Natural Resources
Conservation Service
Ecological site R010XC029OR
SR Shallow Cool 12-16 PZ
Last updated: 3/11/2025
Accessed: 04/02/2025
General information
Provisional. A provisional ecological site description has undergone quality control and quality assurance review. It contains a working state and transition model and enough information to identify the ecological site.
MLRA notes
Major Land Resource Area (MLRA): 010X–Central Rocky and Blue Mountain Foothills
This MLRA is characterized by gently rolling to steep hills, plateaus, and low mountains at the foothills of the Blue Mountains in Oregon and the Central Rocky Mountains in Idaho. The geology of this area is highly varied and ranges from Holocene volcanics to Cretaceous sedimentary rocks. Mollisols are the dominant soil order and the soil climate is typified by mesic or frigid soil temperature regimes, and xeric or aridic soil moisture regimes. Elevation ranges from 1,300 to 6,600 feet (395 to 2,010 meters), increasing from west to east. The climate is characterized by dry summers and snow dominated winters with precipitation averaging 8 to 16 inches (205 to 405 millimeters) and increasing from west to east. These factors support plant communities with shrub-grass associations with considerable acreage of sagebrush grassland. Big sagebrush, bluebunch wheatgrass, and Idaho fescue are the dominant species. Stiff sagebrush, low sagebrush, and Sandberg bluegrass are often dominant on sites with shallow restrictive layers. Western juniper is one of the few common tree species and since European settlement has greatly expanded its extent in Oregon. Nearly half of the MLRA is federally owned and managed by the Bureau of Land Management. Most of the area is used for livestock grazing with areas accessible by irrigation often used for irrigated agriculture.
Ecological site concept
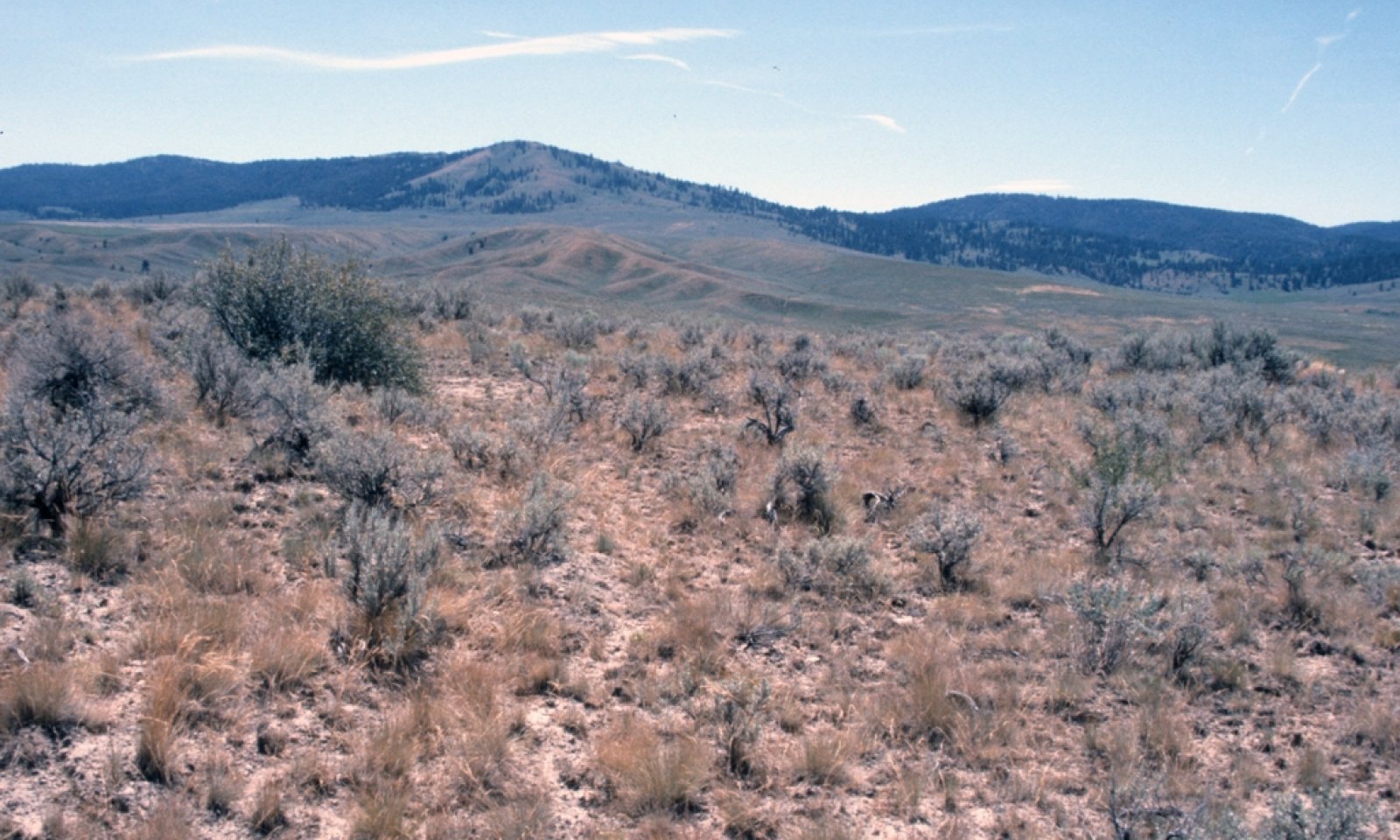
The potential native plant community is dominated by Idaho fescue and a complex of mountain, xeric and basin big sagebrush. Bluebunch wheatgrass and Sandberg bluegrass are common along with a variety of forbs. Thurber’s needlegrass, wild crab apple, and antelope bitterbrush occur sporadically. Vegetative composition of the community is approximately 70 percent grasses, 10 percent forbs and 20 percent shrubs. Approximate ground cover is 70 to 80 percent (basal and crown).
The soils of this site are shallow over bedrock or duripan. The surface layer is typically very cobbly to stony and the subsoil is very cobbly silty clay loam to stony clay loam over an extremely cobbly clay.
Idaho fescue increases on silt loam surfaces and at higher elevations. Bluebunch wheatgrass increases at lower elevations and on slight south and west exposures. Mountain big sagebrush increases in relationship to xeric and basin big sagebrush with elevation. Wyoming big sagebrush increases at lower elevation and on shallower soils. Thurber’s needlegrass increases on coarse surfaces. Antelope bitterbrush and wild crab apple increase over fractured substratums. Production increases with soil depth and precipitation.
Associated sites
| R010XC047OR |
SR Mountain South 12-16 PZ SR Mountain South 12-16 PZ (greater soil depth, south aspect, higher production, different composition – higher proportion of PSSPS) |
|---|---|
| R010XC054OR |
SR Mountain Shallow South 12-16 PZ SR Mountain Shallow South 12-16 PZ (south aspect, different composition – higher proportion of PSSPS) |
| R010XC068OR |
SR Cool Mountain North 12-16 PZ SR Cool Mountain North 12-16 PZ (greater soil depth, north aspect, higher production) |
| R010XC075OR |
SR Mountain Shallow North 12-16 PZ SR Mountain Shallow North 12-16 PZ (north aspect, different composition – higher proportion of ARTRV and FEID) |
| R010XC033OR |
SR Cool 12-16 PZ SR Cool 12-16 PZ (greater soil depth, higher production) |
| R010XC039OR |
SR Very Shallow 12-16 PZ SR Very Shallow 12-16 PZ (very shallow soil depth, lower production, different composition – ARRI2/POSE association) |
| R010XC041OR |
SR Very Shallow Rockland 12-16 PZ SR Very Shallow Rockland 12-16 PZ (very shallow soil depth with areas of exposed bedrock, lower production, different composition – ACTH7-POSE/ERIOG association) |
| R010XC042OR |
SR Juniper Tableland 12-16 PZ SR Juniper Tableland 12-16 PZ (very shallow soil depth, lower production, fractured substratum, different composition – JUOC/ARRI2/POSE association) |
Similar sites
| R010XC033OR |
SR Cool 12-16 PZ SR Cool 12-16 PZ (greater soil depth, higher production) |
|---|---|
| R010XC075OR |
SR Mountain Shallow North 12-16 PZ SR Mountain Shallow North 12-16 PZ (north aspect, different composition – higher proportion of ARTRV and FEID) |
| R010XC032OR |
SR Mountain 12-16 PZ SR Mountain 12-16 PZ (higher elevation, greater soil depth, higher production, different composition – ARTRV and FEID strongly dominant) |
| R010XC037OR |
SR Mountain Shallow 12-16 PZ SR Mountain Shallow 12-16 PZ (higher elevation, different composition – ARTRV and FEID strongly dominant) |
Table 1. Dominant plant species
| Tree |
Not specified |
|---|---|
| Shrub |
(1) Artemisia tridentata ssp. vaseyana |
| Herbaceous |
(1) Festuca idahoensis |
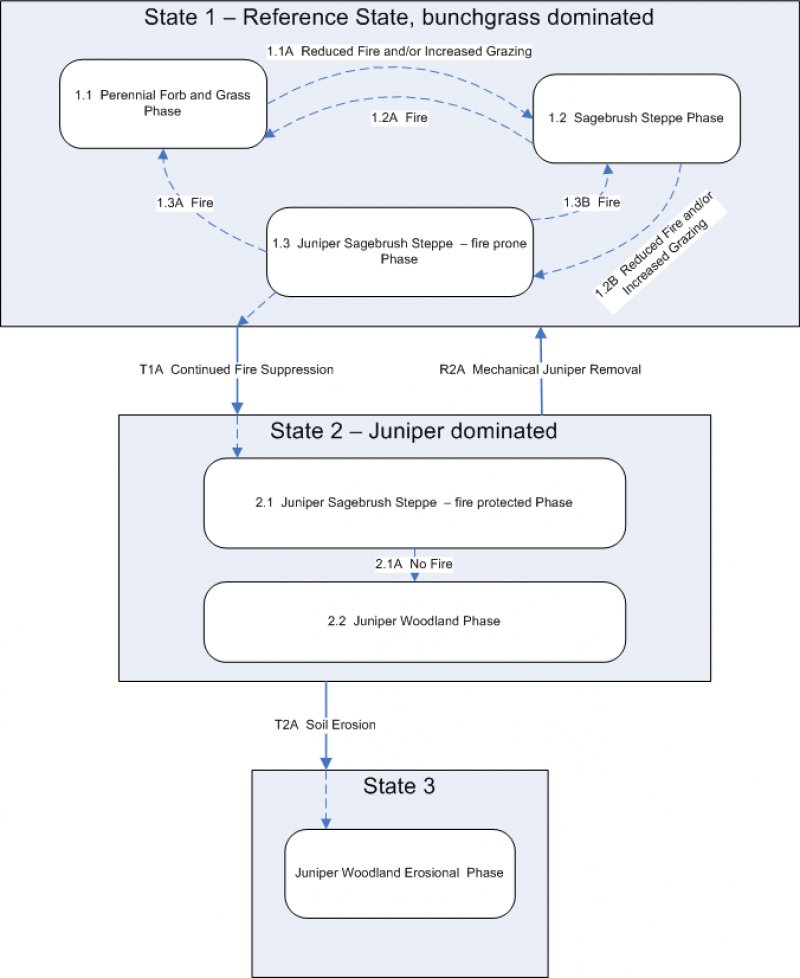
Click on box and path labels to scroll to the respective text.
Ecosystem states
| T1A | - | Continued Fire Suppression |
|---|---|---|
| R2A | - | Mechanical Juniper Removal |
| T2A | - | Soil Erosion |
State 1 submodel, plant communities
| 1.1A | - | Reduced fire and increased grazing |
|---|---|---|
| 1.2A | - | Fire |
| 1.2B | - | Reduced fire and increased grazing |
| 1.3A | - | Fire |
| 1.3B | - | Fire |
State 2 submodel, plant communities
| 2.1A | - | No Fire |
|---|