green needlegrass | NAVI4 | Nassella viridula | 49–247 | – | ||
| porcupinegrass | HESP11 | Hesperostipa spartea | 0–197 | – | ||
| needle and thread | HECOC8 | Hesperostipa comata ssp. comata | 0–99 | – | ||
| Canada wildrye | ELCA4 | Elymus canadensis | 0–49 | – | ||
| 3 | Tall Warm-Season Grasses | 25–247 | ||||
| big bluestem | ANGE | Andropogon gerardii | 25–197 | – | ||
| Indiangrass | SONU2 | Sorghastrum nutans | 0–74 | – | ||
| prairie sandreed | CALO | Calamovilfa longifolia | 0–49 | – | ||
| 4 | Wheatgrass | 0–148 | ||||
| western wheatgrass | PASM | Pascopyrum smithii | 0–148 | – | ||
| slender wheatgrass | ELTR7 | Elymus trachycaulus | 0–49 | – | ||
| 5 | Other Native Grasses | 25–173 | ||||
| blue grama | BOGR2 | Bouteloua gracilis | 25–148 | – | ||
| Graminoid (grass or grass-like) | 2GRAM | Graminoid (grass or grass-like) | 0–123 | – | ||
| Scribner's rosette grass | DIOLS | Dichanthelium oligosanthes var. scribnerianum | 0–49 | – | ||
| prairie Junegrass | KOMA | Koeleria macrantha | 0–49 | – | ||
| 6 | Grass-likes | 25–123 | ||||
| sun sedge | CAINH2 | Carex inops ssp. heliophila | 25–123 | – | ||
| Grass-like (not a true grass) | 2GL | Grass-like (not a true grass) | 0–74 | – | ||
| 7 | Non-Native Grasses | 25–296 | ||||
| Kentucky bluegrass | POPR | Poa pratensis | 25–247 | – | ||
| smooth brome | BRIN2 | Bromus inermis | 0–123 | – | ||
| quackgrass | ELRE4 | Elymus repens | 0–74 | – | ||
|
Forb
|
||||||
| 8 | Forbs | 123–370 | ||||
| goldenrod | SOLID | Solidago | 25–74 | – | ||
| white heath aster | SYER | Symphyotrichum ericoides | 25–74 | – | ||
| scurfpea | PSORA2 | Psoralidium | 25–74 | – | ||
| Forb, introduced | 2FI | Forb, introduced | 25–74 | – | ||
| Forb, native | 2FN | Forb, native | 0–74 | – | ||
| white sagebrush | ARLU | Artemisia ludoviciana | 25–74 | – | ||
| western yarrow | ACMIO | Achillea millefolium var. occidentalis | 25–49 | – | ||
| Cuman ragweed | AMPS | Ambrosia psilostachya | 25–49 | – | ||
| blacksamson echinacea | ECAN2 | Echinacea angustifolia | 0–49 | – | ||
| blazing star | LIATR | Liatris | 25–49 | – | ||
| field sagewort | ARCA12 | Artemisia campestris | 0–49 | – | ||
| cutleaf anemone | PUPAM | Pulsatilla patens ssp. multifida | 0–25 | – | ||
| upright prairie coneflower | RACO3 | Ratibida columnifera | 0–25 | – | ||
| compassplant | SILA3 | Silphium laciniatum | 0–25 | – | ||
| American vetch | VIAM | Vicia americana | 0–25 | – | ||
| lacy tansyaster | MAPI | Machaeranthera pinnatifida | 0–25 | – | ||
| Nuttall's sensitive-briar | MINU6 | Mimosa nuttallii | 0–25 | – | ||
| purple locoweed | OXLA3 | Oxytropis lambertii | 0–25 | – | ||
| Indian breadroot | PEDIO2 | Pediomelum | 0–25 | – | ||
| stiff sunflower | HEPA19 | Helianthus pauciflorus | 0–25 | – | ||
| pussytoes | ANTEN | Antennaria | 0–25 | – | ||
| onion | ALLIU | Allium | 0–25 | – | ||
| milkvetch | ASTRA | Astragalus | 0–25 | – | ||
| wavyleaf thistle | CIUN | Cirsium undulatum | 0–25 | – | ||
| purple prairie clover | DAPU5 | Dalea purpurea | 0–25 | – | ||
|
Shrub/Vine
|
||||||
| 9 | Shrubs | 123–247 | ||||
| snowberry | SYMPH | Symphoricarpos | 25–123 | – | ||
| smooth sumac | RHGL | Rhus glabra | 0–74 | – | ||
| rose | ROSA5 | Rosa | 25–49 | – | ||
| Shrub (>.5m) | 2SHRUB | Shrub (>.5m) | 0–49 | – | ||
| leadplant | AMCA6 | Amorpha canescens | 0–49 | – | ||
| prairie sagewort | ARFR4 | Artemisia frigida | 0–49 | – | ||
| American plum | PRAM | Prunus americana | 0–49 | – | ||
| chokecherry | PRVI | Prunus virginiana | 0–25 | – | ||
Table 12. Community 2.3 plant community composition
| Group | Common name | Symbol | Scientific name | Annual production (kg/hectare) | Foliar cover (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Grass/Grasslike
|
||||||
| 1 | Mid Warm-Season Grasses | 560–1121 | ||||
| little bluestem | SCSC | Schizachyrium scoparium | 560–1121 | – | ||
| sideoats grama | BOCU | Bouteloua curtipendula | 45–336 | – | ||
| 2 | Cool-season Bunchgrasses | 0–179 | ||||
| green needlegrass | NAVI4 | Nassella viridula | 0–135 | – | ||
| porcupinegrass | HESP11 | Hesperostipa spartea | 0–67 | – | ||
| needle and thread | HECOC8 | Hesperostipa comata ssp. comata | 0–45 | – | ||
| 3 | Tall Warm-Season Grasses | 0–112 | ||||
| big bluestem | ANGE | Andropogon gerardii | 0–112 | – | ||
| 4 | Wheatgrass | 0–157 | ||||
| western wheatgrass | PASM | Pascopyrum smithii | 0–157 | – | ||
| 5 | Other Native Grasses | 45–179 | ||||
| blue grama | BOGR2 | Bouteloua gracilis | 45–179 | – | ||
| Graminoid (grass or grass-like) | 2GRAM | Graminoid (grass or grass-like) | 0–112 | – | ||
| Scribner's rosette grass | DIOLS | Dichanthelium oligosanthes var. scribnerianum | 0–22 | – | ||
| prairie Junegrass | KOMA | Koeleria macrantha | 0–22 | – | ||
| 6 | Grass-likes | 22–157 | ||||
| sun sedge | CAINH2 | Carex inops ssp. heliophila | 22–157 | – | ||
| Grass-like (not a true grass) | 2GL | Grass-like (not a true grass) | 0–112 | – | ||
| 7 | Non-Native Grasses | 112–448 | ||||
| Kentucky bluegrass | POPR | Poa pratensis | 45–448 | – | ||
| quackgrass | ELRE4 | Elymus repens | 0–112 | – | ||
| smooth brome | BRIN2 | Bromus inermis | 0–67 | – | ||
|
Forb
|
||||||
| 8 | Forbs | 112–336 | ||||
| Forb, introduced | 2FI | Forb, introduced | 22–135 | – | ||
| white sagebrush | ARLU | Artemisia ludoviciana | 22–112 | – | ||
| goldenrod | SOLID | Solidago | 22–112 | – | ||
| white heath aster | SYER | Symphyotrichum ericoides | 22–90 | – | ||
| Cuman ragweed | AMPS | Ambrosia psilostachya | 22–90 | – | ||
| western yarrow | ACMIO | Achillea millefolium var. occidentalis | 22–90 | – | ||
| Forb, native | 2FN | Forb, native | 0–67 | – | ||
| field sagewort | ARCA12 | Artemisia campestris | 0–67 | – | ||
| scurfpea | PSORA2 | Psoralidium | 22–67 | – | ||
| pussytoes | ANTEN | Antennaria | 0–22 | – | ||
| onion | ALLIU | Allium | 0–22 | – | ||
| milkvetch | ASTRA | Astragalus | 0–22 | – | ||
| wavyleaf thistle | CIUN | Cirsium undulatum | 0–22 | – | ||
| blacksamson echinacea | ECAN2 | Echinacea angustifolia | 0–22 | – | ||
| blazing star | LIATR | Liatris | 0–22 | – | ||
|
Shrub/Vine
|
||||||
| 9 | Shrubs | 112–224 | ||||
| snowberry | SYMPH | Symphoricarpos | 22–157 | – | ||
| smooth sumac | RHGL | Rhus glabra | 0–90 | – | ||
| prairie sagewort | ARFR4 | Artemisia frigida | 0–67 | – | ||
| American plum | PRAM | Prunus americana | 0–67 | – | ||
| Shrub (>.5m) | 2SHRUB | Shrub (>.5m) | 0–45 | – | ||
| rose | ROSA5 | Rosa | 22–45 | – | ||
Table 13. Community 3.1 plant community composition
| Group | Common name | Symbol | Scientific name | Annual production (kg/hectare) | Foliar cover (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Grass/Grasslike
|
||||||
| 1 | Mid Warm-Season Grasses | 0–280 | ||||
| little bluestem | SCSC | Schizachyrium scoparium | 0–224 | – | ||
| sideoats grama | BOCU | Bouteloua curtipendula | 0–140 | – | ||
| 2 | Cool-Season Bunchgrasses | 0–224 | ||||
| green needlegrass | NAVI4 | Nassella viridula | 0–224 | – | ||
| porcupinegrass | HESP11 | Hesperostipa spartea | 0–140 | – | ||
| needle and thread | HECOC8 | Hesperostipa comata ssp. comata | 0–84 | – | ||
| Canada wildrye | ELCA4 | Elymus canadensis | 0–56 | – | ||
| 3 | Tall Warm-Season Grasses | 0–140 | ||||
| big bluestem | ANGE | Andropogon gerardii | 0–140 | – | ||
| 4 | Wheatgrass | 0–196 | ||||
| western wheatgrass | PASM | Pascopyrum smithii | 0–196 | – | ||
| slender wheatgrass | ELTR7 | Elymus trachycaulus | 0–84 | – | ||
| 5 | Other Native Grasses | 0–140 | ||||
| Graminoid (grass or grass-like) | 2GRAM | Graminoid (grass or grass-like) | 0–140 | – | ||
| blue grama | BOGR2 | Bouteloua gracilis | 0–112 | – | ||
| Scribner's rosette grass | DIOLS | Dichanthelium oligosanthes var. scribnerianum | 0–28 | – | ||
| prairie Junegrass | KOMA | Koeleria macrantha | 0–28 | – | ||
| 6 | Grass-likes | 28–140 | ||||
| sun sedge | CAINH2 | Carex inops ssp. heliophila | 28–140 | – | ||
| Grass-like (not a true grass) | 2GL | Grass-like (not a true grass) | 0–84 | – | ||
| 7 | Non-Native Grasses | 841–1681 | ||||
| Kentucky bluegrass | POPR | Poa pratensis | 420–1541 | – | ||
| smooth brome | BRIN2 | Bromus inermis | 140–981 | – | ||
| quackgrass | ELRE4 | Elymus repens | 0–168 | – | ||
|
Forb
|
||||||
| 8 | Forbs | 140–420 | ||||
| Forb, introduced | 2FI | Forb, introduced | 28–280 | – | ||
| white sagebrush | ARLU | Artemisia ludoviciana | 28–168 | – | ||
| goldenrod | SOLID | Solidago | 28–168 | – | ||
| white heath aster | SYER | Symphyotrichum ericoides | 28–112 | – | ||
| Cuman ragweed | AMPS | Ambrosia psilostachya | 28–112 | – | ||
| scurfpea | PSORA2 | Psoralidium | 28–112 | – | ||
| Forb, native | 2FN | Forb, native | 0–84 | – | ||
| western yarrow | ACMIO | Achillea millefolium var. occidentalis | 0–56 | – | ||
| pussytoes | ANTEN | Antennaria | 0–28 | – | ||
| field sagewort | ARCA12 | Artemisia campestris | 0–28 | – | ||
| American vetch | VIAM | Vicia americana | 0–28 | – | ||
| blazing star | LIATR | Liatris | 0–28 | – | ||
|
Shrub/Vine
|
||||||
| 9 | Shrubs | 140–420 | ||||
| snowberry | SYMPH | Symphoricarpos | 140–420 | – | ||
| smooth sumac | RHGL | Rhus glabra | 0–280 | – | ||
| American plum | PRAM | Prunus americana | 0–140 | – | ||
| chokecherry | PRVI | Prunus virginiana | 0–56 | – | ||
| rose | ROSA5 | Rosa | 0–56 | – | ||
| Shrub (>.5m) | 2SHRUB | Shrub (>.5m) | 0–56 | – | ||
| prairie sagewort | ARFR4 | Artemisia frigida | 0–28 | – | ||
Table 14. Community 3.2 plant community composition
| Group | Common name | Symbol | Scientific name | Annual production (kg/hectare) | Foliar cover (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Grass/Grasslike
|
||||||
| 1 | Mid Warm-Season Grasses | 18–215 | ||||
| little bluestem | SCSC | Schizachyrium scoparium | 18–215 | – | ||
| sideoats grama | BOCU | Bouteloua curtipendula | 0–54 | – | ||
| 2 | Cool-Season Bunchgrasses | 0–54 | ||||
| green needlegrass | NAVI4 | Nassella viridula | 0–54 | – | ||
| needle and thread | HECOC8 | Hesperostipa comata ssp. comata | 0–36 | – | ||
| 3 | Tall Warm-Season Grasses | 0–54 | ||||
| big bluestem | ANGE | Andropogon gerardii | 0–54 | – | ||
| 4 | Wheatgrass | 0–36 | ||||
| western wheatgrass | PASM | Pascopyrum smithii | 0–36 | – | ||
| 5 | Other Native Grasses | 0–90 | ||||
| blue grama | BOGR2 | Bouteloua gracilis | 0–90 | – | ||
| Graminoid (grass or grass-like) | 2GRAM | Graminoid (grass or grass-like) | 0–54 | – | ||
| Scribner's rosette grass | DIOLS | Dichanthelium oligosanthes var. scribnerianum | 0–18 | – | ||
| prairie Junegrass | KOMA | Koeleria macrantha | 0–18 | – | ||
| 6 | Grass-likes | 36–179 | ||||
| sun sedge | CAINH2 | Carex inops ssp. heliophila | 18–126 | – | ||
| Grass-like (not a true grass) | 2GL | Grass-like (not a true grass) | 18–108 | – | ||
| 7 | Non-Native Grasses | 628–1255 | ||||
| Kentucky bluegrass | POPR | Poa pratensis | 359–1076 | – | ||
| quackgrass | ELRE4 | Elymus repens | 90–538 | – | ||
| smooth brome | BRIN2 | Bromus inermis | 0–90 | – | ||
|
Forb
|
||||||
| 8 | Forbs | 90–269 | ||||
| goldenrod | SOLID | Solidago | 18–108 | – | ||
| Forb, introduced | 2FI | Forb, introduced | 18–108 | – | ||
| white sagebrush | ARLU | Artemisia ludoviciana | 18–108 | – | ||
| western yarrow | ACMIO | Achillea millefolium var. occidentalis | 18–72 | – | ||
| Cuman ragweed | AMPS | Ambrosia psilostachya | 18–72 | – | ||
| white heath aster | SYER | Symphyotrichum ericoides | 18–72 | – | ||
| scurfpea | PSORA2 | Psoralidium | 18–54 | – | ||
| Forb, native | 2FN | Forb, native | 0–36 | – | ||
| pussytoes | ANTEN | Antennaria | 0–36 | – | ||
| field sagewort | ARCA12 | Artemisia campestris | 0–36 | – | ||
|
Shrub/Vine
|
||||||
| 9 | Shrubs | 36–179 | ||||
| snowberry | SYMPH | Symphoricarpos | 18–108 | – | ||
| smooth sumac | RHGL | Rhus glabra | 0–72 | – | ||
| prairie sagewort | ARFR4 | Artemisia frigida | 18–72 | – | ||
| Shrub (>.5m) | 2SHRUB | Shrub (>.5m) | 0–36 | – | ||
| American plum | PRAM | Prunus americana | 0–18 | – | ||
| rose | ROSA5 | Rosa | 0–18 | – | ||
Interpretations
Animal community
Animal Community – Grazing Interpretations
The following table lists annual, suggested initial stocking rates with average growing conditions. These are conservative estimates that should be used only as guidelines in the initial stages of conservation planning. Often, the current plant composition does not entirely match any particular plant community (as described in this ecological site description). Because of this a resource inventory is necessary to document plant composition and production. More accurate carrying capacity estimates should eventually be calculated using the following stocking rate information along with animal preference data and actual stocking records, particularly when grazers other than cattle are involved. With consultation of the land manager, more intensive grazing management may result in improved harvest efficiencies and increased carrying capacity.
Bluestem/Needlegrass/Sideoats Grama (1.1 & 2.1)
Average Annual Production (lbs./acre, air-dry): 2700
Stocking Rate* (AUM/acre): 0.74
Little Bluestem/Grama/Needlegrass/Bluegrass (2.2)
Average Annual Production (lbs./acre, air-dry): 2200
Stocking Rate* (AUM/acre): 0.60
Little Bluestem/Bluegrass (2.3)
Average Annual Production (lbs./acre, air-dry): 2000
Stocking Rate* (AUM/acre): 0.55
Kentucky Bluegrass/Smooth Bromegrass/Forbs/Shrubs (3.1)
Average Annual Production (lbs./acre, air-dry): 2500
Stocking Rate* (AUM/acre): 0.69
Kentucky Bluegrass/Quackgrass/Little Bluestem (3.2)
Average Annual Production (lbs./acre, air-dry): 1600
Stocking Rate* (AUM/acre): 0.44
Annual/Pioneer, Non-Native Perennial (3.3)
Average Annual Production (lbs./acre, air-dry): 1000
Stocking Rate* (AUM/acre): 0.27
* Based on 912 lbs./acre (air-dry weight) per Animal Unit Month (AUM), and on 25% harvest efficiency (refer to USDA NRCS, National Range and Pasture Handbook).
Grazing by domestic livestock is one of the major income-producing industries in the area. Rangeland in this area may provide yearlong forage. During the dormant period, the forage for livestock will likely be lacking protein to meet livestock requirements, and added protein will allow ruminants to better utilize the energy stored in grazed plant materials. A forage quality test (either directly or through fecal sampling) should be used to determine the level of supplementation needed.
Hydrological functions
Water is the principal factor limiting forage production on this site. This site is dominated by soils in hydrologic group D. Infiltration is typically moderate to moderately slow and runoff potential for this site varies from medium to high depending on soil hydrologic group, slope and ground cover. In many cases, areas with greater than 75% ground cover have the greatest potential for high infiltration and lower runoff. An example of an exception would be where shortgrasses form a strong sod and dominate the site. Dominance by blue grama, bluegrass, and/or smooth bromegrass will result in reduced infiltration and increased runoff. Areas where ground cover is less than 50% have the greatest potential to have reduced infiltration and higher runoff (refer to Section 4, NRCS National Engineering Handbook for runoff quantities and hydrologic curves).
Recreational uses
This site provides hunting, hiking, photography, bird watching and other opportunities. The wide variety of plants that bloom from spring until fall have an esthetic value that appeals to visitors.
Wood products
No appreciable wood products are typically present on this site.
Other products
Seed harvest of native plant species can provide additional income on this site.
Supporting information
Inventory data references
There is no NRCS clipping data and other inventory currently available for this site. Information presented here has been derived using field observations from range-trained personnel. Those involved in developing this site include: Stan Boltz, Range Management Specialist, NRCS; and Bruce Kunze, Soil Scientist, NRCS.
Other references
Cleland, D.T., J.A. Freeouf, J.E. Keys, G.J. Nowacki, C. Carpenter, and W.H. McNab. 2007. Ecological Subregions: Sections and Subsections of the Coterminous United States. USDA Forest Service, General Technical Report WO-76. Washington, DC. 92 pps.
Gilbert, M. C., Whited, P. M., Clairain Jr, E. J., & Smith, R. D. (2006). A Regional Guidebook for Applying the Hydrogeomorphic Approach to Assessing Wetland Functions of Prairie Potholes. Washington DC.
Samson, F. B., & Knopf, F. L. (1996). Prairie Conservation Preserving North America's Most Endagered Ecosystem. Washington D.C.: Island Press.
Soil Survey Staff, Natural Resources Conservation Service, United States Department of Agriculture. Official Soil Series Descriptions. Available online. Accessed March 2018.
United States Department of Agriculture – Natural Resource Conservation Service (USDA-NRCS). 2003. National Range and Pasture Handbook, Revision 1. Grazing Lands Technology Institute. 214 pps.
United States Department of Agriculture – Natural Resource Conservation Service (USDA-NRCS). 2006. Land Resource Regions and Major Land Resource Areas of the United States, the Caribbean, and the Pacific Basin. U.S. Department of Agriculture Handbook 296. 672pps.
USDA, NRCS. National Soil Information System, Information Technology Center, 2150 Centre Avenue, Building A, Fort Collins, CO 80526. (http://soils.usda.gov/technical/nasis/)
USDA, NRCS. 2018. The PLANTS Database (http://plants.usda.gov, 27 March 2018). National Plant Data Team, Greensboro, NC 27401-4901 USA.
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency [EPA]. 2013. Level III and Level IV Ecoregions of the Continental United States. Corvallis, OR, U.S. EPA, National Health and Environmental Effects Research Laboratory, map scale 1:3,000,000. Available at http://www.epa.gov/eco-research/level-iii-and-iv-ecoregions- continental-united-states. (Accessed 1 March 2018).
Contributors
Lance Howe
Steve Winter
Approval
Suzanne Mayne-Kinney, 8/20/2024
Acknowledgments
Contact for Lead Authors: Natural Resources Conservation Service (USDA-NRCS), Redfield Soil Survey Office Redfield, SD; Lance Howe (Lance.Howe@usda.gov), Soil Survey Office Leader, USDA-NRCS, Redfield, SD; and Steve Winter (Steven.Winter@usda.gov), Soil Scientist, USDA-NRCS, Redfield, SD
Additional Information Acknowledgment: Jason Hermann (Jason.Hermann@usda.gov), Area Rangeland Management Specialist, USDA-NRCS, Redfield, SD.
Rangeland health reference sheet
Interpreting Indicators of Rangeland Health is a qualitative assessment protocol used to determine ecosystem condition based on benchmark characteristics described in the Reference Sheet. A suite of 17 (or more) indicators are typically considered in an assessment. The ecological site(s) representative of an assessment location must be known prior to applying the protocol and must be verified based on soils and climate. Current plant community cannot be used to identify the ecological site.
| Author(s)/participant(s) | |
|---|---|
| Contact for lead author | |
| Date | 04/24/2025 |
| Approved by | Suzanne Mayne-Kinney |
| Approval date | |
| Composition (Indicators 10 and 12) based on | Annual Production |
Indicators
-
Number and extent of rills:
-
Presence of water flow patterns:
-
Number and height of erosional pedestals or terracettes:
-
Bare ground from Ecological Site Description or other studies (rock, litter, lichen, moss, plant canopy are not bare ground):
-
Number of gullies and erosion associated with gullies:
-
Extent of wind scoured, blowouts and/or depositional areas:
-
Amount of litter movement (describe size and distance expected to travel):
-
Soil surface (top few mm) resistance to erosion (stability values are averages - most sites will show a range of values):
-
Soil surface structure and SOM content (include type of structure and A-horizon color and thickness):
-
Effect of community phase composition (relative proportion of different functional groups) and spatial distribution on infiltration and runoff:
-
Presence and thickness of compaction layer (usually none; describe soil profile features which may be mistaken for compaction on this site):
-
Functional/Structural Groups (list in order of descending dominance by above-ground annual-production or live foliar cover using symbols: >>, >, = to indicate much greater than, greater than, and equal to):
Dominant:
Sub-dominant:
Other:
Additional:
-
Amount of plant mortality and decadence (include which functional groups are expected to show mortality or decadence):
-
Average percent litter cover (%) and depth ( in):
-
Expected annual annual-production (this is TOTAL above-ground annual-production, not just forage annual-production):
-
Potential invasive (including noxious) species (native and non-native). List species which BOTH characterize degraded states and have the potential to become a dominant or co-dominant species on the ecological site if their future establishment and growth is not actively controlled by management interventions. Species that become dominant for only one to several years (e.g., short-term response to drought or wildfire) are not invasive plants. Note that unlike other indicators, we are describing what is NOT expected in the reference state for the ecological site:
-
Perennial plant reproductive capability:
Print Options
Sections
Font
Other
The Ecosystem Dynamics Interpretive Tool is an information system framework developed by the USDA-ARS Jornada Experimental Range, USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service, and New Mexico State University.
Click on box and path labels to scroll to the respective text.
Ecosystem states
| T1 | - | Heavy continuous grazing, no use, no fire, invasion |
|---|---|---|
| T2A | - | No use, no fire, heavy continuous grazing |
| R3 | - | Long term prescribed grazing, prescribed burning |
State 1 submodel, plant communities
| 1.1A | - | Heavy continuous grazing |
|---|---|---|
| 1.2A | - | Prescribed grazing with recovery periods, prescribed burning |
State 2 submodel, plant communities
| 2.1A | - | Heavy continuous grazing |
|---|---|---|
| 2.2B | - | Prescribed grazing with recovery periods, prescribed burning |
| 2.2A | - | Heavy continuous grazing |
| 2.3A | - | Prescribed grazing with recovery periods, prescribed burning |
State 3 submodel, plant communities
| 3.1A | - | Heavy continuous grazing |
|---|---|---|
| 3.2A | - | Prescribed grazing with recovery periods |
| 3.3A | - | Time w/wo disturbances |