

Natural Resources
Conservation Service
Ecological site R054XY046ND
Limy Residual
Last updated: 3/31/2025
Accessed: 02/28/2026
General information
Provisional. A provisional ecological site description has undergone quality control and quality assurance review. It contains a working state and transition model and enough information to identify the ecological site.
MLRA notes
Major Land Resource Area (MLRA): 054X–Rolling Soft Shale Plain
MLRA 54 covers 29,280 square miles and encompasses approximately 18.7 million acres. MLRA 54 spans three states with 64 percent of it in North Dakota, 33 percent in South Dakota, and 3 percent in Montana. Most of MLRA 54 is underlain by soft, calcareous shale, siltstone, and sandstone of the Tertiary Fort Union Group and the Cretaceous Fox Hills and Hell Creek Formations. Most of the soils in MLRA 54 developed from residuum weathered in place including colluvial and alluvial deposits from residuum. Along the eastern and northern edges of the MLRA where MLRA 54 transitions into the glaciated Missouri plateau, remnants of glacial till parent materials remain on the high areas of the landscape. The MLRA 54 landscape is characterized by moderately dissected rolling plains with areas of local badlands, hills, and isolated buttes. Elevation is 1,650 feet (505 meters) on the eastern side of the MLRA with a gradual rise to 3,600 feet (1,100 meters) on the western side. The Missouri River runs along the north and east side of MLRA 54. Most of the Standing Rock Indian Reservation, the northwest third of the Cheyenne River Indian Reservation, and the Grand River National Grasslands are in the southern part of the MLRA. Most of the Standing Rock Indian Reservation, the northwest third of the Cheyenne River Indian Reservation, and the Grand River National Grasslands are in the southern part of the MLRA.
Classification relationships
Level IV Ecoregions of the Conterminous United States: 43a – Missouri Plateau; 43c – River Breaks; 43j – Moreau Prairie.
Ecological site concept
The Limy Residual site is located on sedimentary plains; it occurs on hillslopes, pediments, and alluvial fans. When associated with hillslopes, this ecological site occurs on shoulders, backslopes and footslopes. When associated with alluvial fans, these areas are on relatively stable landforms. Soils are moderately deep to very deep (siltstone or mudstone may be as shallow as 20 inches). The soils are silty or loamy throughout (soil forms a ribbon 1 to 2 inches long) with calcium carbonates occurring within 8 inches of soil surface. Slopes range from 0 to 45 percent. On landscape, Shallow Loamy, Thin Loamy, and Very Shallow ecological sites occur higher than the Limy Residual site while Loamy Terrace sites occur lower. Loamy sites can occur on similar landscape positions as Limy Residual sites. Loamy sites are deeper than 8 inches to carbonates. Also, in the Killdeer Mountains, the Upland Hardwood Forest ecological site is associated with the Limy Residual site.
To see a full copy of the ecological site description with all tables and the full version 5 rangeland health worksheet. Please use the following hyperlink:
https://efotg.sc.egov.usda.gov/references/public/ND/54_Limy_Residual_Narrative_FINAL_Ref_FSG.pdf
Associated sites
| R054XY030ND |
Shallow Loamy This site is up-slope from the Limy Residual ecological site on hillslope landforms. The soils have soft, sedimentary bedrock at a depth of 10 to 20 inches; this bedrock affects root growth. |
|---|---|
| R054XY031ND |
Loamy This site occurs on similar landscape positions as the Limy Residual ecological site. The soils are deeper than 8 inches to carbonates and have a mollic epipedon. Production on the Loamy ecological site is higher than on the Limy Residual site. |
| R054XY035ND |
Very Shallow This site occurs higher on the landscape than the Limy Residual ecological site. The soils are either <10 inches to soft, sedimentary bedrock or are <20 inches to porcelanite (Brandenburg soils). Root growth and available water capacity are affected. |
| R054XY038ND |
Thin Loamy This site occurs on higher, convex ridges, knolls, and summits where the sedimentary bedrock is thinly capped with glacial till. The soil is highly calcareous and forms a ribbon 1 to 2 inches long. Depth to sedimentary bedrock is >20 inches. |
| R054XY041ND |
Loamy Terrace This site occurs on terraces along rivers and streams; flooding is very rare to occasional. Where occasional flooding occurs, the vegetation is not significantly influenced by additional water. The soils are very deep and well drained. These landforms received periodic deposition from previous flooding events, so carbonates may be present at or near the surface. The soil is commonly stratified; the soil material forms a ribbon 1 to 2 inches long. |
| F054XY046ND |
Upland Hardwood Forest This site is on similar landscape positions as the Limy Residual ecological site; it occurs on limestone capped buttes (Killdeer Mountains). The soil has forest vegetation. |
Similar sites
| R054XY031ND |
Loamy This site occurs on similar landscape positions as the Limy Residual ecological site. The soils are deeper than 8 inches to carbonates and have a mollic epipedon. Production on the Loamy ecological site is higher than on the Limy Residual site. |
|---|---|
| R054XY038ND |
Thin Loamy This site occurs on higher, convex ridges, knolls, and summits where the sedimentary bedrock is thinly capped with glacial till. The soil is highly calcareous and forms a ribbon 1 to 2 inches long. Depth to sedimentary bedrock is >20 inches. |
| R054XY047ND |
Badland Fan This site is on alluvial fans at the base of badland escarpments. These soils developed in stratified layers of slope alluvium eroding from the adjacent sparsely vegetated, exposed, soft sedimentary bedrock. The Badlands Fan ecological site is less stable and has more bare ground with less production than the Limy Residual site. |
Table 1. Dominant plant species
| Tree |
Not specified |
|---|---|
| Shrub |
Not specified |
| Herbaceous |
(1) Pascopyrum smithii |
Physiographic features
This site occurs on nearly level to very steep sedimentary plains; it occurs on hillslopes, pediments and alluvial flats. Parent materials are residuum or alluvium from residuum. Slope ranges from 0 to 45 percent.
Table 2. Representative physiographic features
| Landforms |
(1)
Hillslope
(2) Pediment (3) Alluvial fan |
|---|---|
| Runoff class | Low to high |
| Flooding frequency | None |
| Ponding frequency | None |
| Elevation | 1,650 – 3,600 ft |
| Slope | 45% |
| Water table depth | 60 – 80 in |
| Aspect | Aspect is not a significant factor |
Climatic features
MLRA 54 is considered to have a continental climate with cold winters and hot summers, low humidity, light rainfall, and much sunshine. Extremes in temperature are common and characteristic of the MLRA. The continental climate is the result of this MLRA’s location in the geographic center of North America. There are few natural barriers on the northern Great Plains, so air masses move unobstructed across the plains and account for rapid changes in temperature.
Annual precipitation ranges from 14 to 18 inches per year. The normal average annual temperature is about 42° F. January is the coldest month with average temperatures ranging from about 13° F (Beach, ND) to about 16° F (Bison, SD). July is the warmest month with temperatures averaging from about 69° F (Beach, ND) to about 72° F (Timber Lake, SD). The range of normal average monthly temperatures between the coldest and warmest months is about 57° F. This large temperature range attests to the continental nature of MLRA 54’s climate. Wind speeds average about 11 miles per hour, ranging from about 13 miles per hour during the spring to about 10 miles per hour during the summer. Daytime wind speeds are generally stronger than nighttime wind speeds, and occasional strong storms may bring brief periods of high winds with gusts to more than 50 miles per hour.
Growth of native cool-season plants begins in late March and continues through early to mid-July. Native warm-season plants begin growth in mid-May and continue to the end of August. Greening up of cool-season plants can occur again in September and October when adequate soil moisture is present.
Table 3. Representative climatic features
| Frost-free period (characteristic range) | 95-111 days |
|---|---|
| Freeze-free period (characteristic range) | 118-127 days |
| Precipitation total (characteristic range) | 15-18 in |
| Frost-free period (actual range) | 91-114 days |
| Freeze-free period (actual range) | 116-129 days |
| Precipitation total (actual range) | 15-18 in |
| Frost-free period (average) | 101 days |
| Freeze-free period (average) | 123 days |
| Precipitation total (average) | 16 in |
Figure 1. Monthly precipitation range
Figure 2. Monthly minimum temperature range
Figure 3. Monthly maximum temperature range
Figure 4. Monthly average minimum and maximum temperature
Figure 5. Annual precipitation pattern
Figure 6. Annual average temperature pattern
Climate stations used
-
(1) FT YATES 4 SW [USC00323207], Fort Yates, ND
-
(2) HETTINGER [USC00324178], Hettinger, ND
-
(3) DUPREE [USC00392429], Dupree, SD
-
(4) WATFORD CITY [USC00329233], Watford City, ND
-
(5) MANDAN EXP STN [USC00325479], Mandan, ND
-
(6) LUDLOW 3 SSE [USC00395048], Ludlow, SD
-
(7) HEBRON [USC00324102], Hebron, ND
Influencing water features
No significant water features influence this site. A seasonal ground water table is typically deeper than 5 feet throughout the growing season. Soils occurring on fans may receive some run-on water from adjacent uplands, but this does significantly influence the plant community. Permeability is moderately slow to moderate. Water loss is through evapotranspiration and percolation below the root zone.
Salinization Risk – The potential salinization of the site can occur in any of the vegetative states; however, it is most prevalent in the State 4.0 Go-Back. Removal of perennial vegetation (e.g., annual cropping), above this ecological site (recharge area), results in increased water moving down through the soil profile. This downward water movement leaches salts over time creating shallow saline groundwater immediately above a less permeable layer. Due to gravity, water moves downward through the soil profile then laterally through a porous layer, such as a coal or sand/gravel seam, transporting salts to the discharge area. Below the porous layer, is a less permeable layer such as soft sedimentary bedrock. Where shallow saline groundwater occurs, salts often concentrate at or near the soil surface through capillary rise (discharge area). In capillary rise, water moves from where the soil is saturated, or nearly so, to drier soil against the force of gravity. Evaporation at the soil surface dries the soil and “pulls” water by capillary flow from the wet soil zone. Because only pure water evaporates, salts are left behind.
Figure 7. Increased salinity levels will make establishment of grasses and forbs more difficult. Treatment of the recharge area is a requirement to reclaim these soils from salinization. Some salinized soils can be excessively wet making establishment of saline tolerant vegetation difficult.

Figure 7.
Soil features
Soils associated with the Limy Residual ES are in the Mollisol and Inceptisol orders. The Mollisols are classified further as Typic Calciustolls. The Inceptisols are classified further as Typic Haplustepts and Calcic Haplustepts. These soils were developed under prairie vegetation. They formed in calcareous, medium- textured residuum (typically siltstone) or slope alluvium eroding from the adjacent uplands. The soils on this site are moderately deep (>20 inches to soft, sedimentary bedrock) to very deep. The sedimentary beds affect root growth. The soils are well drained. Textural family classes are mostly fine silty but fine-loamy may also occur.
This ecological site occurs on two primary landforms: hillslopes and alluvial fans. The residual soils developed on the shoulders, back slopes, and foot slopes of gently sloping to moderately steep hillslopes and pediments. The alluvial soils formed in slope alluvium on relatively stable linear fans. These fans are well vegetated since deposition and erosion are occurring at relatively slower rates than the actively eroding depositional fans (Badlands Fan ecological site) directly adjacent to very steep, soft sedimentary bedrock, (e.g., Badlands). Thin, stratified layers may be evident in the parent material on the fan landform.
Characteristics common to the soil in this site are a dark grayish brown to yellowish brown surface layer (4 to 8 inches thick). Silt loam is the predominant texture above the sedimentary beds, but loam or silty clay loam also occur. The soil forms a ribbon 1 to 2 inches long. Depth to calcium carbonates is <8 inches; typically, the soil effervesces throughout.
Soil reaction typically is neutral to moderately alkaline (pH 6.6 to 8.4) in the surface layer and slightly alkaline to moderately alkaline (pH 7.4 to 8.4) in the subsoil. Salinity is generally none to very slight (E.C. 0 to 4 dS/m); however, in some soils it is slight (E.C. 4 to 8 dS/m) in the substratum. Sodicity is generally low (SAR <5); however, in some soils, the SAR is as high as 10 in the lower subsoil and substratum. Calcium carbonate content typically ranges from 5 to 40 percent. Some soils in native grassland have <5% CaCO3 in the surface few inches.
These soils are particularly susceptible to water and wind erosion. The hazard of water and wind erosion increases where vegetative cover is sparse or non-existent. Loss of the soil surface layer results in a shift in species composition and production.
The major soil series which characterize the Limy Residual ecological site are Chama, Cherry, Lantry, and Maschetah.
Access Web Soil Survey (https://websoilsurvey.sc.egov.usda.gov/App/WebSoilSurvey.aspx) for specific local soils information.
Table 4. Representative soil features
| Parent material |
(1)
Residuum
(2) Slope alluvium (3) Siltstone (4) Mudstone |
|---|---|
| Surface texture |
(1) Loam (2) Silt loam (3) Silty clay loam |
| Family particle size |
(1) Loamy (2) Fine-silty |
| Drainage class | Well drained |
| Permeability class | Moderately slow to moderate |
| Depth to restrictive layer | 20 – 80 in |
| Surface fragment cover <=3" | Not specified |
| Surface fragment cover >3" | 3% |
| Available water capacity (0-40in) |
3.5 – 10 in |
| Calcium carbonate equivalent (0-40in) |
5 – 40% |
| Electrical conductivity (0-40in) |
8 mmhos/cm |
| Sodium adsorption ratio (0-40in) |
10 |
| Soil reaction (1:1 water) (0-40in) |
6.6 – 8.4 |
| Subsurface fragment volume <=3" (0-40in) |
13% |
| Subsurface fragment volume >3" (0-40in) |
3% |
Ecological dynamics
This ecological site description is based on nonequilibrium ecology and resilience theory and utilizes a State and Transition Model (STM) diagram to organize and communicate information about ecosystem change as a basis for management. The ecological dynamics characterized by the STM diagram reflect how changes in ecological drivers, feedback mechanisms, and controlling variables can maintain or induce changes in plant community composition (phases and/or states). The application of various management actions, combined with weather variables, impact the ecological processes which influence the competitive interactions, thereby maintaining or altering plant community structure.
Prior to European influence, the historical disturbance regime for MLRA 54 included frequent fires, both anthropogenic and natural in origin. Most fires, however, were anthropogenic fires set by Native Americans. Native Americans set fires in all months except perhaps January. These fires occurred in two peak periods, one from March-May with the peak in April and another from July-November with the peak occurring in October. Most of these fires were scattered and of small extent and duration. The grazing history would have involved grazing and browsing by large herbivores (such as American bison, elk, and whitetail deer). Herbivory by small mammals, insects, nematodes, and other invertebrates are also important factors influencing the production and composition of the communities. Grazing and fire interaction, particularly when coupled with drought events, influenced the dynamics discussed and displayed in the following state and transition diagram and descriptions.
Following European influence, this ecological site generally has had a history of grazing by domestic livestock, particularly cattle, which along with other related activities (e.g., fencing, water development, fire suppression) has changed the disturbance regime of the site. Changes will occur in the plant communities due to these and other factors.
Weather fluctuations coupled with managerial factors may lead to changes in the plant communities and may, under adverse impacts, result in a slow decline in vegetative vigor and composition. However, under favorable conditions the botanical composition may resemble that prior to European influence.
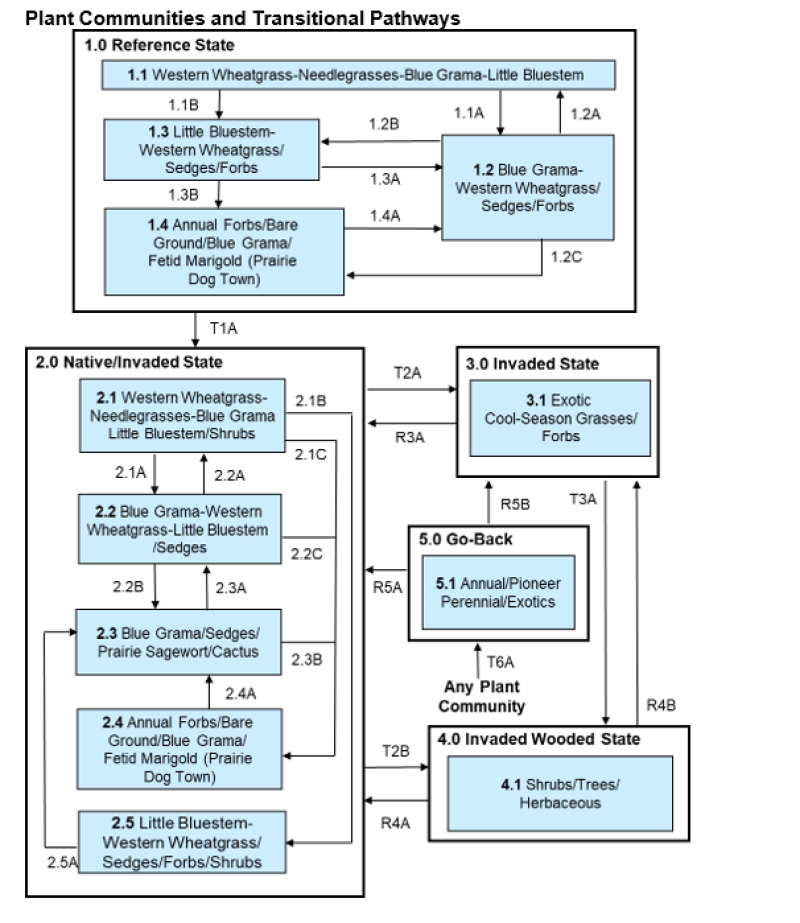
Five vegetative states have been identified for the site (Reference, Native/Invaded, Invaded, Wooded Invaded, and Go-Back). Within each state, one or more community phases have been identified. These community phases are named based on the more dominant and visually conspicuous species; they have been determined by study of historical documents, relict areas, scientific studies, and ecological aspects of plant species and plant communities. Transitional pathways and thresholds have been determined through similar methods.
State 1: Reference State represents the natural range of variability that dominated the dynamics of this ecological site prior to European influence. Dynamics of the state were largely determined by variations in climate and weather (e.g., drought), as well as that of fire (e.g., timing, frequency) and grazing by native herbivores (e.g., frequency, intensity, selectivity). Due to those variations, the Reference State is thought to have shifted temporally and spatially between four community phases.
Currently the primary disturbances include widespread introduction of exotic species, concentrated livestock grazing, lack of fire, and perhaps long-term non-use and no fire. Because of these changes (particularly the widespread occurrence of exotic species), as well as other environmental changes, the Reference State is considered to no longer exist. Thus, the presence of exotic species on the site precludes it from being placed in the Reference State. It must then be placed in one of the other states, commonly State 2: Native/Invaded State (T1A).
State 2: Native/Invaded State. Colonization of the site by exotic species results in a transition from State 1: Reference State to State 2: Native/Invaded State (T1A). This transition was probably inevitable; it often resulted from colonization by exotic cool-season grasses (such as Kentucky bluegrass or smooth brome) which have been particularly and consistently invasive under extended periods of non-use and no fire. Other exotic plants (e.g., Canada thistle, leafy spurge) are also known to invade the site.
Five community phases have been identified for this state; they are similar to the community phases in the Reference State but have now been invaded by exotic cool-season grasses. These exotic cool-season grasses can be expected to increase. As that increase occurs, plants more desirable to wildlife and livestock may decline. A decline in forb diversity can also be expected. Under non-use or minimal use management, mulch increases and may become a physical barrier to plant growth. This changes the micro-climate near the soil surface and may alter infiltration, nutrient cycling, and biological activity near the soil surface. As a result, these factors combined with shading cause desirable native plants to have increasing difficulty remaining viable and recruitment declines.
To slow or limit the invasion of these exotic grasses or other exotic plants, it is imperative that managerial techniques (e.g., prescribed grazing, prescribed burning) be carefully constructed, monitored, and evaluated with respect to that objective. If management does not include measures to control or reduce these exotic plants, the transition to State 3: Invaded State should be expected (T2A). This state may also transition to State 4: Invaded Wooded State during extended periods of no fire (T2B).
State 3: Invaded State. The threshold for this state is reached when the both exotic cool-season grasses (e.g., Kentucky bluegrass, smooth brome) exceed 30% of the plant community and native grasses represent less than 40% of the community. One community phase has been identified for this state.
The exotic cool-season grasses can be quite invasive and often form monotypic stands. As they increase, both forage quantity and quality of the annual production becomes increasingly restricted to late spring and early summer, even though annual production may increase. Forb diversity often declines. Under non-use or minimal use management, mulch can increase and become a physical barrier to plant growth which alters nutrient cycling, infiltration, and soil biological activity. As such, desirable native plants become increasingly displaced.
Once the state is well established, prescribed burning and prescribed grazing techniques have been largely ineffective in suppressing or eliminating the exotic cool-season grasses, even though some short-term reductions may appear successful. However, assuming there is an adequate component of native grasses to respond to treatments, a restoration pathway to State 2: Native/Invaded State may be accomplished with the implementation of long-term prescribed grazing in conjunction with prescribed burning (R3A). This state may also transition to State 4: Invaded Wooded State during extended periods of no fire (T3A).
State 4: Invaded Wooded State. This state is characterized by stands of shrubs (e.g., chokecherry, rose, buffaloberry, western snowberry), along with some green ash. Older stands generally support larger and more abundant green ash. Junipers may also invade the state, particularly in older stands. A marked increase in non-use management and active fire suppression since European influence has enabled this state to become more widespread. One community phase has been identified and often results from extended periods of no fire (T2B, T3A). Prescribed burning or wildfire may lead to State 2: Native/Invaded State (R4A) or State 3: Invaded State R4B) depending upon the abundance of exotic cool-season grasses. However, depending on the abundance of exotic grasses, a range planting may be necessary to complete the restoration to State 2: Native/Invaded State.
State 5: Go-Back State. This state often results following cropland abandonment and consists of only one plant community phase. This weedy assemblage may include noxious weeds that need control. Over time, the exotic cool-season grasses (Kentucky bluegrass or smooth brome) will likely predominate.
Initially, due to extensive bare ground and a preponderance of shallow rooted annual plants the potential for soil erosion is high. Plant species richness may be high, but overall diversity (i.e., equitability) is typically low, with the site dominated by a relatively small assemblage of species. Due to the lack of native perennials and other factors, restoring the site with the associated ecological processes is difficult. However, a successful range planting may result in something approaching State 2: Native/Invaded State (R5A). Following seeding, long-term prescribed grazing and prescribed burning, haying, and the use of herbicides will generally be necessary to achieve the desired result and control weeds, some of which may be noxious weeds. A failed range planting and/or secondary succession will lead to State 3: Invaded State (R5B).
Juniper Invasion - Juniper species may have been present as scattered trees or shrubs prior to European influence. Since that time, decreased fire frequency, increased fire suppression, and dispersal from shelterbelts have been particularly important in enabling junipers to increase and, potentially, dominate a wide range of rangeland and forest land ecological sites in MLRA 54. Extended periods of non-use or very light grazing may also be factors.
Where a conifer seed source is available, woody encroachment begins to expand, exploit, and eventually dominate the sites, threatening the ecological integrity of the sites. Without managerial intervention these sites may transition to a Conifer Invaded State. As depicted in the following diagram, confer seeds disperse into an intact grassland beginning the process of woody encroachment.
The following state and transition model diagram illustrates the common states, community phases, community pathways, and transition and restoration pathways that can occur on the site. These are the most common plant community phases and states based on current knowledge and experience; changes may be made as more data are collected. Pathway narratives describing the site’s ecological dynamics reference various management practices (e.g., prescribed grazing, prescribed fire, brush management, herbaceous weed treatment) which, if properly designed and implemented, will positively influence plant community competitive interactions. The design of these management practices will be site specific and should be developed by knowledgeable individuals; based upon management goals and a resource inventory; and supported by an ongoing monitoring protocol.
When the management goal is to maintain an existing plant community phase or restore to another phase within the same state, modification of existing management to ensure native species have the competitive advantage may be required. To restore a previous state, the application of two or more management practices in an ongoing manner will be required. Whether using prescribed grazing, prescribed burning, or a combination of both with or without additional practices (e.g., brush management), the timing and method of application needs to favor the native species over the exotic species. Adjustments to account for variations in annual growing conditions and implementing an ongoing monitoring protocol to track changes and adjust management inputs to ensure desired outcome will be necessary.
The plant community phase composition table(s) has been developed from the best available knowledge including research, historical records, clipping studies, and inventory records. As more data are collected, plant community species composition and production information may be revised.
State and transition model
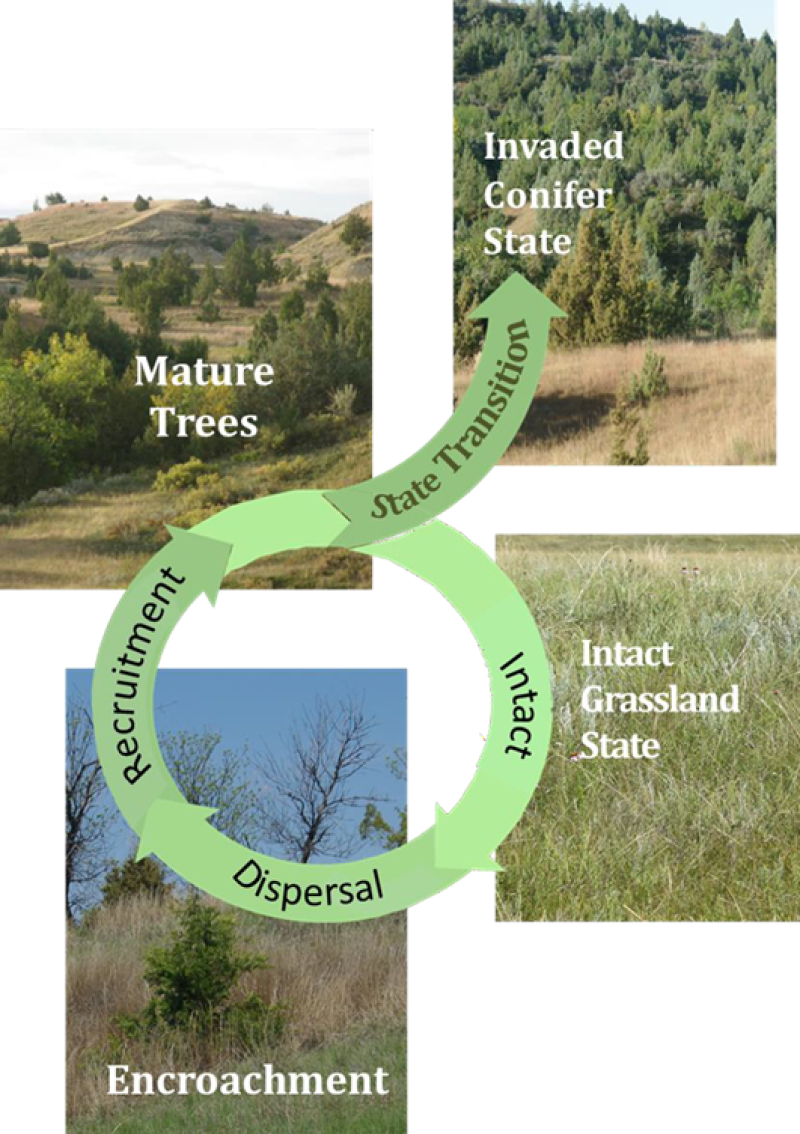
Figure 8. Stages of Woody Encroachment - Adapted from: Reducing Woody Encroachment in Grasslands – A Guide for Understanding Risk and Vulnerability; Oklahoma Cooperative Extension Service
More interactive model formats are also available.
View Interactive Models
More interactive model formats are also available.
View Interactive Models
Click on state and transition labels to scroll to the respective text
Ecosystem states
States 2 and 5 (additional transitions)
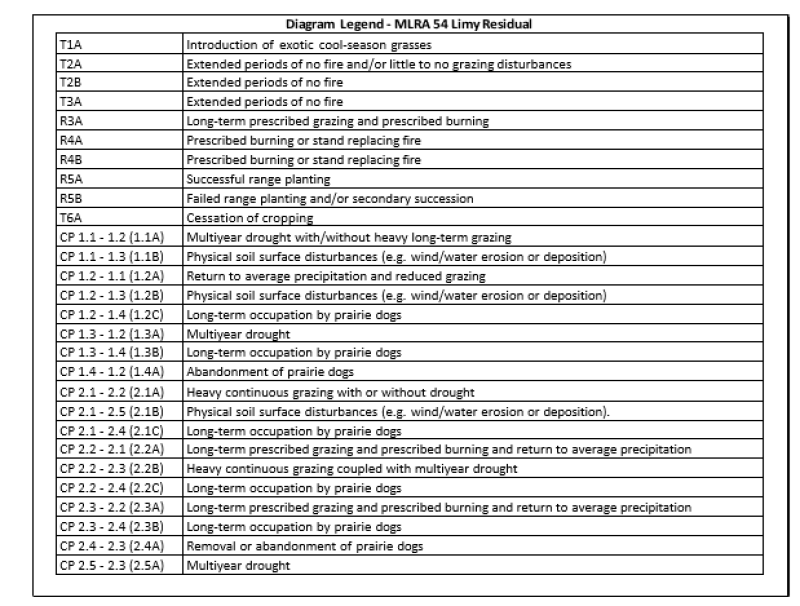
| T1A | - | Introduction of exotic cool-season grasses |
|---|---|---|
| T2A | - | Extended periods of no fire and/or little to no grazing disturbances |
| T2B | - | Extended periods of no fire |
| R3A | - | Long-term prescribed grazing and prescribed burning |
| T3A | - | Extended periods of no fire |
| R4A | - | Prescribed burning or stand replacing fire |
| R4B | - | Prescribed burning or stand replacing fire |
| R5A | - | Successful range planting |
| R5B | - | Failed range planting and/or secondary succession |
| T6A | - | Cessation of cropping |
State 1 submodel, plant communities
| 1.1A | - | Multiyear drought with/without heavy long-term grazing |
|---|---|---|
| 1.1B | - | Physical soil surface disturbances (e.g. wind/water erosion or deposition) |
| 1.2A | - | Return to average precipitation and reduced grazing |
| 1.2B | - | Physical soil surface disturbances (e.g. wind/water erosion or deposition) |
| 1.2C | - | Long-term occupation by prairie dogs |
| 1.3A | - | Multiyear drought |
| 1.3B | - | Long-term occupation by prairie dogs |
| 1.4A | - | Abandonment of prairie dogs |
State 2 submodel, plant communities
Communities 1 and 5 (additional pathways)
| 2.1A | - | Heavy continuous grazing with or without drought |
|---|---|---|
| 2.1B | - | Physical soil surface disturbances (e.g. wind/water erosion or deposition). |
| 2.2A | - | Long-term prescribed grazing and prescribed burning and return to average precipitation |
| 2.2B | - | Heavy continuous grazing coupled with multiyear drought |
| 2.2C | - | Long-term occupation by prairie dogs |
| 2.3A | - | Long-term prescribed grazing and prescribed burning and return to average precipitation |
| 2.3B | - | Long-term occupation by prairie dogs |
| 2.4A | - | Removal or abandonment of prairie dogs |
| 2.5A | - | Multiyear drought |
State 3 submodel, plant communities
State 4 submodel, plant communities
State 5 submodel, plant communities
State 1
Reference State
This state represents the natural range of variability that dominated the dynamics of this ecological site prior to European influence. The primary disturbance mechanisms for this site in the reference condition included frequent fire and grazing by large herding ungulates. Timing of fires and grazing, coupled with weather events, dictated the dynamics that occurred within the natural range of variability. These factors likely caused the community to shift both spatially and temporally between four community phases.
Characteristics and indicators. Because of changes in disturbances and other environmental factors (particularly the widespread occurrence of exotic species), the Reference State is considered to no longer exist.
Resilience management. If intact, the reference state should probably be managed with current disturbance regimes which has permitted the site to remain in reference condition, as well as maintaining the quality and integrity of associated ecological sites. Maintenance of the reference condition is contingent upon a monitoring protocol to guide management.
Community 1.1
Western Wheatgrass-Needlegrasses-Blue Grama-Little Bluestem (Pascopyrum smithii-Hesperostipa spp., Nasella viridula-Bouteloua gracilis-Schizachyrium scoparium)
This community phase was historically the most dominant both temporally and spatially. It was dominated by cool-season grasses, such as western wheatgrass and needle and thread. There were also other needlegrasses (e.g., green needlegrass, porcupinegrass) and sedges, as well as small amounts of warm-season grasses (such as blue grama, Fendler threeawn, and perhaps little bluestem). A variety of leguminous and non-leguminous perennial forbs were present in slight amounts. Common forbs included blue lettuce, dotted blazing star, upright prairie coneflower, silverleaf Indian breadroot, scarlet beeblossom, and stiff sunflower. Shrubs included prairie sagewort, plains prickly pear, and prairie rose. Annual production likely varied from about 1700-2400 pounds per acre with grasses and grass-likes, forbs, and shrubs contributing about 80%, 15% and 5%, respectively. Because cool-season grasses and grass-likes dominated this plant community, the bulk of the annual production was primarily mid to late spring and early summer. This community represents the plant community phase upon which interpretations are primarily based and is described in the “Plant Community Composition and Group Annual Production” portion of this ecological site description.
Figure 9. Annual production by plant type (representative values) or group (midpoint values)
Table 5. Annual production by plant type
| Plant type | Low (lb/acre) |
Representative value (lb/acre) |
High (lb/acre) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grass/Grasslike | 1485 | 1732 | 1970 |
| Forb | 200 | 256 | 325 |
| Shrub/Vine | 15 | 62 | 105 |
| Total | 1700 | 2050 | 2400 |
Community 1.2
Blue Grama-Western Wheatgrass/Sedges/Forbs (Bouteloua gracilis- Pascopyrum smithii/Carex spp./Forbs)

Figure 10. Foreground depicts Plant Community Phase 1.2
This community phase resulted from multiyear drought with or without heavy long-tern grazing. Repeated spring grazing depleted stored carbohydrates, resulting in weakening and eventual decline of the cool- season mid-statured grasses. Blue grama and western wheatgrass were the dominant species. Other grasses included reduced amounts of needle and thread and sedges. Forbs (such as Indian breadroot, white sagebrush, and scarlet globemallow) may also have been present. This plant community may have existed across the site, on spot-grazed areas, or around water sources. Annual production was reduced 85 to 95 percent of Community Phase 1.1. Due to a decline in the cool- season dominance, the bulk of the production would have shifted slightly towards early to mid-summer.
Community 1.3
Little Bluestem-Western Wheatgrass/Sedges/Forbs (Schizachyrium scoparium-Pascopyrum smithii/Carex spp./Forbs)
This community phase can be characterized by an increase in little bluestem resulting from soil disturbances (such as soil erosion, soil deposition, and large herbivore trailing). Soil disturbance, coupled with high calcium carbonates, provided a competitive advantage to little bluestem as it tends to act as an invader on disturbed areas. Large herbivores typically avoid little bluestem; the lack of grazing preference likely acted as a driver to further favor the plants abundance once it becomes established.
Community 1.4
Annual Forbs/Bare Ground/Blue Grama/Fetid Marigold (Annual Forbs/Bare Ground/Bouteloua gracilis/Dyssodia papposa): Prairie Dog Town
This community phase formed during periods of long-term occupation by prairie dogs. It is characterized by the abundance of annual forbs (e.g., fetid marigold, wooly plantain) and bare ground. Some perennial native species remain but are greatly reduced in vigor and may not be readily visible.
Pathway 1.1A
Community 1.1 to 1.2
Community Phase Pathway 1.1 to 1.2 occurred during periods of multiyear drought with or without heavy long- tern grazing. This resulted in increases in short-statured, drought–tolerant, warm-season grasses, sedges, and forbs with corresponding decreases of mid-statured cool-season grasses.
Pathway 1.1B
Community 1.1 to 1.3
Community Phase Pathway 1.1 to 1.3 was initiated following events resulting in a reduction in plant cover, increased bare ground, and increased rates of soil erosion and deposition due to wind and/or water erosion (e.g., periods of reduced moisture or periods of severe, multiyear drought and larger herbivore trailing). Naturally occurring soil slumping on slopes (“steps”) may also have contributed to increases in bare ground. Soil disturbance resulted in elevated calcium carbonate levels at the soil surface which further favored an increase in little bluestem.
Pathway 1.2A
Community 1.2 to 1.1
Community Phase Pathway 1.2 to 1.1 occurred with the return to average precipitation and reduced grazing which enabled cool-season mid- statured grasses regain vigor.
Pathway 1.2B
Community 1.2 to 1.3
Community Phase Pathway 1.2 to 1.3 was initiated following events resulting in a reduction in plant cover, increased bare ground, and increased rates of soil erosion and deposition due to wind and/or water erosion (e.g., periods of reduced moisture or periods of severe, multiyear drought and larger herbivore trailing). Naturally occurring soil slumping on slopes (“steps”) may also have contributed to increases in bare ground. Soil disturbance resulted in elevated calcium carbonate levels at the soil surface, which further favored an increase in little bluestem.
Pathway 1.2C
Community 1.2 to 1.4
Community Phase Pathway 1.2 to 1.4 resulted from long-term occupation by prairie dogs. This resulted in marked increases in annual forbs, bare ground, blue grama, and fetid marigold along with corresponding decreases in perennial grasses and forbs. Reduced vegetative cover resulting from drought and/or heavy grazing may have facilitated this pathway.
Pathway 1.3A
Community 1.3 to 1.2
Community Phase Pathway 1.3 to 1.2 occurred with site stabilization and a reduction in little bluestem resulting from multiyear drought.
Pathway 1.3B
Community 1.3 to 1.4
Community Phase Pathway 1.3 to 1.4 resulted from long-term occupation by prairie dogs. This resulted in marked increases in annual forbs, bare ground, blue grama, and fetid marigold along with corresponding decreases in perennial grasses and forbs. Reduced vegetative cover resulting from drought and/or heavy grazing may have facilitated this pathway.
Pathway 1.4A
Community 1.4 to 1.2
Community Phase Pathway 1.4 to 1.2 occurred with the abandonment of prairie dogs. This resulted in marked increases in perennial grasses and forbs along with corresponding decreases in annual forbs, bare ground, blue grama, and fetid marigold.
State 2
Native/Invaded State
This state is similar to State 1: Reference State but has now been colonized by the exotic cool-season grasses (commonly Kentucky bluegrass and/or smooth brome) which are now present in small amounts. Although the state is still dominated by native grasses, an increase in these exotic cool-season grasses can be expected. These exotic cool-season grasses can be quite invasive on the site and are particularly well adapted to heavy grazing. They also often form monotypic stands. As these exotic cool-season grasses increase, both forage quantity and quality become increasingly restricted to late spring and early summer due to the monotypic nature of the stand, even though annual production may increase. Native forbs generally decrease in production, abundance, diversity, and richness compared to that of State 1: Reference State. These exotic cool-season grasses have been particularly and consistently invasive under extended periods of no use and no fire. To slow or limit the invasion of these exotic grasses, it is imperative that managerial techniques (e.g., prescribed grazing, prescribed burning) be carefully constructed, monitored, and evaluated with respect to that objective. If management does not include measures to control or reduce these exotic cool-season grasses, the transition to State 3: Invaded State should be expected. The annual production of this state can be quite variable, in large part due to the amount of exotic cool-season grasses.
Characteristics and indicators. The presence of trace amounts of exotic cool-season grasses indicates a transition from State 1 to State 2. The presence of exotic biennial or perennial leguminous forbs (i.e., sweet clover, black medic) may not, on their own, indicate a transition from State 1 to State 2 but may facilitate that transition.
Resilience management. To slow or limit the invasion of these exotic grasses, it is imperative that managerial techniques (e.g., prescribed grazing, prescribed burning) be carefully constructed, constructed, and evaluated with respect to that objective. Grazing management should be applied that enhances the competitive advantage of native grass and forb species. This may include: (1) early spring grazing when exotic cool-season grasses are actively growing and native cool-season grasses are dormant; (2) applying proper deferment periods allowing native grasses to recover and maintain or improve vigor; (3) adjusting overall grazing intensity to reduce excessive plant litter (above that needed for rangeland health indicator #14 – see Rangeland Health Reference Worksheet); (4) incorporating early heavy spring utilization which focuses grazing on exotic cool-season grasses and reduces plant litter, provided that livestock are moved when grazing selection shifts from exotic cool-season grasses to native grasses. Prescribed burning should be applied in a manner that maintains or enhances the competitive advantage of native grass and forb species. Prescribed burns should be applied as needed to adequately reduce/remove excessive plant litter and maintain the competitive advantage for native species. Timing of prescribed burns (spring vs. summer vs. fall) should be adjusted to account for differences in annual growing conditions and applied during windows of opportunity to best shift the competitive advantage to the native species.
Community 2.1
Western Wheatgrass-Needlegrasses-Blue Grama-Little Bluestem/Shrubs (Pascopyrum smithii-Hesperostipa spp., Nasella viridula-Bouteloua gracilis- Schizachyrium scoparium/ Shrubs)

Figure 11. Community Phase 2.1: Western Wheatgrass-Needlegrasses-Blue Grama-Little Bluestem/Shrubs;15-20% slope.
This community phase is similar to Community Phase 1.1 but has been colonized by exotic cool-season grasses (commonly Kentucky bluegrass and/or smooth brome), often with an increased shrub component. The exotic cool-season grasses, however, are present in smaller amounts with the community still dominated by native grasses. Annual production may be comparable to that of Community Phase 1.1 (1400-2100 pounds per acre). However, as the exotic cool-season grasses increase, peak production will shift to earlier in the growing season. This cool-season grass dominated community can be maintained with grazing systems that allow for adequate recovery periods following grazing events and, potentially, the combination of prescribed grazing and prescribed burning which closely mimics the natural disturbance regime.
Community 2.2
Blue Grama-Western Wheatgrass-Little Bluestem/Sedges (Bouteloua gracilis-Pascopyrum smithii-Schizachyrium scoparium /Carex spp.)
This community phase occurs when natural or management actions favor the development of a short- statured grass-dominated community. It is dominated by blue grama, western wheatgrass and upland sedges. Western wheatgrass would make up approximately 25–30 percent of the canopy cover, blue grama 20–25 percent, needle and thread 15–20 percent, and threadleaf sedge 5–10 percent of the canopy cover. Annual production will be around 60–80 percent of the biomass produced by Community Phase 1.1. This community phase is often dispersed throughout a pasture in an overgrazed/ undergrazed pattern, typically referred to as patch grazing. Some overgrazed areas will exhibit the impacts of heavy use, while the ungrazed areas will have a build-up of litter and increased plant decadence. This is a typical pattern found in properly stocked pastures grazed season-long. As a result, Kentucky bluegrass tends to increase more in the undergrazed areas while the more grazing tolerant short statured species (such as blue grama and sedges) increase in the heavily grazed areas. If present, Kentucky bluegrass may increase under heavy grazing.
Community 2.3
Blue Grama/Sedges/Prairie Sagewort/Cactus (Bouteloua gracilis/Carex spp./Artemisia frigida/Opuntia spp.)
This plant community phase is dominated by species that tolerate multiyear drought and heavy grazing. It is dominated by blue grama and sedges with minor amounts of western wheatgrass and Fendler threeawn. Common yarrow, western rockjasmine, common chickweed, pussytoes, spiny phlox and rough false pennyroyal can be common forbs along with shrubs (such as prairie sagewort and plains prickly pear and, perhaps, brittle pricklypear). Bare ground increases while annual production decreases.
Community 2.4
Annual Forbs/Bare Ground/Blue Grama/Fetid Marigold (Annual Forbs/Bare Ground/Bouteloua gracilis/Dyssodia papposa): Prairie Dog Town
This community phase forms during periods of long-term occupation by prairie dogs. It is characterized by the abundance of annual forbs (e.g., fetid marigold, wooly plantain) and bare ground. Some perennial native species remain but are greatly reduced in vigor and may not be readily visible.
Community 2.5
Little Bluestem-Western Wheatgrass/Sedges/Forbs/Shrubs (Schizachyrium scoparium-Pascopyrum smithii/Carex spp./Forbs/Shrubs)
This plant community phase is characterized by an increase in little bluestem resulting from soil disturbance (such as soil erosion, soil deposition, pipelines, abandoned roads, and livestock trailing). Soil disturbance, coupled with high calcium carbonates, gives the competitive advantage to little bluestem as it tends to act as an invader on disturbed areas. Livestock typically avoid little bluestem; the lack of grazing preference may act as a driver to further favor this plants abundance once it becomes established. The deep-rooted nature of little bluestem stabilizes soil on slopes and can act as a snow trap allowing the site to collect additional moisture during spring runoff.
Pathway 2.1A
Community 2.1 to 2.2
Community Phase Pathway 2.1 to 2.2 occurs with heavy continuous grazing with or without drought, leading to an increase in the shorter-statured grasses, such as blue grama and sedges. Drought accelerates the pathway. Changes in plant functional and structural groups and the composition/distribution of the vegetation causes a decrease in production, the main period of which shifts from spring and early summer to early spring and mid-summer.
Pathway 2.1B
Community 2.1 to 2.5
Community Phase Pathway 2.1 to 2.5 occurs with heavy continuous grazing with or without drought. It is initiated following events resulting in a reduction in plant cover, increased bare ground, and increased rates of soil erosion and deposition due to wind and/or water erosion (e.g., periods of reduced moisture or periods of severe, multiyear drought, pipelines, abandoned roads, livestock trailing). Naturally occurring soil slumping on slopes (“steps”) may also contribute to increases in bare ground. Soil disturbance results in elevated calcium carbonate levels at the soil surface, which further favors an increase in little bluestem.
Pathway 2.2A
Community 2.2 to 2.1
Community Phase Pathway 2.2 to 2.1 occurs with the implementation of long-term prescribed grazing and prescribed burning and return to average precipitation. It is initiated by implementing grazing management which includes adequate recovery periods following each grazing event and stocking levels which match the available resources. If properly implemented, this will shift the competitive advantage from the exotic cool-season species to native cool-season grasses.
Pathway 2.2B
Community 2.2 to 2.3
Community Phase Pathway 2.2 to 2.3 during periods of heavy continuous grazing coupled with multiyear drought which favors a shift to shorter-statured grasses (such as blue grama, sedges, shrubs and cactus). Along this pathway, peak production shifts from spring and early summer to early spring and mid-summer. Plant diversity declines as does annual production.
Pathway 2.2C
Community 2.2 to 2.4
Community Phase Pathway 2.2 to 2.4 results from long-term occupation by prairie dogs. This results in marked increases in annual forbs, bare ground, blue grama, and fetid marigold along with corresponding decreases in perennial grasses and forbs. Reduced vegetative cover resulting from drought and/or heavy grazing may facilitate this pathway.
Pathway 2.3A
Community 2.3 to 2.2
Community Phase Pathway 2.3 to 2.2 is initiated by implementation of long-term prescribed grazing and prescribed burning and return to average precipitation. It is initiated by implementing grazing management which includes adequate recovery periods following each grazing event and stocking levels which match the available resources. If properly implemented, this will shift the competitive advantage to the remnant native cool-season grasses, such as western wheatgrass.
Pathway 2.3B
Community 2.3 to 2.4
Community Phase Pathway 2.3 to 2.4 results from long-term occupation by prairie dogs. This results in marked increases in annual forbs, bare ground, blue grama, and fetid marigold along with corresponding decreases in perennial grasses and forbs. Reduced vegetative cover resulting from drought and/or heavy grazing may facilitate this pathway.
Pathway 2.4A
Community 2.4 to 2.3
Community Phase Pathway 2.4 to 2.3 occurs with the removal or abandonment of prairie dogs. This results in marked increases in perennial grasses and forbs along with corresponding decreases in annual forbs, bare ground, blue grama, and fetid marigold.
Pathway 2.5A
Community 2.5 to 2.3
Community Phase Pathway 2.5 to 2.3 occurs with multiyear drought, leading to marked increases in the more drought tolerant plants (e.g., blue grama, sedges, prairie sagewort, cactus) and corresponding decreases in the less drought tolerant plants (e.g., western wheatgrass, little bluestem).
State 3
Invaded State
This state is the result of invasion and dominance by the exotic cool-season grasses, commonly Kentucky bluegrass and/or smooth brome. Other exotic plants (e.g., Canada thistle, leafy spurge) may also invade the site. These exotic cool-season grasses can be quite invasive on the site and are particularly well adapted to heavy grazing. They also often form monotypic stands. As these exotic cool-season grasses increase, both forage quantity and quality become increasingly restricted to late spring and early summer due to the monotypic nature of the stand, even though annual production may increase. Native forbs generally decrease in production, abundance, diversity, and richness compared to that of State 1: Reference State. Common forbs often include white heath aster, goldenrod, common yarrow, and white sagebrush. Shrubs (such as rose and silver sagebrush) may show marked increases. Once the state is well established, prescribed burning and grazing techniques have been largely ineffective in suppressing or eliminating these species, even though some short-term reductions may appear successful. Annual production of this state may vary widely, in part due to variations in the extent of invasion by exotic cool-season grasses. However, as the exotic cool-season grasses increase, peak production will shift to earlier in the growing season.
Characteristics and indicators. This site is characterized by exotic cool-season grasses constituting greater than 30 percent of the annual production and native grasses constituting less than 40 percent of the annual production.
Resilience management. Light or moderately stocked continuous, season-long grazing or a prescribed grazing system which incorporates adequate deferment periods between grazing events and proper stocking rate levels will maintain this State. Application of herbaceous weed treatment, occasional prescribed burning and/or brush management may be needed to manage noxious weeds and increasing shrub (e.g., western snowberry) populations.
Community 3.1
Exotic Cool-Season Grasses/Forbs
This community phase is dominated by exotic cool-season grasses (such as Kentucky bluegrass and/or smooth brome), often with a much-reduced forb and shrub component. Excessive accumulation of mulch may also be present, particularly when dominated by Kentucky bluegrass. Common forb and shrub species often include white heath aster, goldenrod, common yarrow, white sagebrush, rose, and silver sagebrush. The exotic forbs, leafy spurge and Canada thistle, may also invade the site. The longer this community phase exists the more resilient it becomes. Natural or management disturbances that reduce the cover of Kentucky bluegrass or smooth brome are typically short-lived.
State 4
Invaded Wooded State
This state results from extended periods of no fire and is characterized by stands of shrubs (e.g., chokecherry, rose, buffaloberry, western snowberry), along with some green ash. Older stands generally support larger and more abundant green ash. Junipers may also invade the state, particularly in older stands. A marked increase in non-use management and active fire suppression since European influence has enabled this state to become more widespread.
Characteristics and indicators. The dominance of woody species (by cover and production) distinguishes this state from other herbaceously dominated states.
Resilience management. This state is resistant to change in the long-term absence of fire. Restoration efforts would require the use of prescribed burning, mechanical treatment, and prescribed grazing. Considerable time and effort will be required to restore to other States.
Community 4.1
Shrubs/Trees/Herbaceous
This community phase is characterized by stands of shrubs (e.g., chokecherry, rose, buffaloberry, western snowberry), along with some green ash. Older stands generally support larger and more abundant green ash. The herbaceous component can be quite variable depending on variations in shading and other factors, but often includes exotic cool-season grasses (e.g., Kentucky bluegrass, smooth brome) and few forbs (e.g., common yarrow, white sagebrush, goldenrod). Junipers may also invade the state, particularly in older stands. A marked increase in non-use management and active fire suppression since European influence have enabled this state to become more widespread.
State 5
Go-Back State
This state is highly variable depending on the level and duration of disturbance related to the T6A transitional pathway. In this MLRA, the most probable origin of this state is plant succession following cropland abandonment. This plant community will initially include a variety of annual forbs and grasses, some of which may be noxious weeds and need control. Over time, the exotic cool-season grasses (Kentucky bluegrass and/or smooth brome) will likely predominate.
Characteristics and indicators. Tillage has destroyed the native plant community, altered soil structure and biology, reduced soil organic matter, and resulted in the formation of a tillage induced compacted layer which is restrictive to root growth. Removal of perennial grasses and forbs results in decreased infiltration and increased runoff.
Resilience management. Continued tillage will maintain the state. Control of noxious weeds will be required.
Community 5.1
Annual/Pioneer Perennial/Exotics
This community phase is highly variable depending on the level and duration of disturbance related to the T6A transitional pathway. In this MLRA, the most probable origin of this phase is secondary succession following cropland abandonment. This plant community will initially include a variety of annual forbs and grasses, including noxious weeds (e.g., Canada thistle) which may need control. Over time, the exotic cool-season grasses (Kentucky bluegrass and/or smooth brome) will likely predominate.
State 6
Any Plant Community
Transition T1A
State 1 to 2
This is the transition from the State 1: Reference State to the State 2: Native/Invaded State due to the introduction and establishment of exotic cool-season grasses (typically Kentucky bluegrass and/or smooth brome). This transition was probably inevitable and corresponded to a decline in native warm-season and cool-season grasses; it may have been exacerbated by chronic season-long or heavy late season grazing. Complete rest from grazing and suppression of fire could also have hastened the transition. The threshold between states was crossed when Kentucky bluegrass, smooth brome, or other exotic species became established on the site.
Constraints to recovery. Current knowledge and technology will not facilitate a successful restoration to Reference State.
Transition T2A
State 2 to 3
This transition from the State 2: Native/Invaded State to State 3: Invaded State generally occurs during extended periods of no fire and/or little to no grazing disturbances. Exotic cool-season grasses, such as Kentucky bluegrass and/or smooth brome, become the dominant graminoids. Studies indicate that a threshold may exist in this transition when both Kentucky bluegrass exceeds 30% of the plant community and native grasses represent less than 40% of the plant community composition. Similar thresholds may exist for other exotic cool-season grasses. This transition may also occur under other managerial conditions (e.g., heavy season-long grazing, primarily Kentucky bluegrass).
Constraints to recovery. Variations in growing conditions (e.g., cool, wet spring) will influence effects of various management activities on exotic cool-season grass populations.
Transition T2B
State 2 to 4
This transition from the State 2: Native/Invaded to State 4: Woody Invaded State generally occurs during extended periods of no fire. It frequently occurs when the site is in close proximity to wooded areas where the woodland vegetation may serve as a seed source for these species to colonize the site. It has also become more frequent following European settlement when the historic fire regime was markedly reduced.
Constraints to recovery. The extended fire interval may make recovery doubtful due to the abundance of exotic cool-season grasses and lack of native grasses. Fire intensity along with consumption of available fuels may cause incomplete or patchy burns. Continued recruitment of tree seeds from adjacent sites will hamper site restoration. Reticence to undertake tree removal and the perception that trees may be a desirable vegetation component for wildlife habitat, carbon sequestration, aesthetics, etc. are some of the constraints to recovery. Managers wanting to manage the site for white-tailed or mule deer, livestock, or grassland nesting birds will need to consider the intensive management required to restore and maintain the site in State 2. The disturbance regime necessary to restore this site to State 2: Native/Invaded State is very labor intensive and costly; therefore, addressing woody removal earlier in the encroachment phase is the most cost-effective treatment for woody control.
Restoration pathway R3A
State 3 to 2
This restoration pathway from State 3: Invaded State to State 2: Native/Invaded State may be accomplished with the implementation of long-term prescribed grazing and prescribed burning, assuming there is an adequate component of native grasses to respond to the treatments. Both prescribed grazing and prescribed burning are likely necessary to successfully initiate this restoration pathway, the success of which depends upon the presence of a remnant population of native grasses in Community Phase 3.1. That remnant population, however, may not be readily apparent without close inspection. The application of several prescribed burns may be needed at relatively short intervals in the early phases of this restoration process, in part because some shrubs (e.g., western snowberry) sprout profusely following one burn. Early season prescribed burns have been successful; however, fall burning may also be an effective technique. The prescribed grazing should include adequate recovery periods following each grazing event and stocking levels which match the available resources. If properly implemented, this will shift the competitive advantage from the exotic cool-season grasses to the native cool-season grasses.
Context dependence. Grazing management should be applied in a manner that enhances/maximizes the competitive advantage of native grass and forb species over the exotic species. This may include the use of prescribed grazing to reduce excessive plant litter accumulations above that needed for rangeland health indicator #14 (see Rangeland Health Reference Worksheet). Increasing livestock densities may facilitate the reduction in plant litter provided length and timing of grazing periods are adjusted to favor native species. Grazing prescriptions designed to address exotic grass invasion and favor native species may involve earlier, short, intense grazing periods with proper deferment to improve native species health and vigor. Fall (e.g., September, October) prescribed burning followed by an intensive, early spring graze period with adequate deferment for native grass recovery may shift the competitive advantage to the native species, facilitating the restoration to State 2: Native/Invaded. Prescribed burning should be applied in a manner that enhances the competitive advantage of native grass and forb species over the exotic species. Prescribed burns should be applied at a frequency which mimics the natural disturbance regime, or more frequently as is ecologically (e.g., available fuel load) and economically feasible. Burn prescriptions may need adjustment to: (1) account for change in fine fuel orientation (e.g., “flopped” Kentucky bluegrass); (2) fire intensity and duration by adjusting ignition pattern (e.g., backing fires vs head fires); (3) account for plant phenological stages to maximize stress on exotic species while favoring native species (both cool- and warm-season grasses).
Transition T3A
State 3 to 4
This transition from the State 3: Invaded to State 4: Invaded Wooded State generally occurs during extended periods of no fire. It frequently occurs when the site is in close proximity to wooded areas where the woodland vegetation may serve as a seed source for these species to colonize the site. It has also become more frequent following European settlement when the historic fire regime was markedly reduced.
Constraints to recovery. The extended fire interval may make recovery doubtful due to the abundance of exotic cool-season grasses and lack of native grasses. Fire intensity along with consumption of available fuels may cause incomplete or patchy burns. Continued recruitment of tree seeds from adjacent sites will hamper site restoration. Constraints to recovery include reticence to undertake tree removal and the perception that trees may be a desirable vegetation component for wildlife habitat, carbon sequestration, aesthetics, etc. Managers wanting to manage the site for deer, livestock, or grassland nesting birds will need to consider the intensive management required to restore and maintain the site in State 2. The disturbance regime necessary to restore this site to State 2: Native/Invaded State is very labor intensive and costly; therefore, addressing woody removal earlier in the encroachment phase is the most cost-effective treatment for woody control.
Restoration pathway R4A
State 4 to 2
This restoration pathway from State 4: Invaded Wooded State to State 2: Native/Invaded State can occur with mechanical treatment and/or prescribed burning or a stand replacing fire. This restoration is similar to Restoration R4B but results in a grass composition composed largely of native species when native grasses dominate the understory prior to restoration.
Context dependence. Fire intensity along with consumption of available fuels may cause incomplete or patchy burns. Ladder fuel and/or fuel loading are required for successfully controlling ponderosa pine (crown vs. ground fire). Continued recruitment of seeds (juniper and pine) from adjacent sites will hamper site restoration. Intensive management is required to restore and maintain the site in State 2.: Native/Invaded State.
Restoration pathway R4B
State 4 to 3
This restoration pathway from State 4: Invaded Wooded State to State 3: Invaded State can occur with mechanical treatment and/or prescribed burning or a stand replacing fire. This restoration is similar to Restoration R4A but results in a grass composition composed largely of exotic cool-season species when exotic cool-season grass species dominate the understory prior to restoration.
Context dependence. Fire intensity along with consumption of available fuels may cause incomplete or patchy burns. Ladder fuel and/or fuel loading are required for successfully controlling ponderosa pine (crown vs. ground fire). Continued recruitment of seeds (juniper and pine) from adjacent sites will hamper site restoration. Intensive management is required to restore and maintain the site in State 3: Invaded State.
Restoration pathway R5A
State 5 to 2
This Restoration Pathway from State 5: Go-Back State to the State 2: Native/Invaded State can be accomplished with a successful range planting. Following seeding, prescribed grazing, prescribed burning, haying, or use of herbicides will generally be necessary to achieve the desired result and control any noxious weeds. It may be possible using selected plant materials and agronomic practices to approach something very near the functioning of State 2: Native/Invaded State. Application of chemical herbicides and the use of mechanical seeding methods using adapted varieties of the dominant native grasses are possible and can be successful. After establishment of the native plant species, prescribed grazing should include adequate recovery periods following each grazing event and stocking levels which match the available resources; management objectives must include the maintenance of those species, the associated reference state functions, and continued treatment of exotic grasses.
Context dependence. A successful range planting will include proper seedbed preparation, weed control (both prior to and after the planting), selection of adapted native species representing functional/structural groups inherent to the State 1, and proper seeding technique. Management (e.g., prescribed grazing, prescribed burning) during and after establishment must be applied in a manner that maintains the competitive advantage for the seeded native species. Adding non-native species can impact the above and below ground biota. Elevated soil nitrogen levels have been shown to benefit smooth brome and Kentucky bluegrass more than some native grasses. As a result, fertilization, exotic legumes in the seeding mix, and other techniques that increase soil nitrogen may promote smooth brome and Kentucky bluegrass invasion. The method or methods of herbaceous weed treatment will be site specific to each situation; but generally, the goal would be to apply the pesticide, mechanical control, or biological control (either singularly or in combination) in a manner that shifts the competitive advantage from the targeted species to the native grasses and forbs. The control method(s) should be as specific to the targeted species as possible to minimize impacts to non-target species.
Restoration pathway R5B
State 5 to 3
A failed range planting and/or secondary succession will lead to State 3: Invaded State.
Context dependence. Failed range plantings can result from many causes (both singularly and in combination) including drought, poor seedbed preparation, improper seeding methods, seeded species not adapted to the site, insufficient weed control, herbicide carryover, poor seed quality (purity & germination), and/or improper management.
Restoration pathway T6A
State 6 to 5
This transition from any plant community to State 4: Go-Back State. It is most commonly associated with the cessation of cropping without the benefit of range planting, resulting in a “go-back” situation. Soil conditions can be quite variable on the site, in part due to variations in the management/cropping history (e.g., development of a tillage induced compacted layer (plow pan), erosion, fertility, and/or herbicide/pesticide carryover). Thus, soil conditions should be assessed when considering restoration techniques.
Additional community tables
Table 6. Community 1.1 plant community composition
| Group | Common name | Symbol | Scientific name | Annual production (lb/acre) | Foliar cover (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Grass/Grasslike
|
||||||
| 1 | Cool-Season Grasses | 513–820 | ||||
| western wheatgrass | PASM | Pascopyrum smithii | 513–718 | – | ||
| prairie sandreed | CALO | Calamovilfa longifolia | 103–410 | – | ||
| needle and thread | HECOC8 | Hesperostipa comata ssp. comata | 103–308 | – | ||
| prairie Junegrass | KOMA | Koeleria macrantha | 21–62 | – | ||
| plains reedgrass | CAMO | Calamagrostis montanensis | 21–62 | – | ||
| 2 | Warm-Season Grasses | 103–308 | ||||
| blue grama | BOGR2 | Bouteloua gracilis | 205–410 | – | ||
| little bluestem | SCSC | Schizachyrium scoparium | 0–103 | – | ||
| Fendler threeawn | ARPUL | Aristida purpurea var. longiseta | 0–21 | – | ||
| 3 | Other native grasses | 41–144 | ||||
| plains muhly | MUCU3 | Muhlenbergia cuspidata | 21–103 | – | ||
| porcupinegrass | HESP11 | Hesperostipa spartea | 0–62 | – | ||
| Grass, perennial | 2GP | Grass, perennial | 21–62 | – | ||
| 4 | Grass-likes | 103–205 | ||||
| threadleaf sedge | CAFI | Carex filifolia | 21–103 | – | ||
| sun sedge | CAINH2 | Carex inops ssp. heliophila | 0–62 | – | ||
| needleleaf sedge | CADU6 | Carex duriuscula | 21–62 | – | ||
|
Forb
|
||||||
| 5 | Forbs | 205–308 | ||||
| Forb, perennial | 2FP | Forb, perennial | 21–62 | – | ||
| aster | ASTER | Aster | 21–62 | – | ||
| silverleaf Indian breadroot | PEAR6 | Pediomelum argophyllum | 21–62 | – | ||
| common yarrow | ACMI2 | Achillea millefolium | 21–41 | – | ||
| field pussytoes | ANNE | Antennaria neglecta | 21–41 | – | ||
| white sagebrush | ARLU | Artemisia ludoviciana | 21–41 | – | ||
| blacksamson echinacea | ECAN2 | Echinacea angustifolia | 21–41 | – | ||
| sanddune wallflower | ERCAC | Erysimum capitatum var. capitatum | 21–41 | – | ||
| stiff sunflower | HEPA19 | Helianthus pauciflorus | 21–41 | – | ||
| blue lettuce | LATA | Lactuca tatarica | 21–41 | – | ||
| dotted blazing star | LIPU | Liatris punctata | 21–41 | – | ||
| scarlet beeblossom | OESU3 | Oenothera suffrutescens | 21–41 | – | ||
| spiny phlox | PHHO | Phlox hoodii | 21–41 | – | ||
| woolly plantain | PLPA2 | Plantago patagonica | 21–41 | – | ||
| eastern pasqueflower | PUPA5 | Pulsatilla patens | 21–41 | – | ||
| upright prairie coneflower | RACO3 | Ratibida columnifera | 21–41 | – | ||
| scarlet globemallow | SPCO | Sphaeralcea coccinea | 21–41 | – | ||
| littleleaf pussytoes | ANMI3 | Antennaria microphylla | 0–21 | – | ||
| western rockjasmine | ANOC2 | Androsace occidentalis | 0–21 | – | ||
| tower rockcress | ARGL | Arabis glabra | 0–21 | – | ||
| plains milkweed | ASPU | Asclepias pumila | 0–21 | – | ||
| Flodman's thistle | CIFL | Cirsium flodmanii | 0–21 | – | ||
| bastard toadflax | COUM | Comandra umbellata | 0–21 | – | ||
| rough false pennyroyal | HEHI | Hedeoma hispida | 0–21 | – | ||
| common pepperweed | LEDE | Lepidium densiflorum | 0–21 | – | ||
| Lewis flax | LILE3 | Linum lewisii | 0–21 | – | ||
| stiffstem flax | LIRI | Linum rigidum | 0–21 | – | ||
| yellow owl's-clover | ORLU2 | Orthocarpus luteus | 0–21 | – | ||
| Indian breadroot | PEDIO2 | Pediomelum | 0–21 | – | ||
| sawsepal penstemon | PEGL3 | Penstemon glaber | 0–21 | – | ||
| white milkwort | POAL4 | Polygala alba | 0–21 | – | ||
| Pennsylvania cinquefoil | POPE8 | Potentilla pensylvanica | 0–21 | – | ||
| velvety goldenrod | SOMO | Solidago mollis | 0–21 | – | ||
| common chickweed | STME2 | Stellaria media | 0–21 | – | ||
| white heath aster | SYER | Symphyotrichum ericoides | 0–21 | – | ||
| smooth blue aster | SYLA3 | Symphyotrichum laeve | 0–21 | – | ||
|
Shrub/Vine
|
||||||
| 6 | Shrubs | 21–103 | ||||
| prairie sagewort | ARFR4 | Artemisia frigida | 21–62 | – | ||
| plains pricklypear | OPPO | Opuntia polyacantha | 21–41 | – | ||
| prairie rose | ROAR3 | Rosa arkansana | 21–41 | – | ||
| Shrub (>.5m) | 2SHRUB | Shrub (>.5m) | 21–41 | – | ||
| silver sagebrush | ARCA13 | Artemisia cana | 0–21 | – | ||
| Missouri foxtail cactus | ESMI3 | Escobaria missouriensis | 0–21 | – | ||
| winterfat | KRLA2 | Krascheninnikovia lanata | 0–21 | – | ||
Interpretations
Animal community
Animal Community – Wildlife Interpretations
Landscape
The MLRA 54 landscape is characterized by moderately dissected rolling plains with areas of local badlands, buttes, and isolated hills. MLRA 54 is considered to have a continental climate with cold winters and hot summers, low humidity, light rainfall, and much sunshine. Extremes in temperature are common and characteristic of the MLRA. This area supports natural mixed-grass prairie vegetation with prairie rose, leadplant, and patches of western snowberry interspersed throughout the area. Green ash, chokecherry, and buffaloberry occur in draws and narrow valleys creating woody riparian corridors. Complex intermingled ecological sites create diverse grass/shrub land habitats interspersed with varying densities linear, slope, depressional, and in-stream wetlands associated with headwater streams and tributaries to the Missouri River. These habitats provide critical life-cycle components for many wildlife species.
Historic Communities/Conditions within MLRA:
The northern mixed-grass prairie was a disturbance-driven ecosystem with fire, herbivory, and climate functioning as the primary ecological drivers (either singly or often in combination). Many species of grassland birds, small mammals, insects, reptiles, amphibians, and large herds of roaming American bison, elk, and pronghorn were historically among the inhabitants adapted to this semi-arid region. Roaming herbivores, as well as several small mammal and insect species, were the primary consumers linking the grassland resources to large predators (such as the wolf, mountain lion, and grizzly bear) and smaller carnivores (such as the coyote, bobcat, red fox, and raptors). The black-tailed prairie dog was once abundant and provided ecological services by manipulating the plant and soil community, thus providing habitat for the black-footed ferret, burrowing owl, ferruginous hawk, mountain plover, swift fox, small mammals, and amphibians and reptiles. Extirpated species include free-ranging American bison, grizzly bear, gray wolf, black- footed ferret, mountain plover, and peregrine falcon (breeding). Extinct from the region is the Rocky Mountain locust.
Present Communities/Conditions within MLRA:
Following European influence, domestic livestock grazing, elimination of fire, energy development, and other anthropogenic factors influenced plant community composition and abundance. Agriculture, transportation corridors, and energy development are the main factors contributing to habitat fragmentation, reducing habitat quality for area-sensitive species. These influences fragmented the landscape; reduced or eliminated ecological drivers (fire); and introduced exotic species including smooth brome, crested wheatgrass, Kentucky bluegrass, and leafy spurge. This further impacted plant and animal communities. The loss of the bison, black-tailed prairie dogs, and fire as primary ecological drivers greatly influenced the character of the remaining native plant communities and the associated wildlife, moving towards a less diverse and more homogeneous landscape. Included in this MLRA are the isolated Killdeer Mountains (limestone capped residual butte) containing bur oak, quaking aspen, green ash, paper birch, and American elm. Except for floodplain forests within the MLRA, the Killdeer Mountains contain the largest deciduous forest in southwestern North Dakota.
Some wildlife species in this area are mule deer, white-tailed deer, elk, pronghorn, moose, coyote, red fox, bobcat, prairie rattlesnake, American badger, raccoon, North American porcupine, beaver, striped skunk, American mink, white-tailed jackrabbit, black-tailed prairie dog, Eastern and Merriam’s turkey, golden eagle, ferruginous hawks, sharp-tailed grouse, black-billed magpie, and numerous species of grassland-nesting birds and pollinating insects.
Presence of wildlife species is often determined by ecological site characteristics including grass and forb species, hydrology, aspect, and other associated ecological sites. The home ranges of a majority species are larger than one ecological site or are dependent on more than one ecological site for annual life requisites. Ecological sites offer different habitat elements as the annual life requisites change. Habitat improvement and creation must be conducted within the mobility limits of a known population for the species.
Insects play an important role providing ecological services for plant community development. Insects that are scavengers or aid in decomposition provide the food chain baseline sustaining the carnivorous insects feeding upon them. Many insects provide the ecological services necessary for pollination, keeping plant communities healthy and productive. Insects provide a protein food source for numerous species including grassland-nesting birds and their young.
Species unique to MLRA:
Bald eagle: Bald Eagles prefer large rivers, lakes, reservoirs, or wetlands that are bordered by mature stands of trees or a single large tree. Bald eagles use the Missouri River system, including Lakes Sakakawea and Oahe, and associated tributaries. Mature trees, including cottonwoods, provide nesting sites adjacent to aquatic and upland foraging sites.
Dakota skipper: The extreme northern portion of this MLRA provides limited Dakota skipper habitat. Dakota skipper habitat within MLRA 54 is considered Type B habitat. Type B habitat is described as rolling native-prairie terrain over gravelly glacial moraine deposits dominated by bluestems and needlegrasses with the likely presence of bluebell bellflower, wood lily, blacksamson echinacea, upright prairie coneflower, and blanketflower. The United States Fish and Wildlife Service lists two critical habitat units within the MLRA in McKenzie County, North Dakota.
Golden eagle: The Lake Sakakawea breaks, bluffs, and rock outcroppings within the northwest portion of the MLRA are key areas for golden eagle nesting. Grasslands, shrublands, and black-tailed prairie dog towns are used for foraging.
Black-footed ferret: Black-footed ferrets have been reintroduced as an experimental population in the southern portion of the MLRA located on the Cheyenne Sioux Indian Reservation. Since reintroduction between 1991 and 1996, black-footed ferrets have been documented on the Standing Rock Sioux Indian Reservation approximately 20 miles north of the reintroduction site. Black-footed ferrets rely exclusively on prairie dog towns for shelter, breeding, and food sources (prairie dogs and other species within the town).
Least tern (Interior): Least terns are found on the Missouri River system in MLRA 54. Sparsely vegetated sandbars within the free-flowing portions of the Missouri River or shorelines of Lake Oahe and Sakakawea are used for nesting and foraging.
Species of Concern within the MLRA:
The following is a list of species considered “species of conservation priority” in the North Dakota State Wildlife Action Plan (2015); “species of greatest conservation need” in the Montana State Wildlife Action Plan (2015) and the South Dakota State Wildlife Action Plan (2014); and “species listed as threatened, endangered, or petitioned” under the Endangered Species Act within MLRA 54 at the time this section was developed:
Invertebrates: Dakota skipper, little white tiger beetle, monarch butterfly, Ottoe skipper, regal fritillary, yellow-banded bumble bee, and western bumble bee.
Birds: American Kestrel, Baird’s sparrow, bald eagle, black-billed cuckoo, black tern, bobolink, Brewer’s sparrow, burrowing owl, chestnut-collared longspur, ferruginous hawk, golden eagle, grasshopper sparrow, greater sage-grouse, lark bunting, loggerhead shrike, least tern, long-billed curlew, marbled godwit, McCown’s longspur, mountain plover, northern goshawk, northern harrier, northern pintail, peregrine falcon (migration), piping plover, prairie falcon, red knot (migration), red- headed woodpecker, sharp-tailed grouse, short-eared owl, Sprague’s pipit, Swainson’s hawk, trumpeter swan, upland sandpiper, western meadowlark, willet, Wilson’s phalarope, and whooping crane (migration).
Mammals: Big and little brown bats, long-eared bat, long-legged bat, northern long-eared bat, Townsend’s big-eared bat, western small-footed bat, black-footed ferret, black-tailed prairie dog, dwarf shrew, gray wolf, hispid pocket mouse, Merriam’s shrew, northwestern moose, sagebrush vole, silver-haired bat, and swift fox.
Amphibians/Reptiles: Common snapping turtle, Great Plains toad, false map turtle, greater short- horned lizard, milk snake, northern leopard frog, plains hognose snake, plains spadefoot, smooth green snake, and smooth softshell and spiny softshell turtle.
Fish and Mussels: Blue sucker, burbot, flathead chub, fragile papershell, northern redbelly dace, paddlefish, pallid sturgeon, pearl dace, pink papershell, shortnose gar, sickle-fin chub, sturgeon chub, and sauger.
Grassland Management for Wildlife in the MLRA
Management activities within the community phase pathways impact wildlife. Community phase, transitional, and restoration pathways are keys to long-term management within each state and between states. Significant inputs must occur to cross the threshold between states (e.g., State 3.0 to 2.0) requiring substantial economic inputs and management (mechanical, reseeding, prescribed burning, woody vegetation removal, grazing intensity, etc.). Timing, intensity, and frequency of these inputs can have dramatic positive or negative effects on local wildlife species. Ranchers and other land managers must always consider the long-term beneficial effects of management on the habitat in comparison to potential short-term negative effects to individuals.
Ecological sites occur as intermingled complexes on the landscape with gradual or sometimes abrupt transitions. Rarely do ecological sites exist in large enough acreage to manage independently. Ecological sites that support a dominance of herbaceous vegetation (Loamy/Clayey) can be located adjacent to ecological sites that support medium to tall shrubs (Loamy Overflow). Conversely, ecological sites that are dominated by short- to mid-statured grasses (Claypan) can be adjacent to sites with bare soil only supporting minor amounts of short grasses and forbs (Thin Claypan).
Management of these complex ecological sites can provide a heterogeneous or a homogenous landscape. Grassland bird use declines as the plant community transitions to a homogenous state. Managers should recognize ecological sites and the complexes they occur in to properly manage the landscape. A management regime for one ecological site may negatively impact an adjacent site; for example, alteration of a grazing regime within a Loamy Overflow ecological site to encourage understory growth may encourage exotic cool-season grasses to increase or dominate an adjacent ecological site.
Life requisites and habitat deficiencies are determined for targeted species. Deficiencies must be addressed along community phase, transitional, and restoration pathways as presented in specific state-and-transition models. Ecological sites should be managed and restored within the site’s capabilities to provide sustainable habitat. Managers also should consider habitat provided by adjacent/intermingled ecological sites for species with home ranges or life requisites that cannot be provided by one ecological site.
With populations of many grassland-nesting birds in decline, it is important to maintain these ecological sites in a 1.0 Reference State (rarely found intact) or the 2.0 Native/Invaded. Plant communities optimal for a guild of grassland species serve as a population source where the birth rate exceeds mortality. Species may use marginal plant communities; however, these sites may function as a population sink where mortality exceeds the birth rate.
Understanding preferred vegetative stature and sensitivity to woody encroachment is necessary to manage for the specific grassland species. Various grass heights may be used for breeding, nesting, foraging, or winter habitat. While most species use varying heights, many have a preferred vegetative stature height. The following chart provides preferred vegetative stature heights and sensitivity to woody vegetation encroachment.
For more information:
https://efotg.sc.egov.usda.gov/references/public/ND/54_Limy_Residual_Narrative_FINAL_Ref_FSG.pdf
Limy Residual Wildlife Interpretation:
Limy Residual ecological sites are defined by calcium carbonates in the upper part of the soil profile (within a depth of 8 inches) and soil parent material that weathered from residuum or is alluvium from residuum. They are less productive and less diverse than Loamy and Loamy Overflow sites which occur on similar landscape positions. Limitations within Limy Residual sites support shorter stature and lower diversity of grasses and forbs for wildlife. The expansiveness of the Loamy, Loamy Terrace, Shallow Loamy, Very Shallow and Thin Loamy ecological sites, associated with the Limy Residual sites in MLRA 54, provides generally an unfragmented landscape. This complex of ecological sites provides habitat for many edge-sensitive grassland bird species. Also, in the Killdeer Mountains, the Upland Hardwood Forest ecological site is associated with the Limy Residual site.
Limy Residual vegetative features and components commonly support grassland-nesting birds. Notably, the shorter grass on Limy Residual sites can provide sharp-tailed grouse lekking sites. Insects rely on associated forbs and grasses for survival; insects serve as food sources for birds and their young and as forage for small and large herbivores.
Limy Residual ecological sites may be found in five plant community states (1.0 Reference State, 2.0 Native/Invaded State, 3.0 Invaded State, 4.0 Wooded Invaded, and 5.0 Go-Back) within a local landscape. Multiple plant community phases exist in states 1.0, 2.0 and 3.0. Today, these states occur primarily in response to grazing, drought, and non-use. Secondary influences include anthropogenic disturbances, black-tailed prairie dogs, and fire.
Because there is no known restoration pathway from State 2.0 to State 1.0, it is important to intensively manage using tools in State 1.0 and State 2.0 community phase pathways to prevent further plant community degradation along either the T2A transitional pathway to State 3.0. Native wildlife generally benefits from a heterogeneous composition and stature of grasslands found in States 1.0 and 2.0 which include diverse grass and forb species with varying stature and density. As plant communities degrade within State 2.0, warm-season grasses (particularly short-statured grasses) increase while native forbs are reduced. This transition results in reduced stature and increased plant community homogeneity. When adjacent/intermingled ecological sites undergo the same transition, the result can be an expansive, homogenous landscape.
Success along Restoration Pathway R3A from State 3.0 to State 2.0 is very difficult and is dependent upon presence of a remnant native grass population. This concept also applies to wildlife, as the target species must either be present on adjacent State 1.0 or State 2.0 plant communities or ecological sites within the species’ mobility limits. Species with limited mobility, such as Dakota skippers, must exist near the plant community to utilize restored sites. Mobile species (such as grassland-nesting birds) can more easily locate and utilize isolated, restored plant communities.
Plant community phases within the State 3.0 show dramatic increased homogeneity of exotic cool- season grasses, and further reduction in native forbs. Reduced forb diversity limits insect populations, negatively affecting grassland-nesting bird foraging opportunities. Increased exotic- grass litter can limit access to bare ground by nesting insects and can limit mobility by small chicks. A homogenous grassland landscape does not provide quality escape or winter cover. As a result, many species are not able to meet life requisites on communities in the 3.0 State.
Management along community phases, transition or restoration pathways should focus upon attainable changes. Short- and long-term monetary costs must be evaluated against short- and long- term ecological services in creating and maintaining habitat of sufficient quality to support a sustainable population.
1.0 Reference State
Community Phase 1.1 Western Wheatgrass-Needlegrasses-Blue Grama-Little Bluestem: This plant community offers quality vegetative cover for wildlife; every effort should be made to maintain this ecological site within this community phase. This phase retains high functionality through continued maintenance, including prescribed grazing with adequate recovery period as well as prescribed burning. Predominance of grass species in this community favors grazers and mixed-feeders (animals selecting grasses as well as forbs and shrubs). The structural diversity provides habitat for a wide array of migratory and resident birds. Calcium carbonate in the upper soil profile limits diversity of forbs.
Invertebrates: Insects play a role in maintaining the forb community and provide a forage base for grassland birds, reptiles, and rodents. Ecological services, historically provided by bison, are simulated by domestic livestock. These services include putting plant material and dung in contact with mineral soil to be used by low trophic-level consumers (such as invertebrate shredders, predators, herbivores, dung beetles, and fungal-feeders).
Dakota skippers may use this site due to presence of host plants, such as little bluestem and prairie dropseed. Regal fritillary habitat is limited due to the rarity of Nuttall's violet and prairie violets. Monarch butterfly may use flowering forbs on this site; however, few milkweed species are found on this site to support breeding. Bumblebees and other native bees utilize forbs as a nectar source and bare ground for nesting sites in bunchgrasses. Prescribed grazing with adequate recovery periods (as well as prescribed burning) to maintain the 1.1 phase has little effect on nests of ground-dwelling insects.
Birds: This plant community provides quality nesting, foraging, and escape habitats favored by short- to mid- grass-nesting birds. Plant stature may be too dense or tall for burrowing owl and McCown’s longspur; however, it may be used during periods of drought or management such as rotational grazing or fire, resulting in defoliation (along Community Phase Pathway 1.1A).
Several species of grassland birds that prefer mid-grass stature will use this site. In years with reduced precipitation or drought, use by mid-grass nesting species may be compromised. This plant community provides suitable areas for sharp-tailed grouse leks, nesting, and brood-rearing habitat. Limited stature and diverse prey populations provide good hunting opportunities for grassland raptors.
Mammals: The diversity of grasses and forbs provides high nutrition levels for small and large herbivores including voles, mice, rodents, jackrabbits, pronghorn, and deer (white-tailed and mule). Short to moderate stature provides suitable food and thermal, protective, and escape cover for small herbivores such as the hispid pocket mouse.
Amphibians/Reptiles: This ecological site and associated plant communities provide habitat for smooth green snakes. This ecological site can provide habitat for the northern leopard frog and Great Plains toad if freshwater habitats (such as stock water ponds) are located in or adjacent to the site. This ecological site provides limited habitat for the plains hog-nosed snake (prefer sandy soils) and plains spadefoot (prefer gravelly or sandy soils).
Fish and Mussels: This ecological site is not directly associated with streams, rivers, or water bodies. Associated ecological sites, such as Loamy Terrace, can receive run-on hydrology from Limy Residual sites. Management on these interconnected sites will have limited, secondary effects on aquatic species.
Community Phase 1.2 Blue Grama-Western Wheatgrass/Sedges/Forbs: Blue grama and western wheatgrass will dominate after multiyear drought with or without heavy long-term grazing; forb density, but not diversity, is slightly increased.
Invertebrates: Provides similar life requisites as Community Phase 1.1; however, long-term, heavy continuous grazing may negatively impact ground-nesting sites for bumble bees, other native bees, and other ground-nesting insects due to reduction of forbs, timing of forb flowering, or increased soil compaction.
Birds: This plant community provides quality nesting, foraging, and escape habitats favored by short grass-nesting birds. A shift to shorter plant stature along Community Phase Pathway 1.1A benefits McCown’s longspur, chestnut collared longspur, horned lark, and burrowing owl. Species preferring mid-grass stature will be generally successful with normal to above normal precipitation and a change in management along the 1.2A community phase pathway. In years with reduced precipitation or heavy grazing, nesting recruitment may be compromised for mid-grass-nesting species. This plant community provides areas suitable for sharp-tailed grouse leks. Limited cover and diverse prey populations provide good hunting opportunities for grassland raptors.
Mammals: Provides similar life requisites as Community Phase 1.1.
Amphibians/Reptiles: Provides similar life requisites as Community Phase 1.1.
Fish and Mussels: Provides similar life requisites as Community Phase 1.1.
Community Phase 1.3 Little Bluestem-Western Wheatgrass/Sedges/Forbs: Physical soil surface disturbances, such as wind/water erosion and deposition in Community Phase Pathway 1.1B, cause increased calcium carbonates at the surface giving little bluestem a competitive advantage. This plant community occurs in a mosaic with Community Phase 1.1, creating a patchwork landscape. Little bluestem-dependent species, such as Dakota skipper, can utilize this habitat. Invertebrates: Provides similar life requisites as Community Phase 1.1.
Birds: Provides similar life requisites as Community Phase 1.1.
Mammals: Provides similar life requisites as Community Phase 1.1.
Amphibians/Reptiles: Provides similar life requisites as Community Phase 1.1.
Fish and Mussels: Provides similar life requisites as Community Phase 1.1.
Community Phase 1.4 Annual Forbs/Bare Ground/Blue Grama/Fetid Marigold (Prairie Dog Town): This plant community phase is characterized by grazing-tolerant species and annual forbs (e.g., fetid marigold). Continued heavy grazing, repeated drought, prairie dog occupation, or a combination of these disturbances will shift to increased annual forbs with a reduction in perennial grasses. Perennial forbs stature and abundance are being replaced by short-statured annual forbs. Bare ground increases, litter amounts and infiltration rates decline while soil surface temperatures increase. Scruffy in appearance, this plant community is resilient and retains sufficient grazing sensitive native species to return to the 1.2 community phase (via Community Phase Pathway 1.4A).
Invertebrates: A switch to annual forbs from perennial forbs may have a significant impact to invertebrates, due to the loss of season-long nectar-producing plants for pollinators. Annual forbs’ bloom periods are dependent upon climatic conditions, especially precipitation events, and may not provide season-long nectaring opportunities. Season-long nectar sources may be found on adjacent plant communities or ecological sites for mobile species. Increased bare ground provides increased nesting sites for bumble bees and other ground-nesting insects.
Birds: This short-statured phase, driven by short-term prairie dog occupation, is favored by burrowing owls, chestnut-collared longspur, and McCown’s longspur. Prairie dog towns provide abundant prey populations for grassland raptors. The lack of grass and forb stature limits use by many bird species. Long-term prairie dog occupation following Transitional Phase Pathway T1B leads to the 2.0 State with no known return pathway due to the presence of exotic cool-season grasses. Managing this phase along Community Phase Pathway 1.4A can be an economical and successful method to restore habitat for many grassland-nesting birds.
Mammals: Suitable food, thermal, shelter, and escape cover (reduction in litter) for most mammals becomes limited. The loss of diversity of grasses and forbs reduces nutrition levels for small and large herbivores including rodents, white-tailed jackrabbits, and deer. Grazers, such as pronghorn, use prairie dog towns for foraging and loafing. Long-term prairie dog occupation following Community Phase Pathway T1B leads to the 2.0 State with no known return pathway due to the presence of exotic, cool-season grasses. Managing this phase along Community Phase Pathway 1.4A can be an economical and successful method to restore vegetative cover.
Amphibians/Reptiles: Prairie dog towns provide habitat for both amphibians and reptiles. Tiger salamanders, prairie rattlesnakes, and other snake species will use the burrow systems of prairie dogs for shelter and denning.
Fish and Mussels: Provides similar life requisites as Community Phase 1.1.
2.0 Native/Invaded State
The main ecological driver for the Native/Invaded State is the invasion of exotic cool-season grasses. Limy Residual ecological sites have clumps or patches of naturally occurring buffaloberry and skunkbush sumac. Lack of fire can cause these small clumps to expand into larger clumps. Dominated by buffaloberry, these patches vary in size and are usually located on north and east facing slopes. Found on shoulder, back, or side slopes, a mosaic of grasses and shrubs may dominate the landscape on Limy Residual and associated Shallow Loamy ecological sites. These patches provide escape and thermal cover as well as food for many animals, including deer and sharp-tailed grouse. Loggerhead shrike are known to cache food by impaling prey animals on the long thorns. Bird species which are sensitive to woody species may avoid nesting in grassland areas with large amounts of woody vegetation.
Community Phase 2.1 Western Wheatgrass-Needlegrasses-Blue Grama-Little Bluestem /Shrubs: This plant community develops through Transition pathway T1A, due to changes in management and the presence of exotic, cool-season grasses. The threshold between states 1.0 and 2.0 is crossed when Kentucky bluegrass, crested wheatgrass, smooth brome, or other exotic species become established. This plant community phase has a very similar appearance and function to the Reference State of Community 1.1, except it has a minor amount of cool-season exotic grasses and forbs. This community phase is commonly found in mosaic in association with the 2.2 Community Phase. This phase functions at a high level for native wildlife; therefore, managers should consider the 2.0 Community Phase Pathways to avoid transitioning to State 3.0.
Invertebrates: Provides similar life requisites as Community Phase 1.1.
Birds: Provides similar life requisites as Community Phase 1.1.
Mammals: Provides similar life requisites as Community Phase 1.1.
Amphibians/Reptiles: Provides similar life requisites as Community Phase 1.1.
Fish and Mussels: Provides similar life requisites as Community Phase 1.1.
Community Phase 2.2 Blue Grama-Western Wheatgrass-Little Bluestem/Sedges: Continuous, heavy season-long grazing or heavy seasonal grazing with or without drought (along Community Phase Pathway 2.1A) leads to shorter-statured species, such as blue grama and sedges. Dominated by shorter-stature grasses and a loss of nitrogen-fixing or leguminous native forbs, the diversity of this plant community is reduced. Both tap-rooted and fibrous-rooted perennial forbs increase in this phase but remain a minor component. Prescribed grazing with adequate recovery periods along Community Phase Pathway 2.2A is an efficient, effective method to regain the cool-season grass and forb diversity components in Community Phase 2.1.
Invertebrates: The loss of native forbs and increase in turf-forming grasses limit foraging and nesting sites for all pollinators. Continuous, heavy season-long grazing or heavy seasonal grazing may reduce ground-nesting site availability. Homogeneity of forb species may limit season long nectar availability.
Birds: Continuous, heavy season-long grazing or heavy seasonal grazing will reduce nesting sites, forage (invertebrates), and cover. A reduced forb component may limit foraging opportunities. Stature is generally short, serving both mid- and short-grass-nesting birds. Short-grass nesting birds favor this phase. Species preferring mid-grass stature will be generally successful with normal to above normal precipitation and a change in management along the 2.3A community phase pathway. In years with reduced precipitation or heavy grazing during the nesting season, nesting recruitment may be compromised for mid-grass-nesting species. This plant community provides areas suitable for sharp-tailed grouse lek site development. Limited stature and diverse prey populations provide good hunting opportunities for grassland raptors.
Mammals: Suitable food, thermal, protective, and escape cover (reduction in litter) for most mammals is somewhat reduced due to the increase in blue grama and sedges.
Amphibians/Reptiles: Provides similar life requisites as Community Phase 1.1.
Fish and Mussels: Provides similar life requisites as Community Phase 1.1.
Community Phase 2.3 Blue grama/Sedges/Prairie Sagewort/Cactus: Continued heavy grazing with severe multiyear drought along Community Phase Pathway 2.2B leads to shorter-statured grasses (e.g., blue grama), sedges, shrubs and cacti. Plant community diversity is reduced with a loss of nitrogen-fixing or leguminous native forbs and minor grass components. Prescribed grazing with adequate recovery periods and return to normal precipitation along Community Phase Pathway 2.3A is the most effective method to regain diverse cool-season grass and forb components in Community Phase 2.2.
Insects: Provides similar life requisites as Community Phase 2.2.
Birds: Continued heavy grazing with severe multiyear drought, will reduce nesting sites, forage (insects and other invertebrates), and cover. Burrowing owl and McCown’s longspur rely on the stature and composition this plant community provides. This plant community provides areas suitable for sharp-tailed grouse leks. Diverse prey populations are available for grassland raptors. Management for bird species preferring mid-statured grasses should follow Community Phase Pathway 2.3A and 2.2A.
Mammals: Provides similar life requisites as Community Phase 2.2. The loss of diversity of grasses and forbs reduces nutrition levels for some small and large herbivores.
Amphibians/Reptiles: Provides similar life requisites as Community Phase 1.1.
Fish and Mussels: Provides similar life requisites as Community Phase 1.1.
Community Phase 2.4 Annual Forbs/Bare Ground/Blue Grama/Fetid Marigold (Prairie Dog Town): This plant community is a result of ecological services provided by long-term, black-tailed prairie dog occupation (via Community Phases 2.1C, 2.2C, or 2.3B) coupled with the introduction of exotic cool- season grasses and annual forbs. Utilizing one or more tools in Community Phase Pathway 2.4A (e.g., removal of black-tailed prairie dogs, control of exotic perennial forbs, implementation of prescribed grazing) can move this community back to phase 2.1; but this may require significant management and economic inputs. Black-tailed prairie dogs provide primary ecological services to transition to and maintain Plant Community Phase 2.4.
Invertebrates: The loss of native forb diversity limits use by all pollinators. However, perennial invasive forbs will provide limited seasonal use dependent on bloom period. Bare ground, burrows, and short plant stature provide nest sites for bumblebees and other ground-nesting insects. Burrowing owls place dung around their burrow entrance, attracting dung beetles and other insects as a food source.
Birds: Burrowing owl and McCown’s longspur rely on the stature and composition that this plant community provides. Presence of black-tailed prairie dogs provided diverse prey populations for grassland raptors, including burrowing owls, prairie falcons, and ferruginous hawks. Burrowing owls nest in abandoned prairie dog burrows.
Mammals: Suitable food, thermal, protective, and escape cover (reduction in litter) for most mammals becomes limited. The loss of grass and forb diversity reduces nutrition levels for small and large herbivores including voles, mice, rodents, white-tailed jackrabbits, cottontail rabbits, and deer. Except for black-tailed prairie dog, this plant community provides little habitat for mid or small herbivores. Nonetheless, black-tailed prairie dog towns provide important habitat for many mammal species, including small rodents. Grazers, such as pronghorn, use prairie dog towns for foraging and loafing.
Amphibians/Reptiles: Prairie dog towns provide habitat for both amphibians and reptiles. Tiger salamanders, prairie rattlesnakes, and other snake species will use the burrow systems of prairie dogs for shelter and denning.
Fish and Mussels: Provides similar life requisites as Community Phase 1.1.
Community Phase 2.5 Little Bluestem-Western Wheatgrass/Sedges/Forbs/Shrubs: This plant community develops through Community Phase Pathway 2.1b due to events (such as wind and/or water erosion, drought, pipeline and road installation and livestock trailing). These soil disturbances result in elevated calcium carbonates at the soil surface which favors an increase in little bluestem.
Invertebrates: Provides similar life requisites as Community Phase 1.1.
Birds: Provides similar life requisites as Community Phase 1.1.
Mammals: Provides similar life requisites as Community Phase 1.1.
Amphibians/Reptiles: Provides similar life requisites as Community Phase 1.1.
Fish and Mussels: Provides similar life requisites as Community Phase 1.1.
3.0 Invaded State
Community Phase 3.1 Exotic Cool-Season Grasses/Forbs: Community Phase Pathway T2A is characterized by non-use or low intensity (<20% utilization) grazing and elimination of fire when exotic cool-season grasses are present as in Community Phase 2.0. This plant community phase is characterized by a dominance (>30%) of exotic cool-season grasses (such as Kentucky bluegrass, crested wheatgrass, and smooth brome). Restoration Pathway R3A requires remnant amounts of native warm-season grasses (i.e., blue grama, red threeawn, plains muhly), cool-season grasses (i.e., needlegrasses, western wheatgrass, prairie Junegrass), and forbs (i.e., white sagebrush, silverleaf Indian breadroot, blacksamson echinacea).
Frequent prescribed burns and high levels of grazing management along Restoration Pathway R3A are necessary to improve competitiveness and increase vigor and density of the remnant native plant community. The R3A pathway will have significant short-term negative impacts on wildlife cover. However, this is necessary to restore long-term native vegetation functions for various species’ habitat needs. Without intensive management, further degradation within State 3.0 will occur, requiring mechanical treatment with reseeding through Restoration Pathway R3B.
Invertebrates: Non-use or low intensity (<20% utilization) grazing, limits use by beneficial insects provided in States 1.0 and 2.0. Increased litter and lack of grazing leads to limited contact between plant material and mineral soil resulting in a cooler micro-climate, which is unfavorable to most insects. Lack of bare soil limits ground-nesting sites for native bees and other ground-nesting insects. The lack of nectar-producing plants limits forage opportunities for bumblebees, regal fritillary, monarch butterfly, and other pollinating species.
Birds: This homogeneous community phase, dominated by exotic plant species, provides limited vegetative cover and life requisites for most obligate grassland-nesting birds. Lack of stature and plant diversity, along with increased litter and the tendency of Kentucky bluegrass and smooth brome to lay down, limits use by many grassland-nesting birds. Litter accumulations reduce use by chestnut-collared and McCown’s longspurs. Burrowing owls may use the site if sufficient burrows of black-tailed prairie dogs or other burrowing mammals exist. Sharp-tailed grouse leks can be found on this plant community; however, winter cover must be provided by adjacent ecological sites or plant communities.
Mammals: Black-tailed prairie dog expansion is possible in this plant community phase. This community phase provides foraging habitat for pronghorn and deer. Litter accumulation favors thermal, protective, and escape cover for small rodents. However, reduced availability of native grass seed may reduce food availability for species such as the hispid pocket mouse.
Amphibians/Reptiles: Provides similar life requisites as Community Phase 1.1.
Fish and Mussels: Provides similar life requisites as Community Phase 1.1.
4.0 Invaded Wooded State
Community Phase 4.1 Shrubs/Trees/Herbaceous: Resulting from pathways T2B and T3A, elimination of fire and grazing are the major contributors to this community phase crossing the threshold from an herbaceous plant community to a community dominated by shrubs and hardwoods. Limy Residual sites did not historically support a woody plant community. This community phase occupies north and east facing slopes.
Invertebrates: Dominated by early season flowering shrubs, pollinating insects may need adjacent herbaceous, and forb dominated ecological sites for mid- to late-season pollen sources. Lower trophic level consumers (such as invertebrate decomposers, scavengers, shredders, predators, herbivores, dung beetles, and fungal-feeders) will use woody plant material, leaves, and a limited number of grasses in contact with mineral soil. The woody component of this site is not conducive to use by the Dakota skipper, regal fritillary, or monarch butterfly. Woody plant material is available for wood nesting bees. These wind-protected, moist plant communities provide favorable habitat for flying insects (flies, mosquitoes, moths, etc.). Favorable climatic conditions can lead to large hatches of insects providing forage.
Birds: This site no longer provides habitat for grassland nesting bird species due to the woody vegetation dominance. Bird species that use and benefit from woodland edge (such as wild turkey, black-billed cuckoo, red-headed woodpecker, black-capped chickadee, gray catbird, and loggerhead shrike) can be found in this community phase. These sites provide sharp-tailed grouse brood cover and winter thermal cover. Wildlife use increases as the depth of snow increases during the winter, thereby becoming critical to the sustainment of winter resident bird populations. The presence of woody plant species may increase mammalian and avian predation and increase brood parasitism by brown-headed cowbirds on adjacent grassland ecological sites.
Mammals: Small herbivores that can use or tolerate woodland edge (such as least chipmunks, American porcupine, and cotton-tail rabbit) will benefit from this plant community phase. Shrubs and trees provide security and thermal cover used by elk and deer for foraging, loafing, and rearing young-of-the-year. Multi-layer shrub/tree communities provide concealment protection from predators during parturition. Plant species provide highly nutritious forage during peak lactation, one of the most energy demanding time periods of the year for female ungulates.
Deer utilize Community Phase 4.1 as primary foraging areas during all seasons of the year. Research at Theodore Roosevelt National Park found utilization of chokecherry and western snowberry by mule deer peaks during the fall accounting for 20 to 25% of their total dietary intake. In addition, mule deer also utilize rose, gooseberry, and serviceberry during the growing season. Winter white-tailed deer diets are dominated by chokecherry, western snowberry, Saskatoon serviceberry, rose, and various species of gooseberry. However, utilization of green ash as a forage by elk and deer was minimal accounting for <3% total dietary intake during all seasons.
Amphibians/Reptiles: Community Phase 4.1 will not support most of the amphibians and reptiles of conservation concern.
Fish and Mussels: Provides similar life requisites as Community Phase 1.1.
5.0 Go-Back State
Community Phase 5.1 Annual/Pioneer Perennial/Exotics: These plant communities are the result of severe soil disturbance (such as cropping, recreational activity, or concentrated livestock activity) for a prolonged period. Following cessation of disturbances, the resulting plant community is dominated by early pioneer annual and perennial plant species. Plant species composition and production are highly variable. Weedy plants can provide pollen sources along with spring and summer cover for many mammals and birds and their young. Dense weed cover can keep soils moist, increasing insect presence. Tall stature provided by some weeds, such as marsh elder and ragweed, offer thermal cover and seeds throughout winter.
Successful restoration of native species along Transition Pathway R5A results in a native grass and forb community in State 2.0. Failed restoration to native species through Restoration Pathway R5B results in Invaded State 3.0. Wildlife species response will be dependent upon plant community composition, vegetative stature, patch size, and management activities (such as prescribed grazing, burning, interseeding, haying, or noxious weed control).
Animal Community – Grazing Interpretations
This site is well adapted to managed grazing by domestic livestock. The predominance of herbaceous plants across all plant community phases best lends these sites to grazing by cattle, but other domestic grazers with differing diet preferences may also be a consideration depending upon management objectives. Often, the current plant community does not match any particular plant community (as described in the ecological site description). Because of this, a resource inventory is necessary to document plant composition and production. Proper interpretation of this inventory data will permit the establishment of a safe, initial stocking rate for the type and class of animals and level of grazing management. More accurate stocking rate estimates should eventually be calculated using actual stocking rate information and monitoring data.
NRCS defines prescribed grazing as “managing the harvest of vegetation with grazing and/or browsing animals with the intent to achieve specific ecological, economic, and management objectives”. As used in this site description, the term ‘prescribed grazing’ is intended to include multiple grazing management systems (e.g., rotational grazing, twice-over grazing, conservation grazing, targeted grazing, etc.) provided that, whatever management system is implemented, it meets the intent of prescribed grazing definition.
The basic grazing prescription addresses balancing forage demand (quality and quantity) with available forage, varying grazing and deferment periods from year-to-year, matching recovery/deferment periods to growing conditions when pastures are grazed more than once in a growing season, implementation of a contingency (e.g., drought) plan, and a monitoring plan. When the management goal is to facilitate change from one plant community phase or state to another, then the prescription needs to be designed to shift the competitive advantage to favor the native grass and forb species.
Grazing levels are noted within the plant community narratives and pathways in reference to grazing management. “Degree of utilization” is defined as the proportion of the current years forage production that is consumed and/or destroyed by grazing animals (may refer to a single plant species or a portion or all the vegetation). “Grazing utilization” is classified as slight, moderate, full, close, and severe (see the following table for description of each grazing use category). The following utilization levels are also described in the Ranchers Guide to Grassland Management IV. Utilization levels are determined by using the landscape appearance method as outlined in the Interagency Technical Reference “Utilization Studies and Residual Measurements” 1734-3.
Utilization Level % Use Description
Slight (Light) 0-20 Appears practically undisturbed when viewed obliquely. Only choice areas and forage utilized.
Moderate 20-40 Almost all of accessible range shows grazing. Little or no use of poor forage. Little evidence of trailing to grazing.
Full 40-60 All fully accessible areas are grazed. The major sites have key forage species properly utilized (about half taken, half left). Points of concentration with overuse limited to 5 to 10 percent of accessible area.
Close (Heavy) 60-80 All accessible range plainly shows use and major sections closely cropped. Livestock forced to use less desirable forage, considering seasonal preference.
Severe > 80 Key forage species completely used. Low-value forages are dominant.
Hydrological functions
Water is the principal factor limiting herbage production on this site. The site is dominated by soils in hydrologic groups B and C. Infiltration rate is moderate and runoff potential for this site varies from low to high depending upon hydrologic group, slope, and ground cover. In many cases, areas with greater than 75% ground cover have the greatest potential for high infiltration and lower runoff. An exception would be where short grasses form a dense sod and dominate the site. Areas where ground cover is less than 50% have the greatest potential to have reduced infiltration and higher runoff (refer to Section 4, NRCS National Engineering Handbook for runoff quantities and hydrologic curves).
Recreational uses
The largest acreage of public land available for recreation in the MLRA is owned and managed by the United States Forest Service (USFS) within the Little Missouri, Grand River, and Cedar River National Grasslands in South Dakota and the Little Missouri National Grasslands in North Dakota (687,398 acres). These areas are available for hunting, fishing, hiking, camping, horse and bike riding, nature viewing, etc. In addition, the Bureau of Land Management (BLM) manages (40,264 acres) in North and South Dakota with the same recreational opportunities as the USFS lands.
The United States Army Corps of Engineers (USAE) owns 496,162 acres of land and water located on and adjacent to Lake Sakakawea and Lake Oahe. The North Dakota and South Dakota Game and Fish Departments manage the fisheries resources. These two Missouri River reservoirs provide excellent fishing and water recreation opportunities. In addition, the United States Fish and Wildlife Service (USFWS) manages a national fish hatchery below Garrison Dam.
The USFWS manages 36,858 acres in the National Wildlife Refuge system while the North Dakota and South Dakota wildlife management agencies manage 72,218 acres as wildlife or game management areas. The North Dakota, South Dakota, and Montana Department of Trust Lands manage 486,482 acres. These areas provide hunting, bird watching, hiking, and other outdoor recreation opportunities. North Dakota Wildlife Management Areas along the shoreline of Lake Sakakawea and the Missouri River account for 60,000 acres of the approximately 72,218 acres of land managed by the states for wildlife habitat in MLRA 54. Located in the northern portion of the MLRA, the Killdeer Mountain WMA is the largest tract of state-owned land managed for wildlife habitat at approximately 7,000 acres.
The largest refuge managed by the United States Fish and Wildlife service is Lake Ilo National Wildlife Refuge totaling approximately 4,000 acres. United States Bureau of Reclamation manages approximately 11,000 acres at Lake Tschida and 8,460 acres at Bowman-Haley Lake for fish and wildlife habitat. The National Park Service manages the Knife River Indian Village National Historic Site; the North Dakota Historical Society manages the Double Ditch Indian Village site.
Bird watching: Public and private grasslands within MLRA 54 provide essential habitat for prairie-dependent bird species such as Sprague's pipits, western meadowlark, and Baird's sparrow along with some of the larger, showy members of the upland prairie include marbled godwits, upland sandpipers, willets, and sharp-tailed grouse. Publicly owned lands provide excellent birding opportunities. MLRA 54 is in the Central Flyway.
Hunting/Fishing: MLRA 54 is a fall destination for thousands of pheasant and upland game bird hunters. This MLRA also provides excellent deer (white-tailed and mule), pronghorn, and coyote hunting opportunities. Lake Sakakawea, Lake Oahe, Lake Tschida, and the Missouri River provide excellent year-round fishing opportunities. The North Dakota Game and Fish Department and South Dakota Game, Fish and Parks manage approximately 40 fishing lakes within the MLRA. Available species include yellow perch, walleye, northern pike, muskellunge, crappie, bluegill, rainbow trout, and smallmouth bass. Chinook salmon are stocked in Lake Sakakawea.
Camping: Numerous state operated campgrounds are located along the shores of Lake Sakakawea, Lake Oahe, Missouri River, and Shadehill Reservoir. Primitive camping is allowed on Grand River and Cedar River National Grasslands in South Dakota and the Little Missouri National Grasslands in North Dakota. Other numerous camping (primitive and improved) sites are available in numerous city and county parks.
Hiking/Biking/Horseback Riding: Hiking is permitted on most state and federally owned lands. Developed hiking and biking trails can be found on Harmon Lake (13.1 miles), Roughrider Trail (Morton County, 16.5 miles), Missouri River State Natural Area (5 miles), Ft. Abraham Lincoln State Park (8 miles), Cross Ranch State Park (14 miles), Grand River National Grasslands (7 miles), Lake Sakakawea State Park (5 miles), and Lewis & Clark State Park (5 miles). In addition, extensive biking and walking trails are found in local county and city parks. Ft. Abraham Lincoln State Park has 6 miles of horseback trails.
Wood products
No appreciable wood products are present on the site.
Other products
Seed harvest of native plant species can provide additional income on this site.
Other information
Site Development and Testing Plan
• NASIS revisions needed:
o Consider relinking Lantry components from Thin Loamy to Limy Residual.
This ESD is the best available current knowledge. The site concept and species composition table have been used in the field and tested for more than five years. It is expected that as additional information becomes available revisions may be required.
Supporting information
Inventory data references
Information presented here has been derived from NRCS and other federal/state agency clipping and inventory data. Also, field knowledge of range-trained personnel was used. All descriptions were peer reviewed and/or field-tested by various private, state, and federal agency specialists.
Other references
Bakker, K.K. 2003. The effect of woody vegetation on grassland nesting birds: an annotated bibliography. The Proceedings of the South Dakota Academy of Science 82:119-141.
Barker, W.T. and W. C. Whitman. 1988. Vegetation of the Northern Great Plains. Rangelands 10(6): 266-272.
Bjugstad, A.J. 1965. Vegetation measurements in relation to range condition classification on the principal range sites of southwestern North Dakota. PhD Thesis. N D State University.
Bluemle, J.P. 2017. North Dakota Notes No. 13, North Dakota’s mountainous areas: the Killdeer Mountains and the Turtle Mountains. Accessed on web, April 10, 2017, at https://www.dmr.nd.gov/ndgs/ndnotes/ndn15- h.htm.
Bluemle. J.P. 2016. North Dakota’s geologic legacy. North Dakota State University Press. 382 pages.
Brand, M. D. and H. Goetz. 1986. Vegetation of exclosures in southwestern North Dakota. Journal of Range Management 39: 434-437.
Briske, D.D. (editor). 2017. Rangeland systems – processes, management, and challenges. Springer Series on Environmental Management. 661 pages.
DeKeyser, E.S., G. Clambey, K. Krabbenhoft, and J. Ostendorf. 2009. Are changes in species composition on central North Dakota rangelands due to non-use management? Rangelands 31:16-19
Dodd, J.L. 1970. Distribution and community site relations of bluebunch wheatgrass in North Dakota. PhD Thesis. N D State University. Fargo, North Dakota.
Dornbusch, M.J., R.F. Limb, and C.K. Gasch. 2018. Facilitation of an exotic grass through nitrogen enrichment by an exotic legume. Rangeland Ecology & Management 71:691-694.
Dyke, S.R., S.K. Johnson, and P.T. Isakson. 2015. North Dakota state wildlife action plan. North Dakota Game and Fish Department, Bismarck, ND. 468 pages.
Ehrenfeld, Joan G. 2002. Effects of exotic plant invasions on soil nutrient cycling processes. Ecosystems 6:503-523.
Ereth, C., J. Hendrickson, D. Kirby, E. DeKeyser, K. Sedevic, and M. West. Controlling Kentucky bluegrass with herbicide and burning is influenced by invasion level. Invasive Plant Science and Management 10: 80-89.
Flesland, J.R. 1964. Composition and structure of the salt-desert shrub type in the badlands of western North Dakota. M.S. Thesis. ND State University.
Franzen, David. 2007. Managing saline soils in North Dakota. SF-1087. NDSU Extension Service. North Dakota State University.
Gilgert, W. and S. Zack. 2010. Integrating multiple ecosystem services into ecological site descriptions. Rangelands: 32:49-54.
Grant, T.A. and R.K. Murphy. 2005. Changes on woodland cover on prairie refuges in North Dakota, USA. Natural Areas Journal 25:359-368.
Hanson, H.C and W. Whitman. 1938. Characteristics of major grassland types in western North Dakota. Ecological Monographs. Vol. 8:57-114.
Heitschmidt, R. K., K. D. Klement, and M. R. Haferkamp. 2005. Interactive effects of drought and grazing on Northern Great Plains rangelands. Rangeland Ecology and Management 58:11-19.
Hendrickson, J.R., P. S. Johnson, M. A. Liebig, K. K. Sedivec, and G. A. Halvorson. 2016. Use of ecological sites in managing wildlife and livestock: an example with prairie dogs. Rangelands 38(1): 23-28.
Hendrickson, J.R., S.L. Kronberg, and E.J. Scholljegerdes. 2020. Can targeted grazing reduce abundance of invasive perennial grass (Kentucky bluegrass) on native mixed-grass prairie? Rangeland Ecology and Management, 73:547-551.
Higgins, K.F. 1984. Lightning fires in grasslands in North Dakota and in pine-savanna lands in nearby South Dakota and Montana. J. Range Manage. 37:100-103.
Higgins, K.F. 1986. Interpretation and compendium of historical fire accounts in the Northern Great Plains. United States Department of Interior, Fish and Wildlife Service. Resource Publication 161. 39 pages.
High Plains Regional Climate Center, University of Nebraska, 830728 Chase Hall, Lincoln, NE 68583-0728. (http://hprcc.unl.edu)
Hirch, K.L. 1985. Habitat type classification of grasslands and shrublands of southwestern North Dakota. Ph.D. Thesis. ND State University.
Hopkins, D.G., M.D Sweeny, D.R. Kirby, J. L. Richardson. 1991. Effects of revegetation of surficial soil salinity on panspot soils. Journal of Range Management 44(3): 215-219.
Hopkins, D.G., M.D Sweeny, J. L. Richardson. 1991. Dispersive erosion and entisol-panspot genesis in sodium-affected landscapes. Soil Science Society American Journal Volume. 55: 171-177.
Johnson, Sandra. 2015. Reptiles and amphibians of North Dakota. North Dakota Game and Fish Department. 64 pages.
Jordan, N. R., D.L. Larson, and S.C. Huerd. 2008. Soil modification by invasive plants: effects on native and invasive species of mixed-grass prairies. Biological Invasions 10:177-190.
Mader, E., M. Shepherd, M. Vaughan, and S.H. Black. 2011. Attracting native pollinators: protecting North America's bees and butterflies. Accessed at https://xerces.org, May 1, 2017.
Montana Fish, Wildlife and Parks. 2015. Montana state wildlife action plan. 2015. Viewed at https://xerces.org/ on May 1, 2017.
North Dakota Division of Tourism, Accessed on February 25, 2019. Available at https://www.ndtourism.com/sports-recreation
North Dakota Parks and Recreation Department, Accessed on February 25, 2019. Available at http://www.parkrec.nd.gov/recreationareas/recreationareas.html
Palit, R., G. and E.S. DeKeyser. 2022. Impacts and drivers of smooth brome (Bromus inermis Leyes.) invasion in native ecosystems. Plants: 10,3390. http://https://www.mdpi.com/2223-7747/11/10/1340
Palit, R., G. Gramig, and E.S. DeKeyser. 2021. Kentucky bluegrass invasion in the Northern Great Plains and prospective management approaches to mitigate its spread. Plants: 10,817. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants10040817
Printz, J.L. and J.R. Hendrickson. 2015. Impacts of Kentucky bluegrass invasion (Poa pratensis) on ecological processes in the Northern Great Plains. Rangelands 37(6):226-232.
Redmann, Robert E. 1975. Production ecology of grassland plant communities in western North Dakota. Ecological Monographs 45:83-106.
Reeves, J.L., J.D. Derner, M.A. Sanderson, J.R. Hendrickson, S.L. Kronberg, M.K. Petersen, and L.T. Vermeire. 2014. Seasonal weather influences on yearling beef steer production in C3-dominated Northern Great Plains rangeland. Agriculture, Ecosystems and Environment 183:110-117.
Royer, R. A., 2003. Butterflies of North Dakota: an atlas and guide. Minot State University, Minot, ND.
Sanford, R.C. 1970. Skunk bush in the North Dakota badlands: ecology, phytosociology, browse production, and utilization. Ph. D. Thesis. ND State University.
Seabloom, R. 2020. Mammals of North Dakota. North Dakota Institute for Regional Studies, Fargo, ND. 470 pages.
Sedivec, K.D., J.L. Printz. 2014. Ranchers guide to grassland management IV. NDSU Extension Service publication R1707.
South Dakota Dept. of Game, Fish and Parks. 2014. South Dakota wildlife action plan. Wildlife Division Report 2014-03.
Spaeth, K.E., Hayek, M.A., Toledo, D., and Hendrickson, J. 2019. Cool season grass impacts on native mixedgrass prairie species in the Northern Great Plains. America’s Grassland Conference: Working Across Boundaries. The Fifth Biennial Conference on the Conservation of America’s Grasslands. Bismarck, ND. 20-22 August.
Tidwell, D., D.T. Fogarty, and J.R. Weir. 2021. Woody encroachment in grasslands, a guide for understanding risk and vulnerability. Oklahoma State University, Oklahoma Cooperative Extension Service publication E- 1054. 32 pages.
Toledo, D., M. Sanderson, K. Spaeth, J. Hendrickson, and J. Printz. 2014. Extent of Kentucky bluegrass and its effect on native plant species diversity and ecosystem services in the Northern Great Plains of the United State. Invasive Plant Science and Management 7(4): 543-552.
USDA, NRCS. 2021. National range and pasture handbook, (https://www.nrcs.usda.gov/wps/portal/nrcs/detailfull/national/landuse/rangepasture/?cid=stelprdb1043084)
USDA, NRCS. 2006. Land resource regions and major land resource areas of the United States, the Caribbean, and the Pacific Basin. U.S. Department of Agriculture Handbook 296.
USDA, NRCS. National Soil Information System, 100 Centennial Mall North, Room 152, Lincoln, NE 68508- 3866. (https://www.nrcs.usda.gov/wps/portal/nrcs/detail/soils/survey/tools/?cid=nrcs142p2_053552)
USDA, NRCS. National Water & Climate Center, 1201 NE Lloyd Blvd, Suite 802, Portland, OR 97232-1274. (https://www.wcc.nrcs.usda.gov/)
USDA, NRCS. 2001. The PLANTS database, Version 3.1
(http://plants.usda.gov). National Plant Data Center, Baton Rouge, LA 70874-4490 USA.
USDA, NRCS, Various published soil surveys.
USDI BLM.1999. Utilization studies and residual measurements. Interagency Technical Reference 1734-3.
U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service. 2015. Endangered and threatened wildlife and plants; designation of critical habitat for the Dakota skipper and Poweshiek skipperling; Vol. 79 No. Final Rule October 1, 2015, 50 CFR Part 17.
Vinton, M.A. and E.M. Goergen. 2006. Plant-soil feedbacks contribute to the persistence of Bromus inermis in tallgrass prairie. Ecosystems 9: 967-976.
Whitman, W.H., H. Hanson, and R. Peterson. 1943. Relation of drought and grazing to North Dakota range lands. North Dakota Agricultural Experimentation Bulletin 340.
Zaczkowski, N. K. 1972. Vascular flora of Billings, Bowman, Golden Valley, and Slope counties, North Dakota. Dissertation, ND State University.
Zimmerman, G. M. 1981. Effects of fire upon selected plant communities in the little Missouri badlands. Thesis, ND State University.
Contributors
ND NRCS: David Dewald, Jonathan Fettig, Jody Forman, Mike Gerbig, Alan Gulsvig, Mark Hayek, Jeanne Heilig, John Kempenich, Chuck Lura, Jeff Printz, Steve Sieler, and Hal Weiser.
Approval
Suzanne Mayne-Kinney, 3/31/2025
Acknowledgments
NRCS would like to acknowledge the United State Forest Service (USFS) and National Park Service (NPS) for access to USFS properties and technical assistance in ESD development. USFS: Jack Dahl, Nickole Dahl, and Chad Prosser.
Rangeland health reference sheet
Interpreting Indicators of Rangeland Health is a qualitative assessment protocol used to determine ecosystem condition based on benchmark characteristics described in the Reference Sheet. A suite of 17 (or more) indicators are typically considered in an assessment. The ecological site(s) representative of an assessment location must be known prior to applying the protocol and must be verified based on soils and climate. Current plant community cannot be used to identify the ecological site.
| Author(s)/participant(s) | M. Hayek, A. Gearhart, J. Printz |
|---|---|
| Contact for lead author | NRCS State Rangeland Management Specialist |
| Date | 03/31/2025 |
| Approved by | Suzanne Mayne-Kinney |
| Approval date | |
| Composition (Indicators 10 and 12) based on | Annual Production |
Indicators
-
Number and extent of rills:
Rills are not expected on this site on slopes of less than 25%. On slopes greater than 25%, short, discontinuous rills may be present but uncommon. -
Presence of water flow patterns:
Water flow patterns are not visible on slopes of less than 25%. Water flow patterns may be present on slopes greater than 25% but will be relatively short (less than 10 feet) and disconnected. -
Number and height of erosional pedestals or terracettes:
Pedestals and terracettes are not present on slopes of less than 25%. Both may be present on slopes of greater than 25%, uncommon and associated with water flow patterns. -
Bare ground from Ecological Site Description or other studies (rock, litter, lichen, moss, plant canopy are not bare ground):
Bare ground ranges from 5 to 25%. Bare ground patches should be small (less than 8 inches in diameter) and not connected. Animal activity (burrows and ant mounds) may occasionally result in isolated bare patches of up to 24 inches in diameter. -
Number of gullies and erosion associated with gullies:
Active gullies are not expected on this site. If present, gully channel(s) are fully vegetated with no active erosion visible. -
Extent of wind scoured, blowouts and/or depositional areas:
No wind-scoured or depositional areas expected on this site. -
Amount of litter movement (describe size and distance expected to travel):
Plant litter movement not expected on this site when slopes are less than 25%. On slopes greater than 25% some short movement of fine class litter would be visible in association with water flow patterns. -
Soil surface (top few mm) resistance to erosion (stability values are averages - most sites will show a range of values):
Stability class averages 5 or greater. -
Soil surface structure and SOM content (include type of structure and A-horizon color and thickness):
Structure is subangular blocky or granular within the upper A-horizon. A- horizons for this ecological site range from 3 to 8 inches thick. Hue 2.5Y or 10YR with value of 4 or less moist or 3 to 6 dry, and chroma 2 or less moist. -
Effect of community phase composition (relative proportion of different functional groups) and spatial distribution on infiltration and runoff:
Mid- and short-statured bunchgrasses and mid- and short-statured rhizomatous grasses are dominant. A diverse forb component is subdominant. Bunchgrasses and forbs are well distributed across the site. -
Presence and thickness of compaction layer (usually none; describe soil profile features which may be mistaken for compaction on this site):
No compaction layers occur naturally on this site. -
Functional/Structural Groups (list in order of descending dominance by above-ground annual-production or live foliar cover using symbols: >>, >, = to indicate much greater than, greater than, and equal to):
Dominant:
Phase 1.1:
Mid & short C3 bunch grasses (3); Mid & short C3 rhizomatous grasses (2)Sub-dominant:
Phase 1.1:
Mid & short C4 bunch grasses (2); Forbs (16)Other:
Minor - Phase 1.1:
Grass-likes; ShrubAdditional:
Due to differences in phenology, root morphology, soil biology relationships, and nutrient cycling Kentucky bluegrass, smooth brome, and crested wheatgrass are included in a new Functional/structural group, mid- and short-statured early cool-season grasses (MSeC3), not expected for this site.
To see a full version 5 rangeland health worksheet with functional/structural group tables. Please use the following hyperlink:
https://efotg.sc.egov.usda.gov/references/public/ND/54_Limy_Residual_Narrative_FINAL_Ref_FSG.pdf -
Amount of plant mortality and decadence (include which functional groups are expected to show mortality or decadence):
Limited dead or dying plants/plant parts would be expected on this site, primarily as scattered dead centers on warm-season bunchgrasses and shrub branches. During and immediately after multi-year drought, dead warm-season bunchgrass and shrub branches would be common and expected. -
Average percent litter cover (%) and depth ( in):
Plant litter cover is 70 to 90% with a depth of less than 0.25 inches. Litter is in contact with soil surface. -
Expected annual annual-production (this is TOTAL above-ground annual-production, not just forage annual-production):
Annual air-dry production is 2050 lbs./ac (reference value) with normal precipitation and temperatures. Low and high production years should yield 1700 lbs./ac to 2400 lbs./ac, respectively. -
Potential invasive (including noxious) species (native and non-native). List species which BOTH characterize degraded states and have the potential to become a dominant or co-dominant species on the ecological site if their future establishment and growth is not actively controlled by management interventions. Species that become dominant for only one to several years (e.g., short-term response to drought or wildfire) are not invasive plants. Note that unlike other indicators, we are describing what is NOT expected in the reference state for the ecological site:
State and local noxious species, Kentucky bluegrass, smooth bromegrass, crested wheatgrass, and Rocky Mountain juniper/cedar. -
Perennial plant reproductive capability:
Noninvasive species in all functional/structural groups are vigorous and capable of reproducing annually under normal weather conditions. Reduced vigor/tiller numbers would be expected during and following a multi-year drought.
Print Options
Sections
Font
Other
The Ecosystem Dynamics Interpretive Tool is an information system framework developed by the USDA-ARS Jornada Experimental Range, USDA Natural Resources Conservation Service, and New Mexico State University.
Click on box and path labels to scroll to the respective text.
Ecosystem states
States 2 and 5 (additional transitions)
| T1A | - | Introduction of exotic cool-season grasses |
|---|---|---|
| T2A | - | Extended periods of no fire and/or little to no grazing disturbances |
| T2B | - | Extended periods of no fire |
| R3A | - | Long-term prescribed grazing and prescribed burning |
| T3A | - | Extended periods of no fire |
| R4A | - | Prescribed burning or stand replacing fire |
| R4B | - | Prescribed burning or stand replacing fire |
| R5A | - | Successful range planting |
| R5B | - | Failed range planting and/or secondary succession |
| T6A | - | Cessation of cropping |
State 1 submodel, plant communities
| 1.1A | - | Multiyear drought with/without heavy long-term grazing |
|---|---|---|
| 1.1B | - | Physical soil surface disturbances (e.g. wind/water erosion or deposition) |
| 1.2A | - | Return to average precipitation and reduced grazing |
| 1.2B | - | Physical soil surface disturbances (e.g. wind/water erosion or deposition) |
| 1.2C | - | Long-term occupation by prairie dogs |
| 1.3A | - | Multiyear drought |
| 1.3B | - | Long-term occupation by prairie dogs |
| 1.4A | - | Abandonment of prairie dogs |
State 2 submodel, plant communities
Communities 1 and 5 (additional pathways)
| 2.1A | - | Heavy continuous grazing with or without drought |
|---|---|---|
| 2.1B | - | Physical soil surface disturbances (e.g. wind/water erosion or deposition). |
| 2.2A | - | Long-term prescribed grazing and prescribed burning and return to average precipitation |
| 2.2B | - | Heavy continuous grazing coupled with multiyear drought |
| 2.2C | - | Long-term occupation by prairie dogs |
| 2.3A | - | Long-term prescribed grazing and prescribed burning and return to average precipitation |
| 2.3B | - | Long-term occupation by prairie dogs |
| 2.4A | - | Removal or abandonment of prairie dogs |
| 2.5A | - | Multiyear drought |